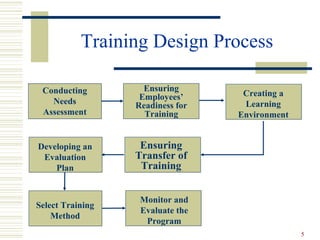
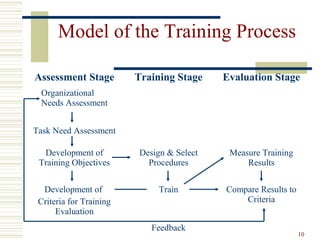
This document discusses training and development in organizations. It begins by defining training and distinguishing it from education and development. It then outlines the training design process, including conducting a needs assessment, selecting training methods, and evaluating the program. The importance and benefits of training are explained. Key principles of learning and a systematic approach to developing a training plan are also covered. The document provides examples of different types of training methods and discusses best practices for implementing, evaluating, and improving training programs.