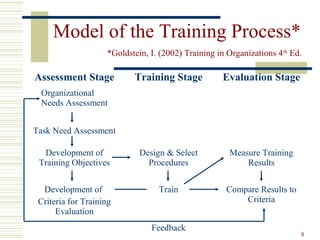
This document discusses the importance and benefits of training for employees. It defines training as a systematic process that improves corporate performance by developing employee skills and knowledge through instruction and practical activities. The document outlines differences between training, education, and development. It also describes principles of learning and a systematic approach to developing a training plan, including assessing needs, specifying objectives, designing programs, and evaluating training effectiveness.