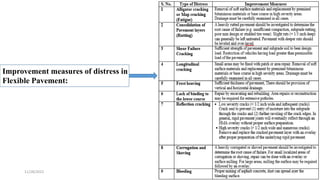
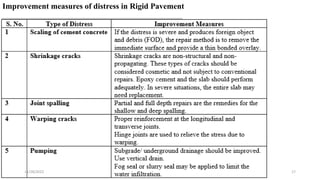
The document discusses different types of distress that can occur in flexible and rigid pavements. For flexible pavements, the main types of distress discussed are alligator cracking, rutting, shear failure cracking, longitudinal cracking, frost heaving, lack of binding between layers, reflection cracking, formation of waves and corrugation, and bleeding. For rigid pavements, the main types of distress discussed are scaling, shrinkage cracks, joint spalling, warping cracks, and pumping. Causes of distress include deficiencies in materials, structural inadequacies, and improper construction and maintenance practices. Understanding the different types and causes of distress can help pavement designers develop effective maintenance and rehabilitation strategies.