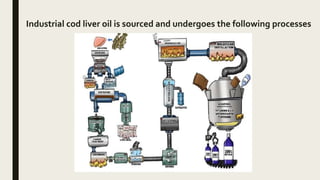
This document discusses fish liver oil and its extraction process. It notes that fish liver oil is a good source of vitamins A and D. It classifies fish livers into three groups based on their oil and vitamin A content. The document outlines methods for preserving fish liver, including storing in ice, freezing, chopping and mixing with salt, or grinding and mixing with preservatives. It also describes the industrial process for extracting cod liver oil, including sourcing the fish from various species, and processing the liver to produce an oil that matches the EPA/DHA ratio of raw cod liver oil.