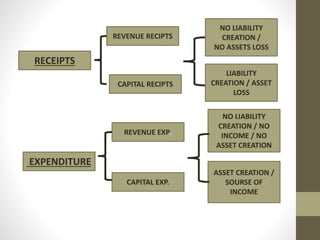
The document discusses government budgets, deficits, and deficit financing. It defines different types of budgets - revenue and capital - and budget receipts and expenditures. It then defines and explains different types of deficits a government can run, including revenue, capital, fiscal, primary, effective revenue, and monetary deficits. It concludes by outlining the typical priority sources for deficit financing: external aid, grants, borrowings, internal borrowings, and printing currency as a last resort.