1. Indeterminate errors, also known as random errors, arise from unknown uncertainties in measurement and cannot be eliminated. They produce a divergence in numerical values.
2. The true value is the population mean for an infinite number of measurements, while the acceptable value is the arithmetic mean for a given finite data set. Absolute error is the difference between measured and true values, while relative error is the ratio of absolute error to true value.
3. Measures of central tendency like the mean, median, and mode describe the central or typical value for a data set. Measures of dispersion like the range, standard deviation, and coefficient of variation describe how spread out the data is around the central value.




![Semester IV S.Y.B.Sc. Paper III Unit III
5
Distribution of Random Errors:
Indeterminate errors or Random errors arise as a consequence of small unknown uncertainty.
This error cannot be eliminated from measurement and at the same time they cannot be
ignored. Apart from personal random errors, some random errors may also be introduced in
measurements due to errors in the methods itself. This may be due to increase in Chemicals
or irregular variation of room temperature.
The task of analytical chemist to make a random error as small as possible. Hence the
distribution for random errors that is like to move the value in either direction is called as the
normal or Gaussian distribution. Such a distribution is characterized by two parameters, the
population mean μ and population standard deviation σ.
Gaussian Distribution Curve
For a large number of replicate measurements readings free of determinant error, the results
will generally be symmetrical distributed around the mean. By determining the relative
frequency of occurrence of a reading and plotting the values for different results, the curve
obtained is known as the normal distribution curve.
The equation of the curve is
y =
1
𝜎√2𝜋
exp − [
(𝑋𝑖 − 𝜇) 2
2𝜎2
]
Where,
y = the relative frequency of occurrence for given set of observation
xi = the value of corresponding observation of the set
μ = the mean of population of Universe with infinite number of observations
σ = standard deviation for the population comprising infinite number of observations.
The equation is the Gauss-Laplace equation and hence the distribution is also called as
Gaussian distribution curve or the normal error curve.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalstatisticaltreatmentdata-210426135914/85/Final-statistical-treatment-data-5-320.jpg)






![Semester IV S.Y.B.Sc. Paper III Unit III
12
The variance Ratio Test- F Test:
The variance ratio test is used to find out whether the two standard deviations obtained for
the two sets of the observations of the same sample differ only numerically or statically.
Variance is defined as the square of the standard deviation. The ratio of the two variances for
the two sets of observations are considered in this test and hence the name is Variance Ratio
Test. The steps involved in the calculation of the variance ratio test are as follows:
i) Calculate the standard deviations S1 and S2 for the two sets of observations.
ii) Calculate the variance ratio which is known as F in such a way that the ratio is greater
than one. This is done by placing the larger standard deviation in the numerator.
𝐹𝑐𝑎𝑙 =
𝑠1
2
𝑠2
2 𝑠1 > 𝑠2
iii) From the table of F values [refer to table] for the given number of observations and
for the given probability level, obtain the appropriate value of F.
Result: There are only two possibilities.
1) Fcal<Ftab: In this case, the two standard deviations are not statistically different but
only numerically different.
2) Fcal>Ftab: In this case, the two standard deviations are not only differing
numerically but statistically as well
Tabulated values of the Statistical Parameter F
(n-1) for
smaller s2
n-1 for larger S2
1 2 3 4 5
1 161 200 216 225 230
2 18.51 19 19.16 19.25 19.30
3 10.13 9.55 9.28 9.12 9.01
4 7.71 6.94 6.59 6.39 6.26
5 6.61 5.79 5.41 5.19 5.05
6 5.99 5.14 4.76 4.53 4.34
7 5.59 4.74 4.35 4.12 3.47
8 5.32 4.46 4.07 3.84 3.69
9 5.12 4.26 3.86 3.63 3.48
10 4.96 4.10 3.71 3.48 3.33
(Numericals)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalstatisticaltreatmentdata-210426135914/85/Final-statistical-treatment-data-12-320.jpg)
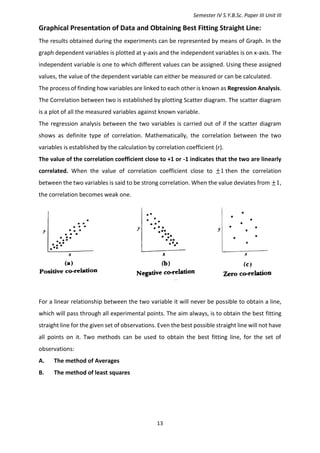

![Semester IV S.Y.B.Sc. Paper III Unit III
15
∑ 𝑦 = ∑ 𝑚𝑥 + ∑ 𝑐
∑ 𝑦 = 𝑚 ∑ 𝑥 + ∑ 𝑐
From the value of m and c equation of best fitting line is obtained.
B. The Method of Least Square:
In this method for the best fitting line sum of square deviation of all points from line is
minimum (equal to zero).
∑(𝑦 − 𝑦𝑐𝑎𝑙)2
= 0
Case I: Line passing from origin
From the equation of line passing from origin
y = mx
But, ycal = mx
∑(𝑦 − 𝑚𝑥)2
= 0
By differentiating,
𝑑
𝑑𝑚
∑(𝑦 − 𝑚𝑥)2
= 0(
𝑑
𝑑𝑚
𝑎𝑠 𝑚 𝑖𝑠 𝑣𝑎𝑟𝑖𝑎𝑏𝑙𝑒)
∑
𝑑
𝑑𝑚
(𝑦 − 𝑚𝑥)2
= 0
∑ 2 (𝑦 − 𝑚𝑥)
𝑑
𝑑𝑚
(𝑦 − 𝑚𝑥) = 0
2 ∑(𝑦 − 𝑚𝑥) [(
𝑑𝑦
𝑑𝑚
) − (𝑥
𝑑𝑚
𝑑𝑚
)] = 0
2 ∑(𝑦 − 𝑚𝑥)(0 − 𝑥) = 0
2 ∑ −𝑥𝑦 + 𝑚𝑥2
= 0
∑(−𝑥𝑦) + ∑(𝑚𝑥2
) = 0
𝑚 ∑ 𝑥2
= ∑ 𝑥𝑦
𝑚 =
∑ 𝑥𝑦
∑ 𝑥2
From the value of ‘m’ equation of best fitting line is obtained.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalstatisticaltreatmentdata-210426135914/85/Final-statistical-treatment-data-15-320.jpg)
![Semester IV S.Y.B.Sc. Paper III Unit III
16
Case II: Line not passing from origin
From the equation of line not passing from origin
y = mx + c
But, ycal = mx + c
∑(𝑦 − 𝑦𝑐𝑎𝑙)2
= 0
∑(𝑦 − (𝑚𝑥 + 𝑐))2
= 0
∑(𝑦 − 𝑚𝑥 − 𝑐)2
= 0
By differentiating,
Here ‘m’ and ‘c’ both are variable
𝑑
𝑑𝑚
∑(𝑦 − 𝑚𝑥 − 𝑐)2
= 0
as well as
𝑑
𝑑𝑐
∑(𝑦 − 𝑚𝑥 − 𝑐)2
= 0
i)
𝑑
𝑑𝑚
∑(𝑦 − 𝑚𝑥 − 𝑐)2
= 0
∑ 2 (𝑦 − 𝑚𝑥 − 𝑐)
𝑑
𝑑𝑚
(𝑦 − 𝑚𝑥 − 𝑐) = 0
2 ∑(𝑦 − 𝑚𝑥 − 𝑐) [(
𝑑𝑦
𝑑𝑚
) − (𝑥
𝑑𝑚
𝑑𝑚
) − (
𝑑𝑐
𝑑𝑚
)] = 0
2 ∑(𝑦 − 𝑚𝑥 − 𝑐)[0 − (𝑥) − 0] = 0
∑(𝑦 − 𝑚𝑥 − 𝑐)( − 𝑥) = 0
∑ −𝑥𝑦 + 𝑚𝑥2
+ 𝑥𝑐 = 0
∑ 𝑥𝑦 = 𝑚 ∑ 𝑥2
+ 𝑐 ∑ 𝑥 ---------------- A](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalstatisticaltreatmentdata-210426135914/85/Final-statistical-treatment-data-16-320.jpg)
![Semester IV S.Y.B.Sc. Paper III Unit III
17
ii.
𝑑
𝑑𝑐
∑(𝑦 − 𝑚𝑥 − 𝑐)2
= 0
∑ 2 (𝑦 − 𝑚𝑥 − 𝑐)
𝑑
𝑑𝑐
(𝑦 − 𝑚𝑥 − 𝑐) = 0
2 ∑(𝑦 − 𝑚𝑥 − 𝑐) [(
𝑑𝑦
𝑑𝑐
) − (𝑥
𝑑𝑚
𝑑𝑐
) − (
𝑑𝑐
𝑑𝑐
)] = 0
2 ∑(𝑦 − 𝑚𝑥 − 𝑐)[0 − 0 − 1] = 0
∑(𝑦 − 𝑚𝑥 − 𝑐) − (1) = 0
∑ −(𝑦 − 𝑚𝑥 − 𝑐) = 0
− ∑ 𝑦 + ∑ 𝑚𝑥 + ∑ 𝑐 = 0
∑ 𝑦 = 𝑚 ∑ 𝑥 + ∑ 𝑐 ---------------- B
(Numericals)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalstatisticaltreatmentdata-210426135914/85/Final-statistical-treatment-data-17-320.jpg)