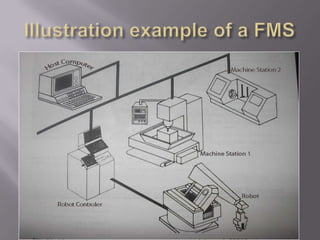
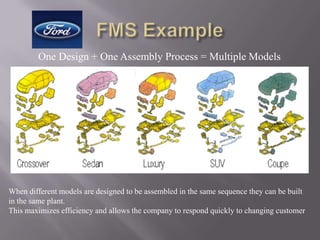
The document discusses flexible manufacturing systems (FMS). It begins with a definition of FMS and describes their history from the early 20th century to widespread adoption in the 1970s-1980s. Key points include: FMS uses numerically controlled machines connected by automated transport and controlled by computers. The first FMS patent was in 1965. In the 1970s/80s, manufacturers needed efficiency, quality, and flexibility to stay competitive. The document then outlines common FMS equipment like machining centers, process stations, and transport systems. It lists applications like machining, forming, assembly and discusses advantages like improved efficiency and quality but also challenges like high costs and need for planning.