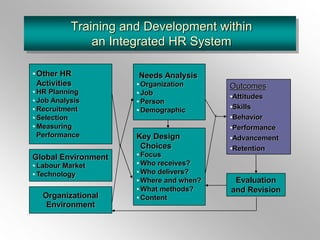
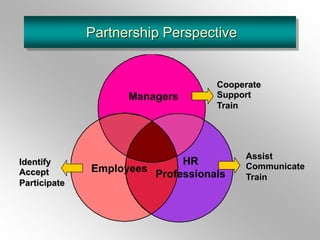
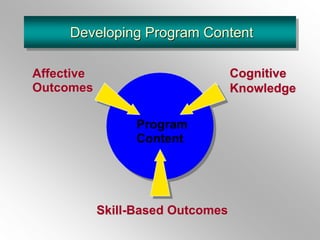
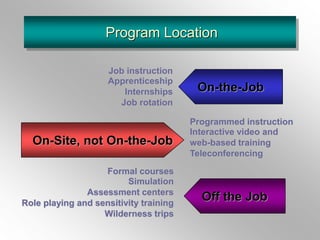
The document discusses employee training and development. It defines training and development, and key related terms like socialization. It outlines factors to consider in training needs analysis, including organizational, job, personal, and demographic needs. Methods of training delivery are addressed, such as on-the-job, on-site, and off-site training. The roles of managers, HR professionals, and employees in training are defined. The document also covers developing program content, evaluating training impact, and maintaining performance after training.