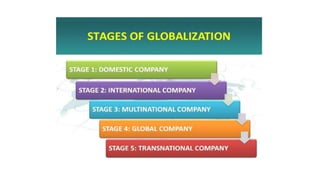
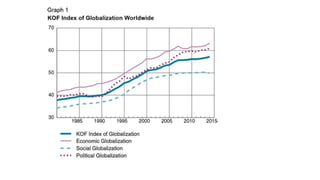
This document discusses globalization and its impact on India. It defines globalization as the intensification of social relations between distant localities such that events in one place can influence those elsewhere. Forces driving globalization include consumer demand, reduced trade barriers, and advances in technology and competition. Globalization occurs through international trade, foreign direct investment, and financial capital flows. While globalization posed some initial obstacles for India, economic reforms embraced openness and helped sectors like agriculture, industry, finance, and exports. Overall, globalization has generated benefits through increased markets, investments, technology, and cultural exchange, though it also brought challenges adapting to more competitive markets.