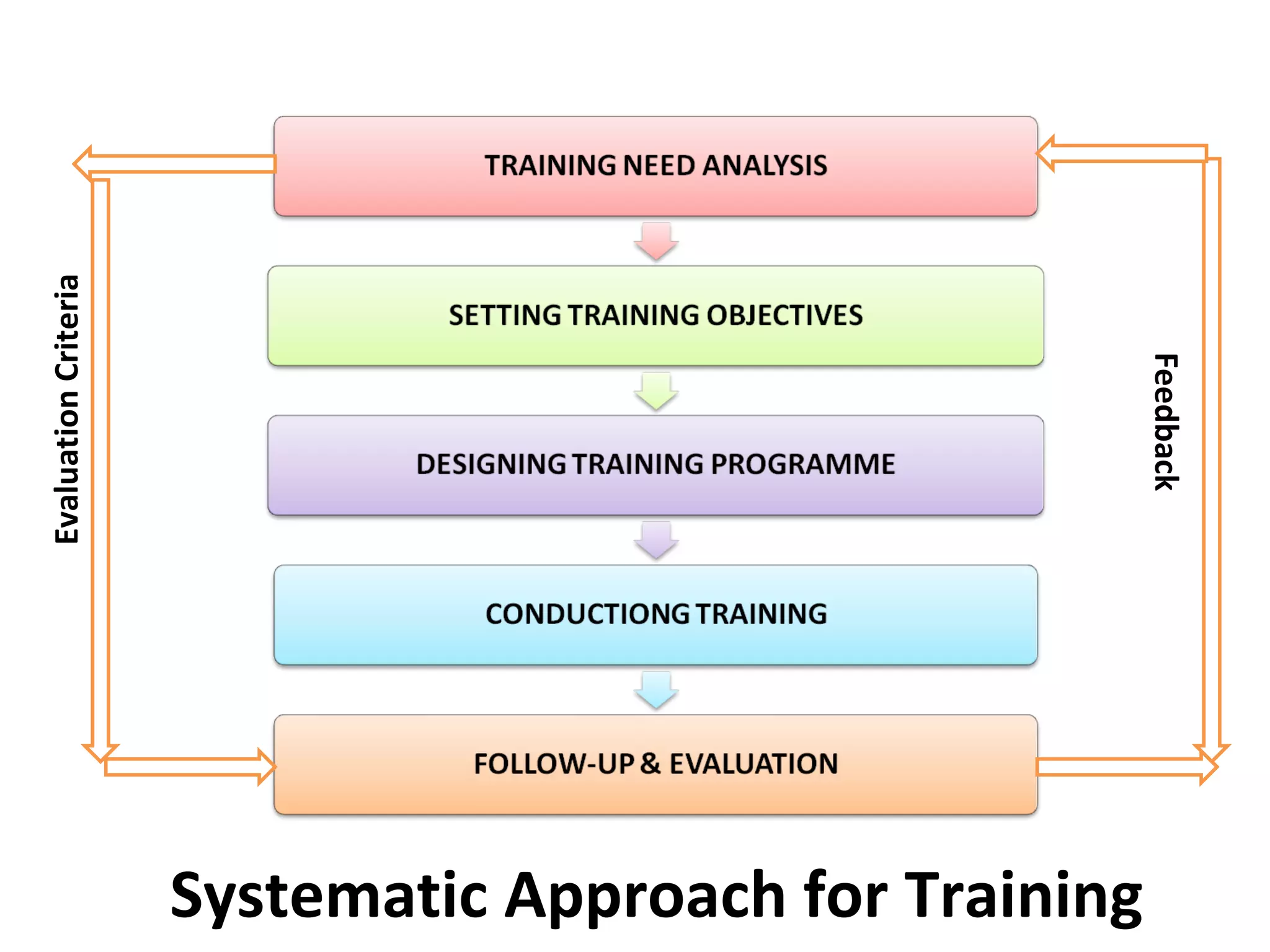
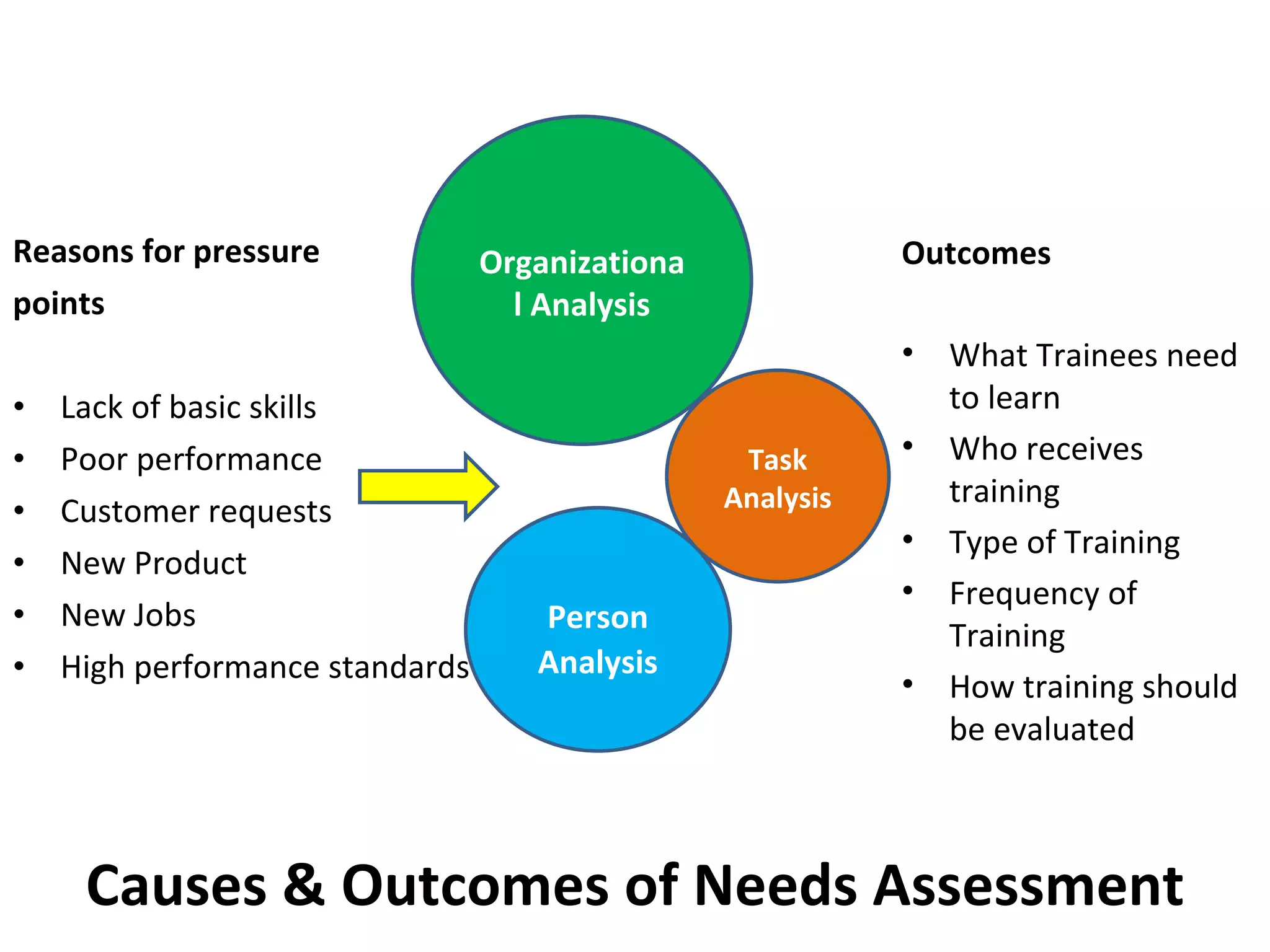
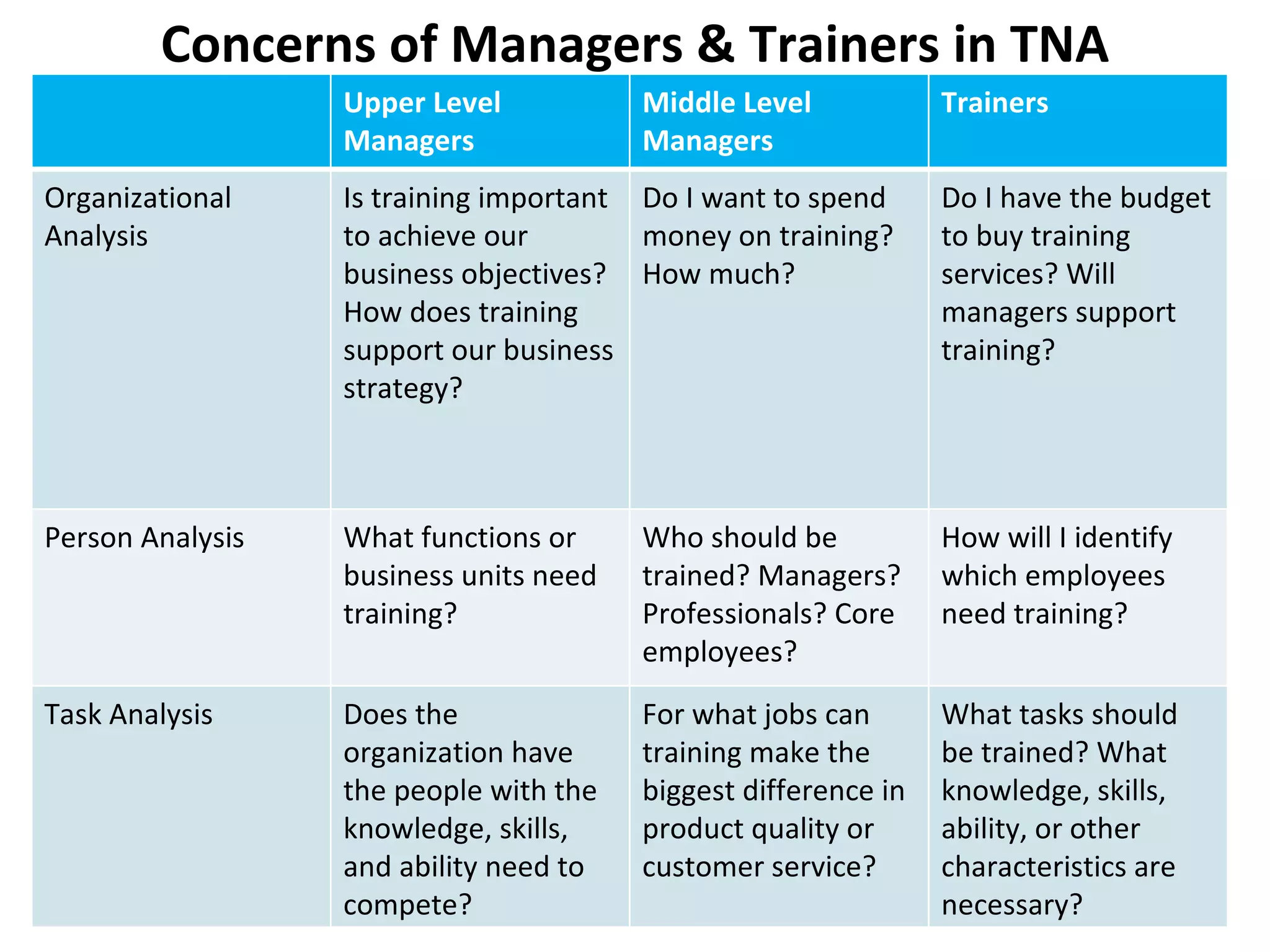
1. The document discusses training initiatives at Godrej, an Indian conglomerate, including the need for change after a joint venture ended in 1995 and the company's emphasis on training programs.
2. Key training programs included TQM awareness in 1995, GALLOP for new recruits in 2002, EVA training for managers in 2001, and E-Gyan's e-learning initiative in 2002.
3. Godrej focused on participative management, total quality management, and imparting knowledge to motivate employees and develop leaders through rotational and self-learning programs.