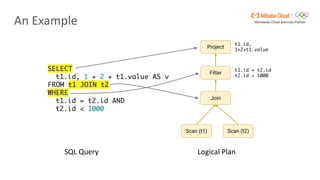
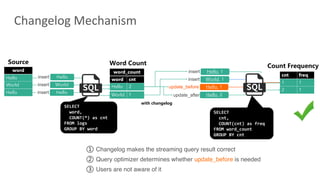
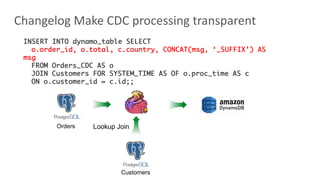
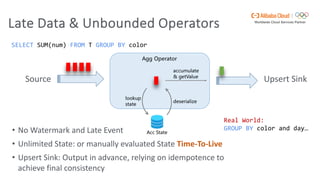
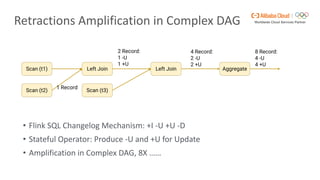
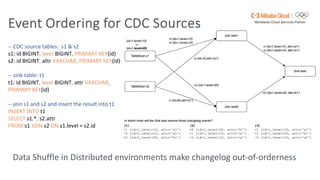
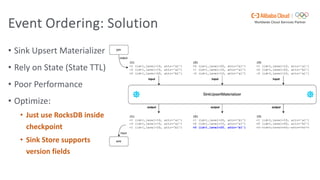
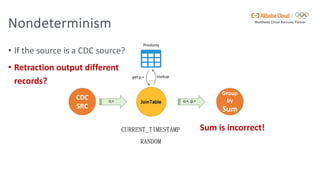
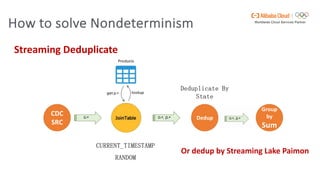
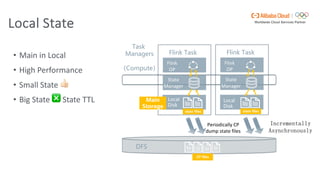
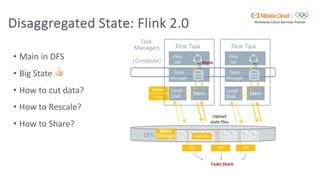
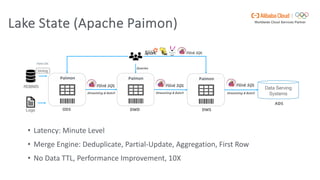
Flink SQL is Apache Flink's streaming SQL engine that supports data movement, data warehousing, and event-driven scenarios. There are four main challenges in building a streaming SQL engine: late data with unbounded operators, retractions amplification in complex query graphs, maintaining event ordering across distributed systems, and dealing with nondeterminism from functions like random and timestamps. The document discusses how Flink SQL addresses these challenges and the state and storage solutions in Flink, including using local state, disaggregated state in external storage, and the Apache Paimon lake storage format which can improve performance by 10x.