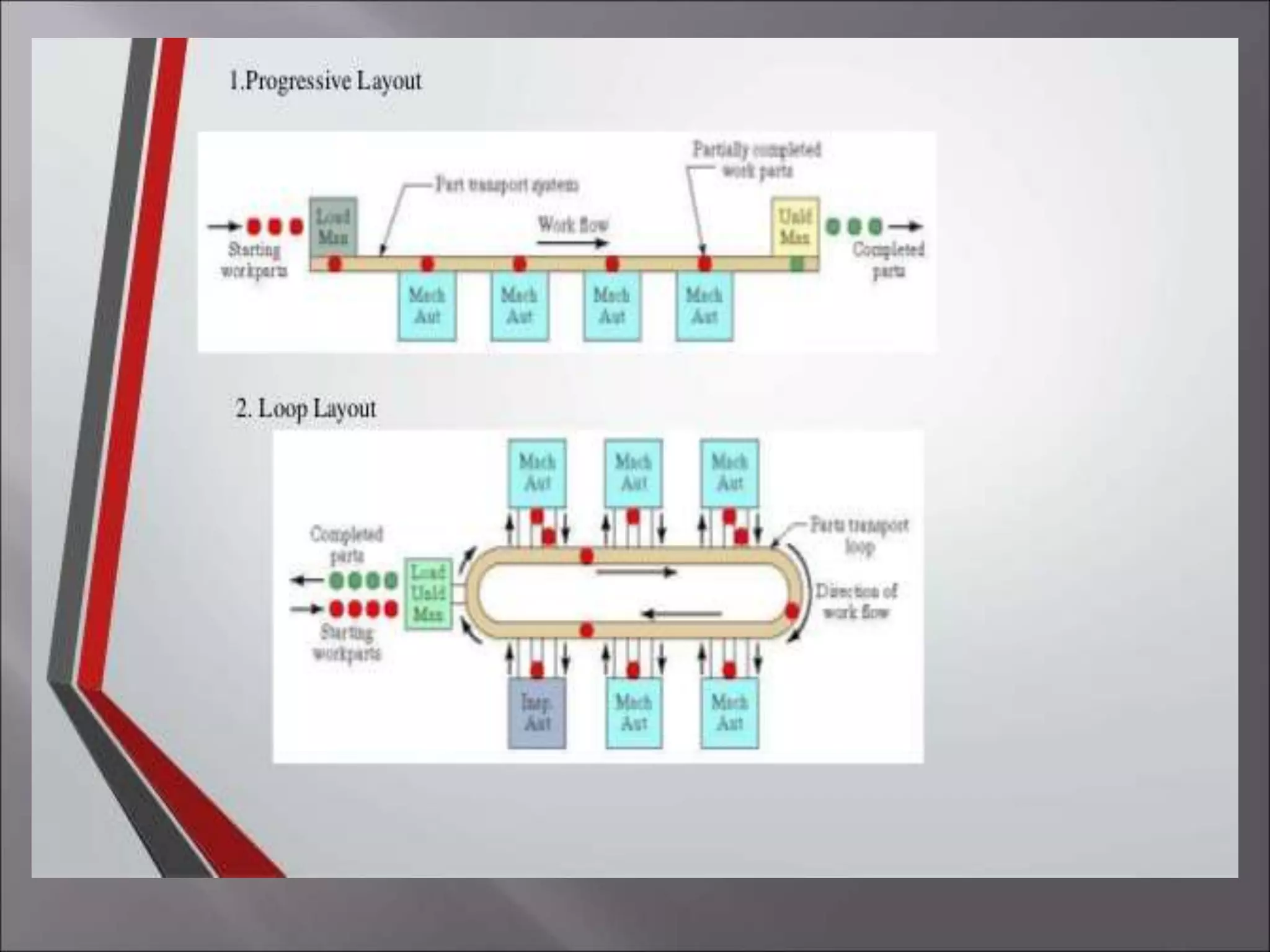
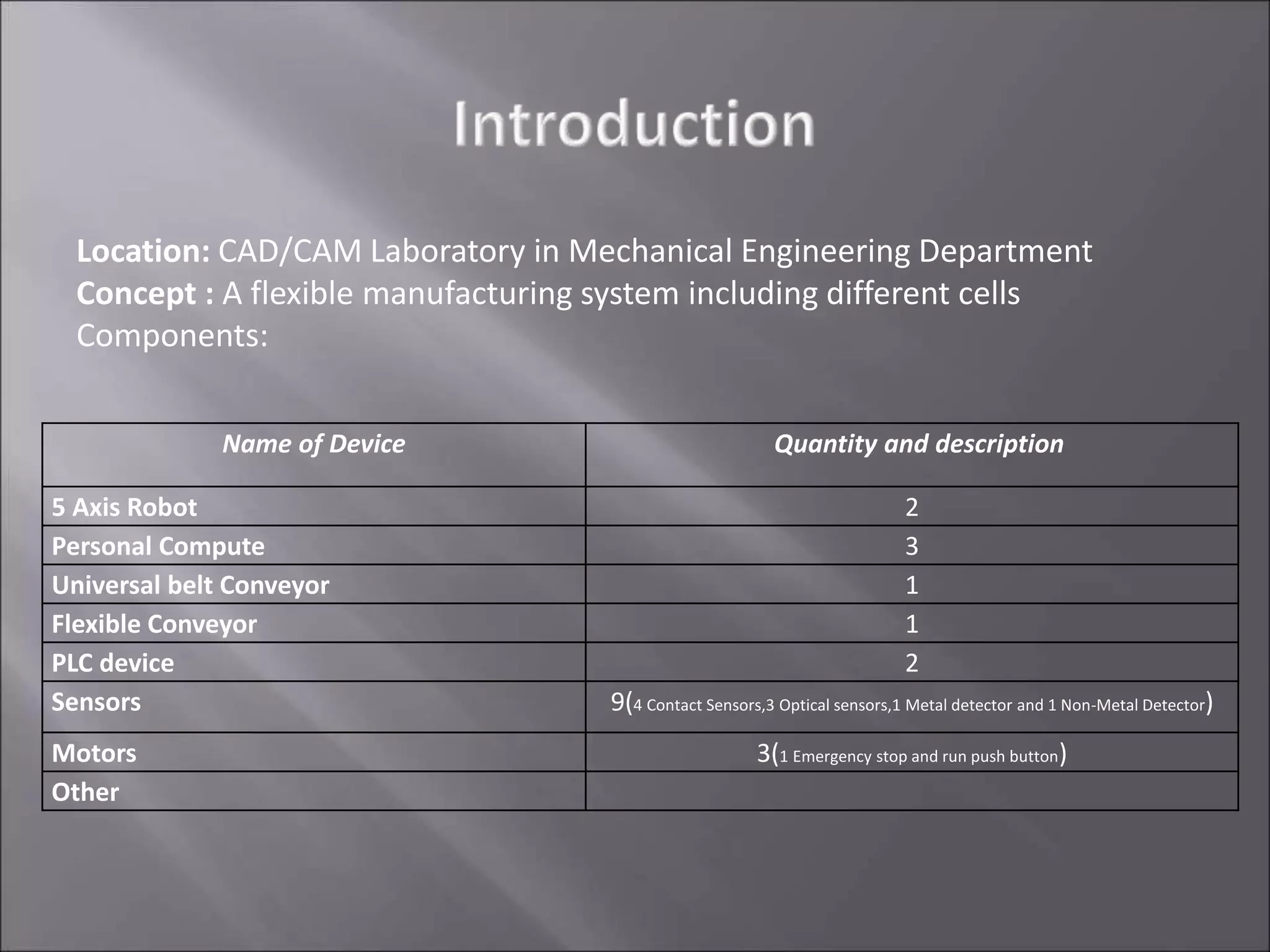
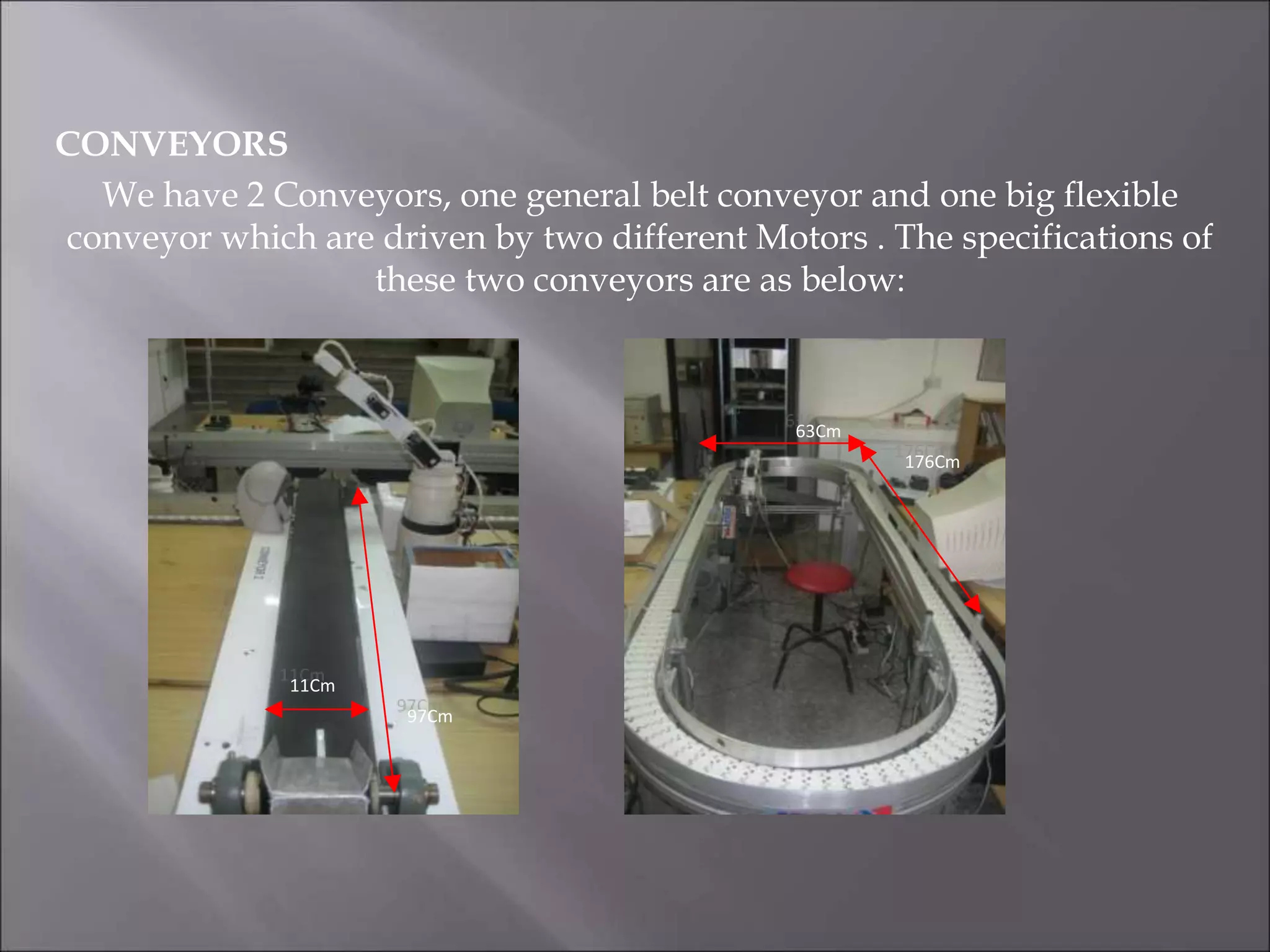
This document provides an overview of a Flexible Manufacturing System (FMS) implemented in a mechanical engineering CAD/CAM laboratory. The FMS consists of multiple components including two 5-axis robots, conveyors, sensors, PLC devices, and computers. One robot picks and places parts based on barcode information while the other picks parts detected by a sensor and moves them to another area. PLCs control the motors, conveyors, sensors and other components. Computers program and monitor the robots and PLCs. The FMS allows for flexible, automated production of different part types in the laboratory environment.