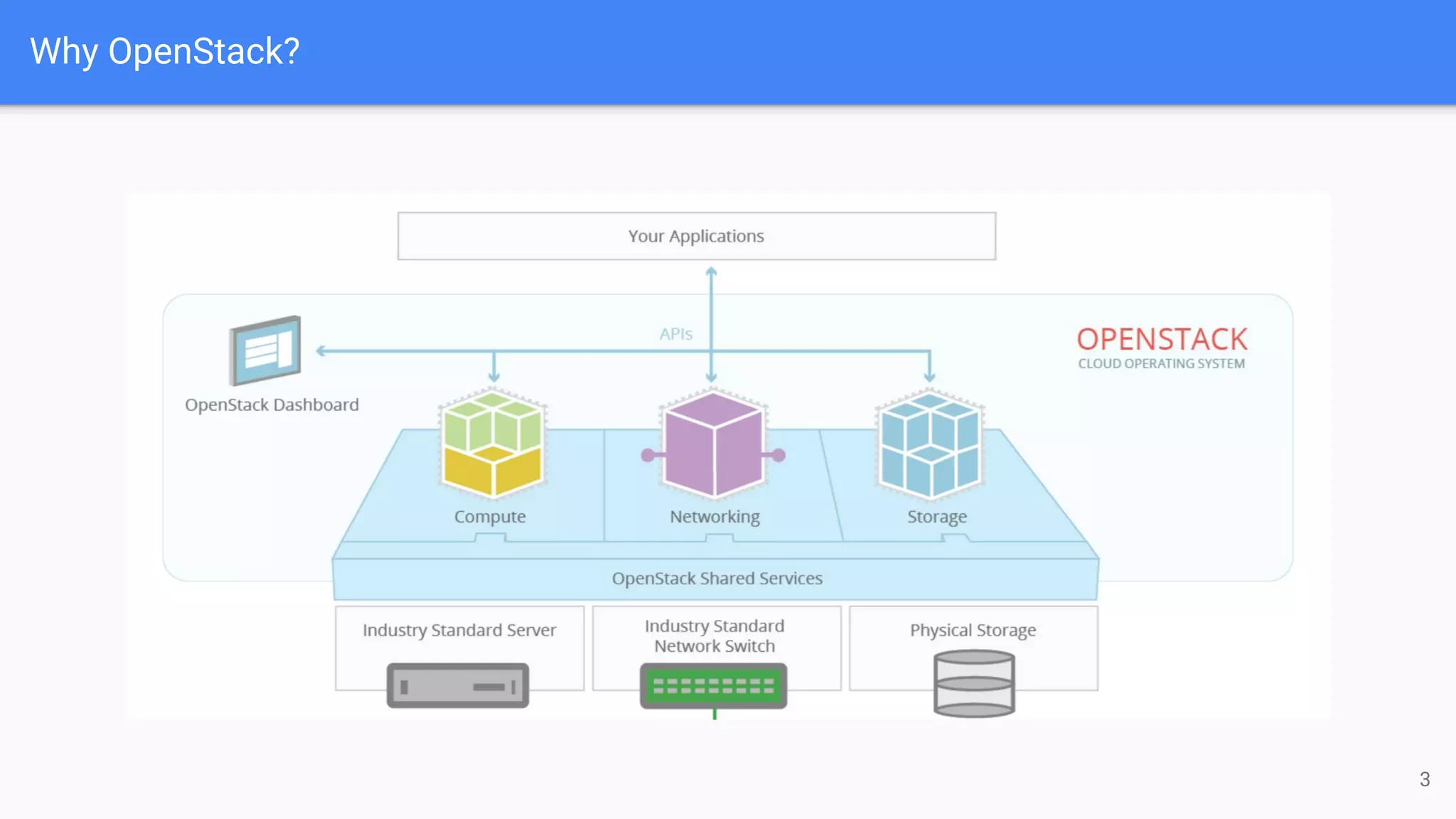
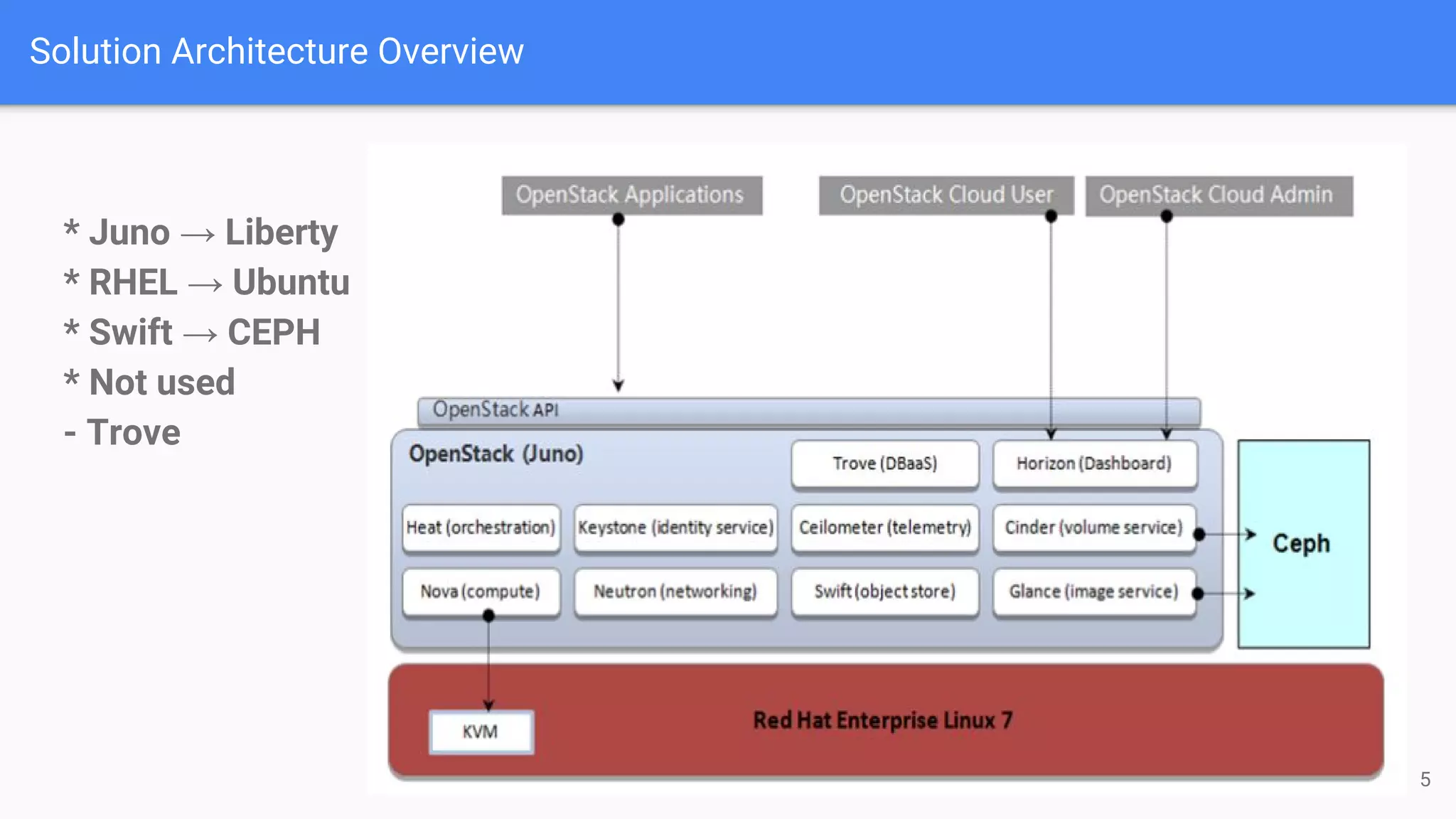
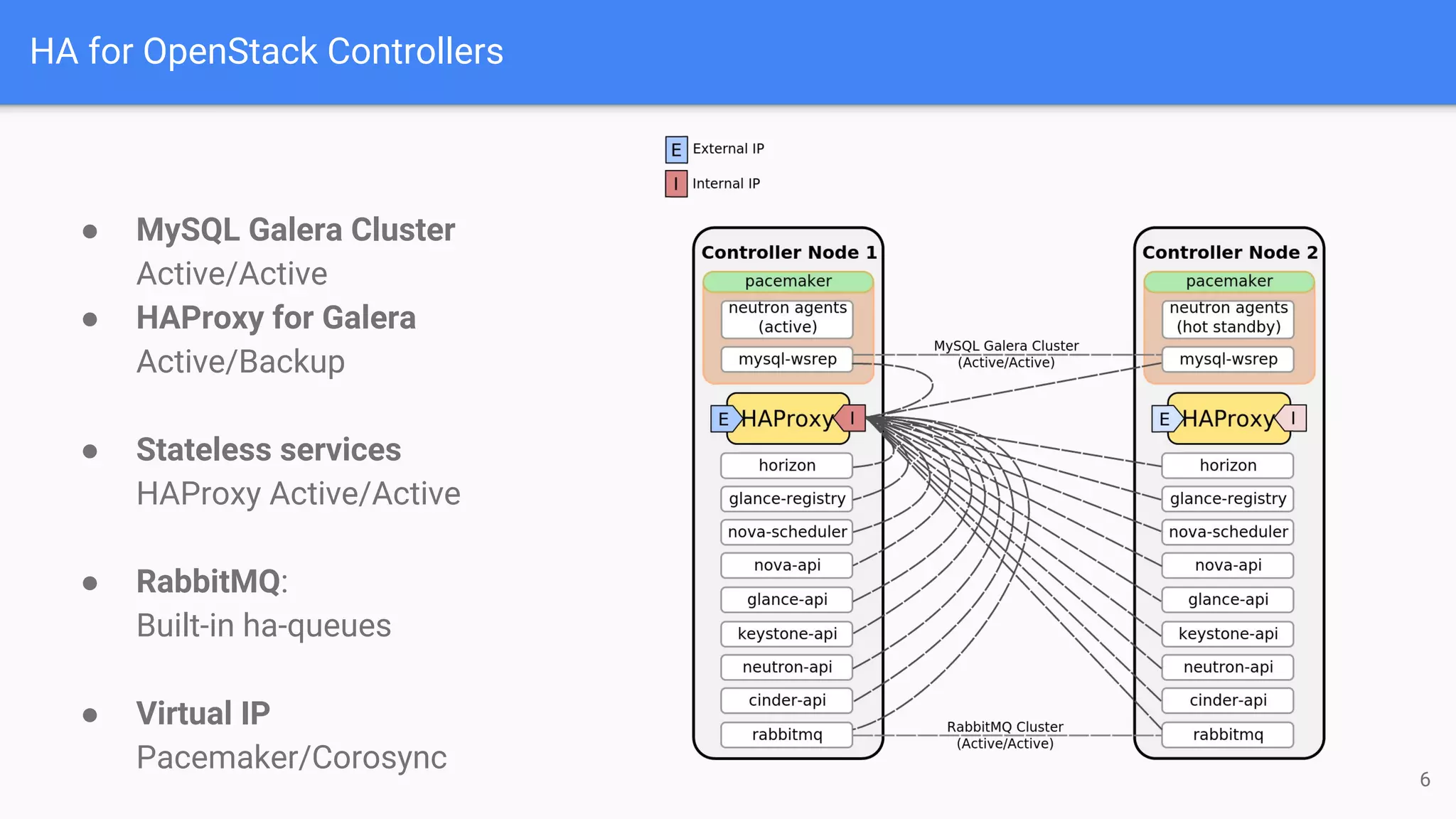
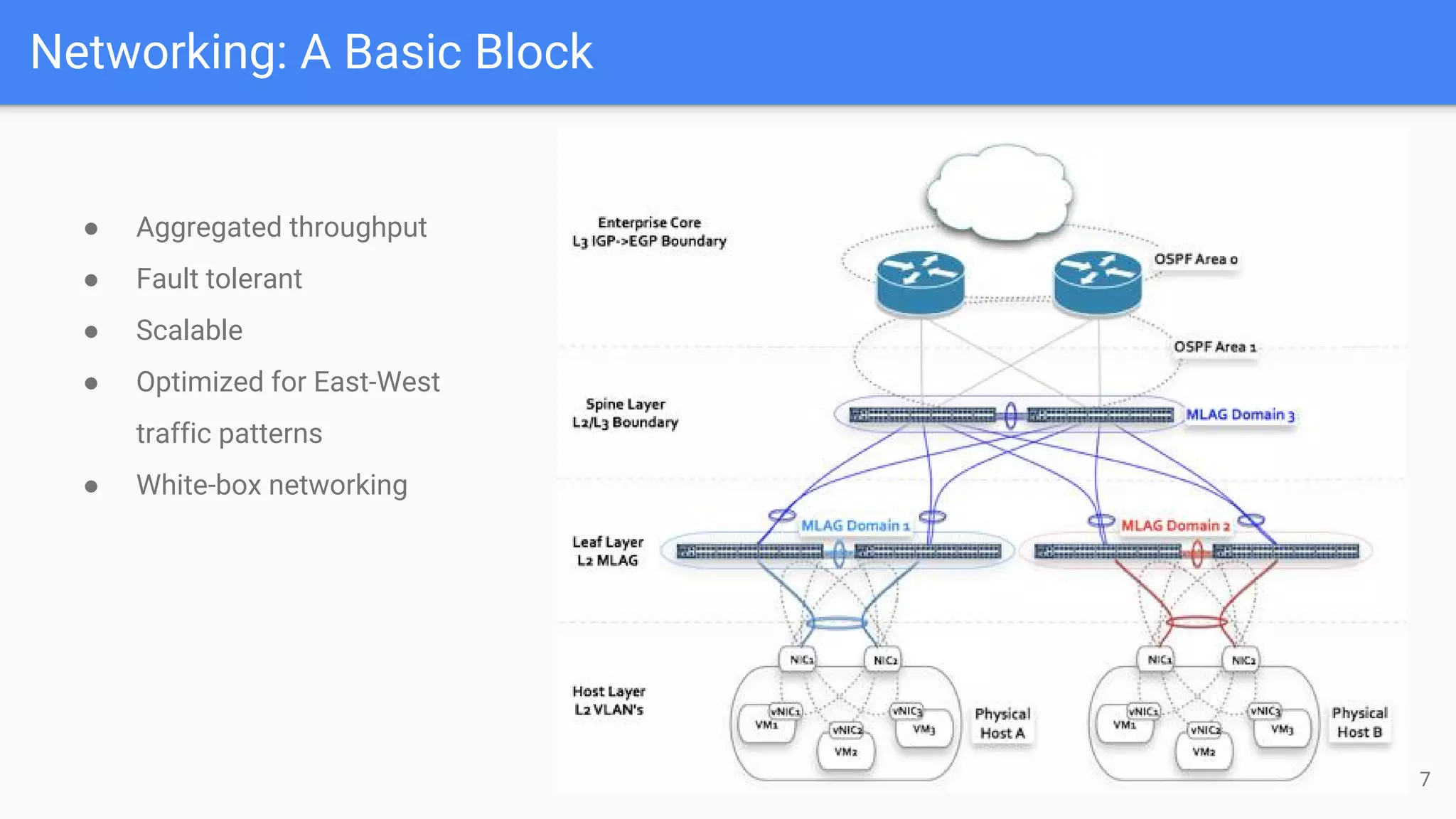
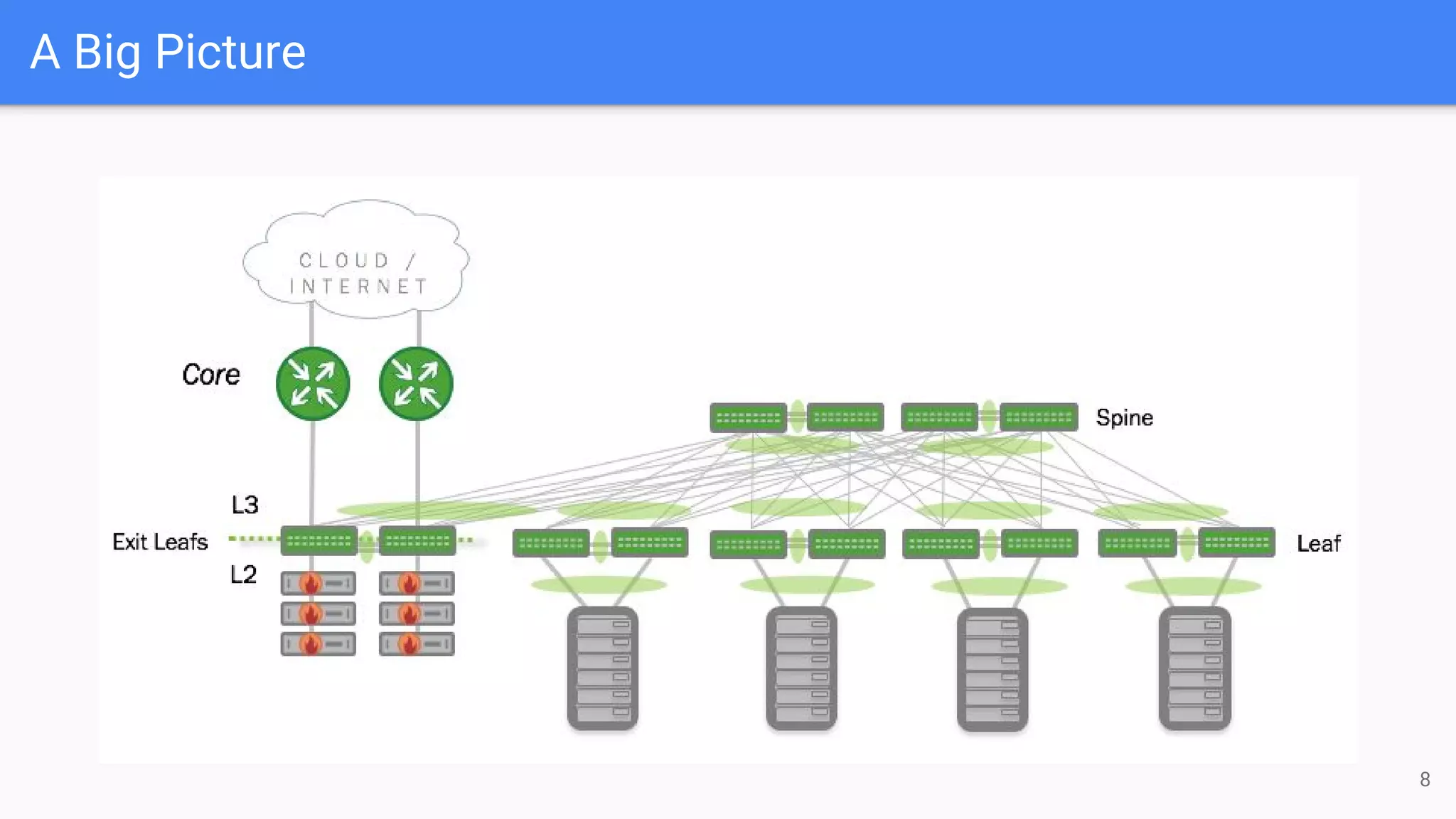
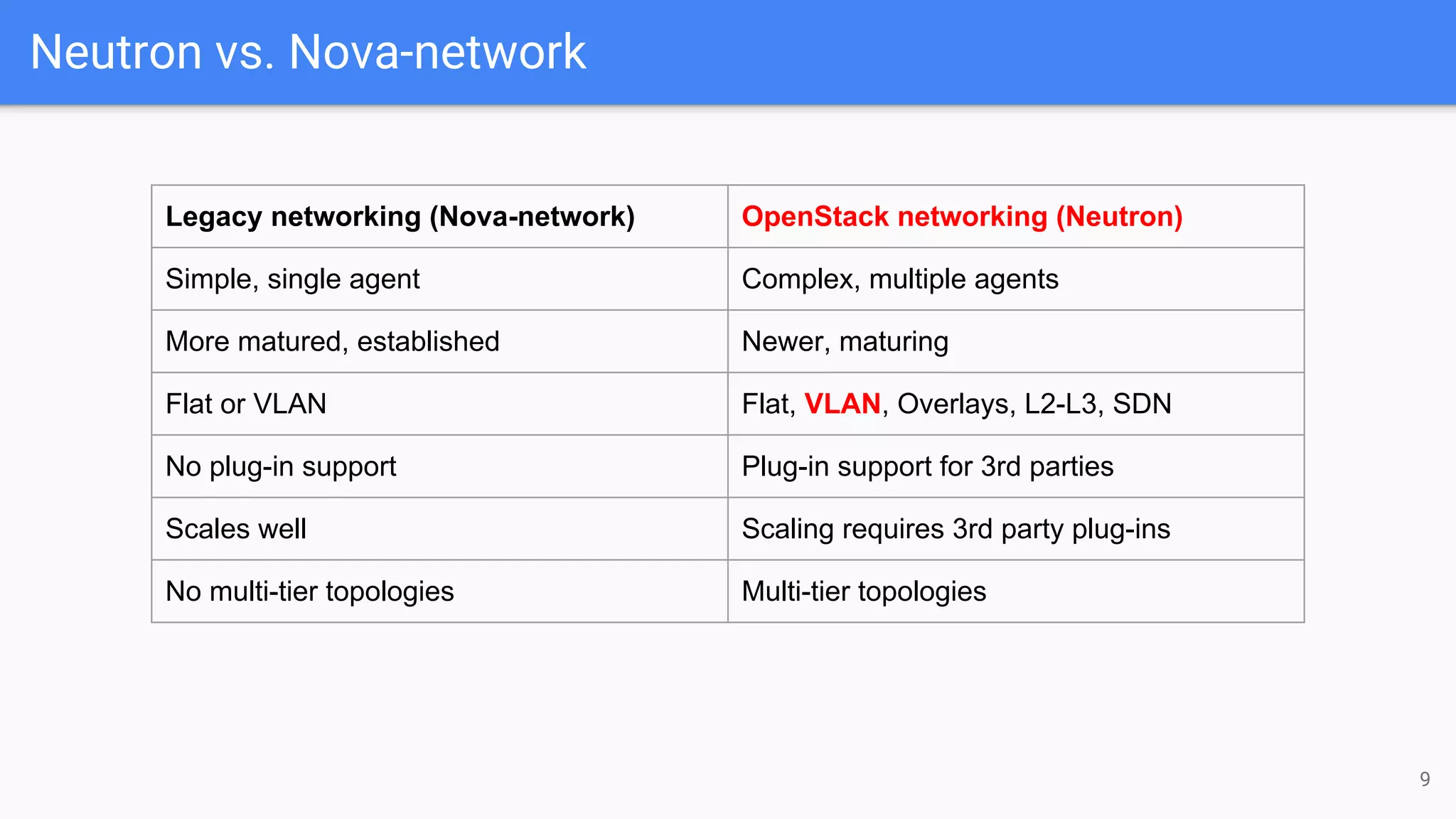
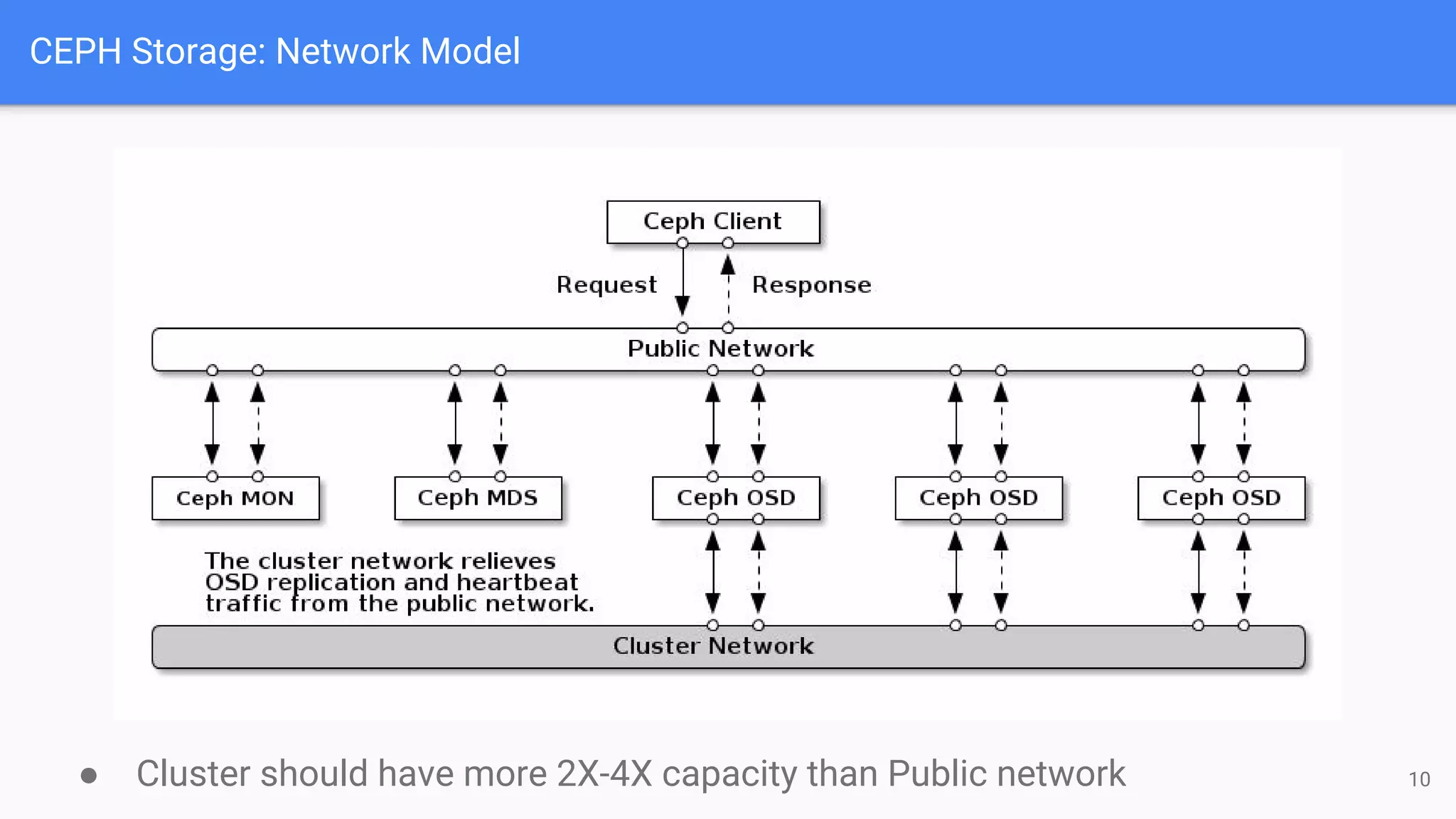
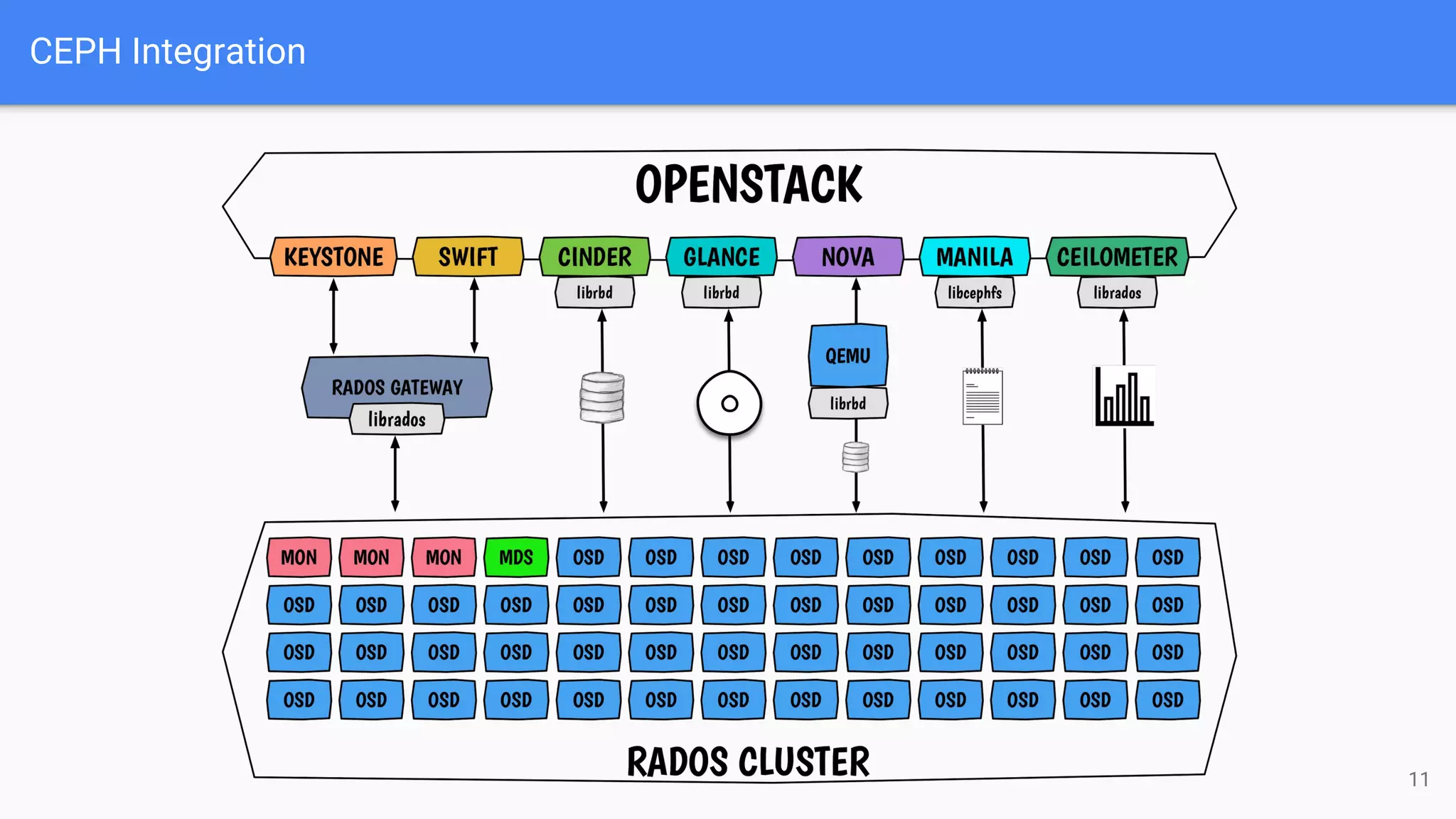
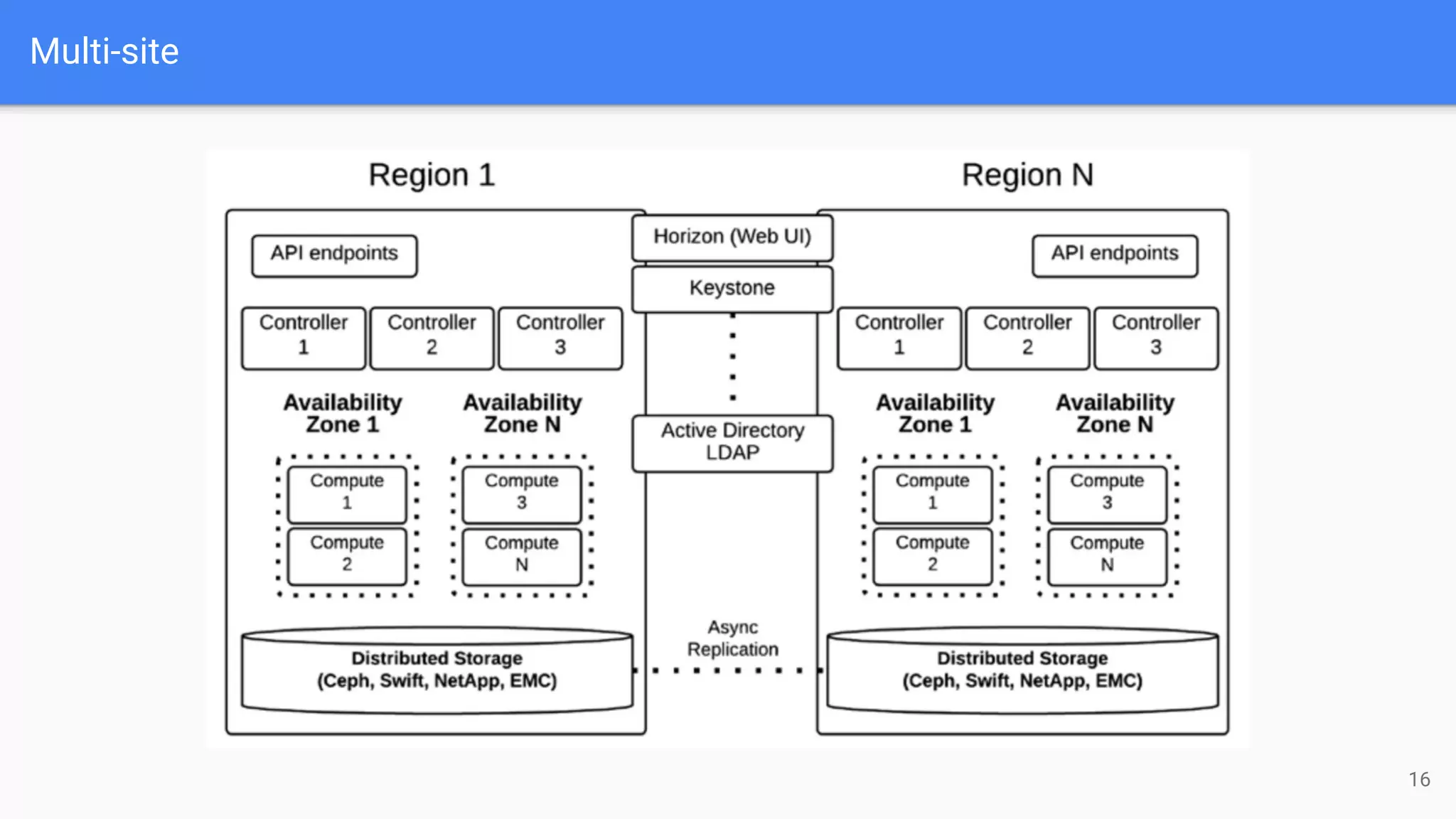
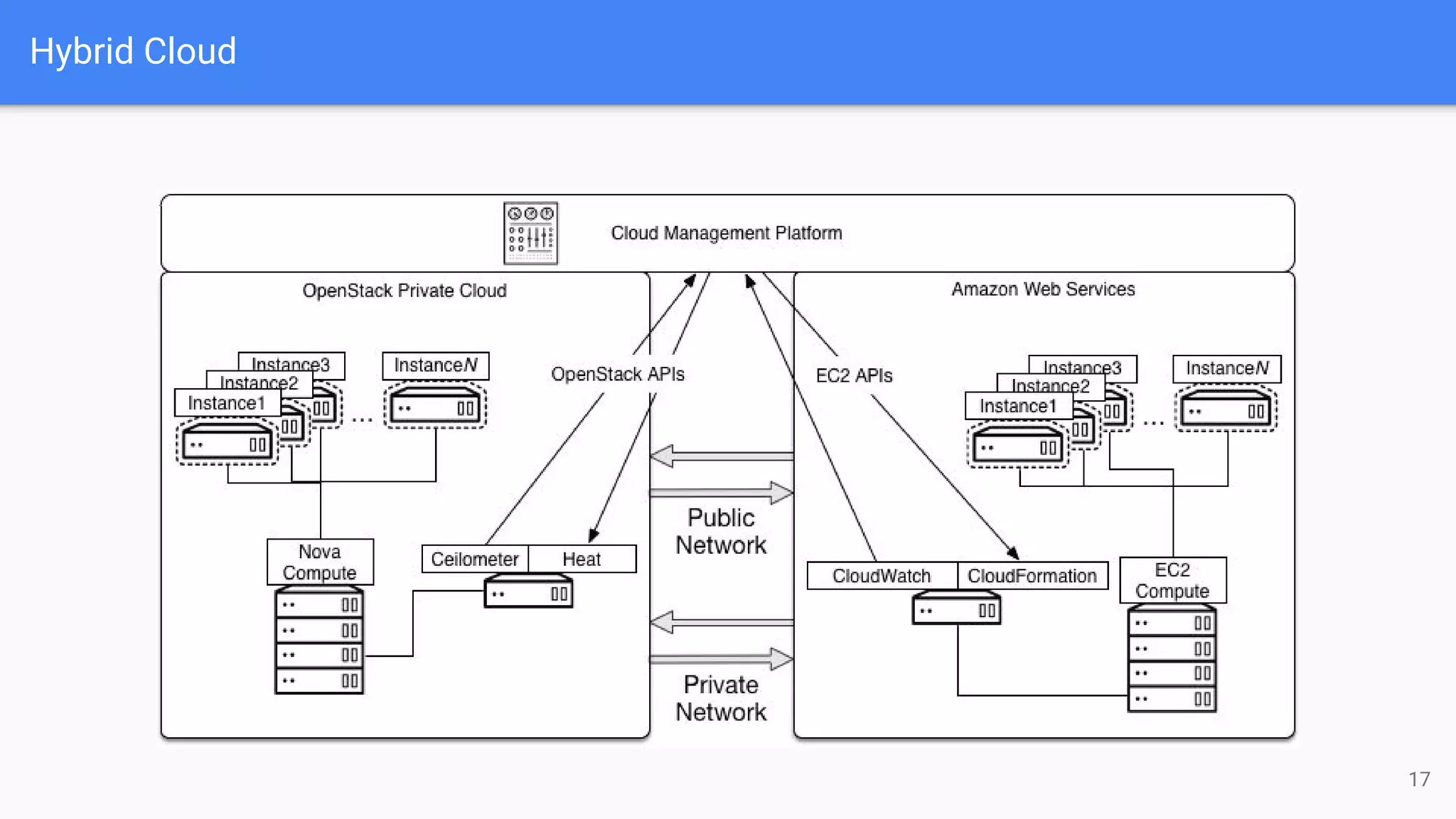
The document outlines a presentation on deploying OpenStack for mission-critical and production workloads, emphasizing the importance of high availability and the architecture of OpenStack components such as Ceph for storage and networking solutions. It provides technical specifications and best practices for configuring and sizing Ceph clusters, as well as considerations for compute resources and scalability. Additionally, it discusses challenges faced, areas for improvement, and the skill sets needed for successful implementation.