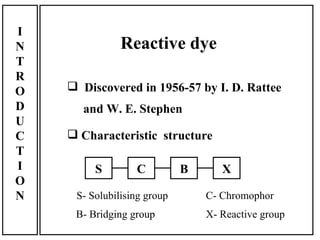
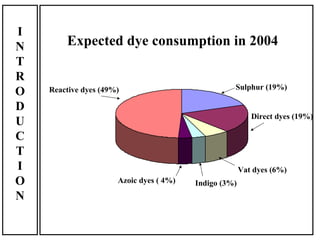
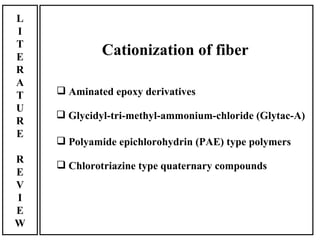
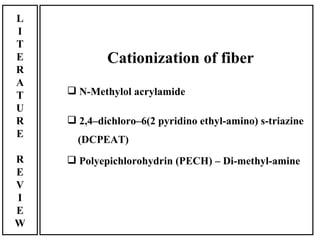
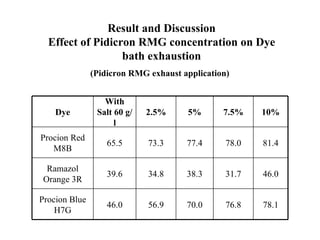
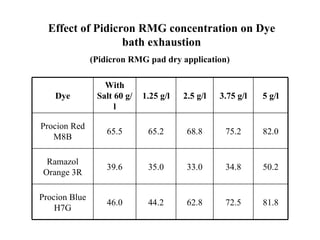
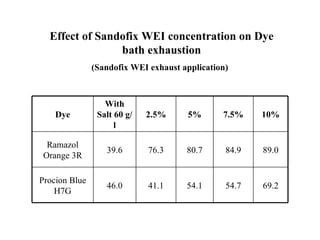
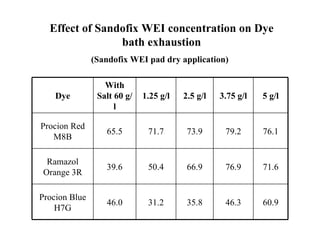
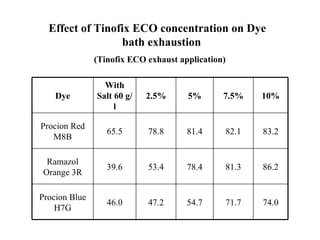
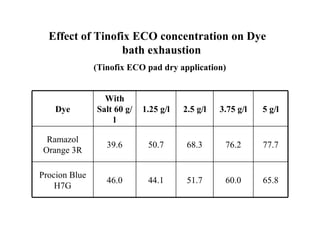
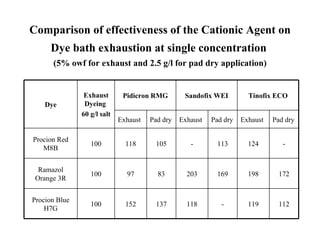
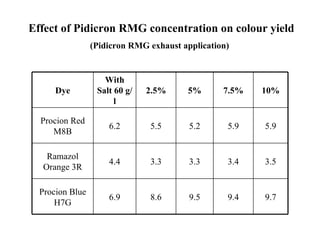
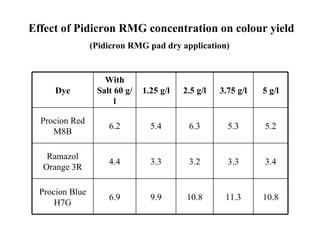
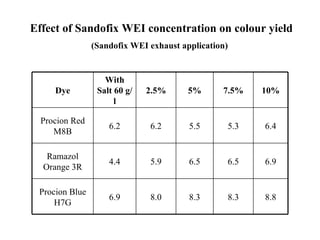
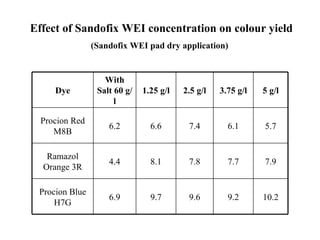
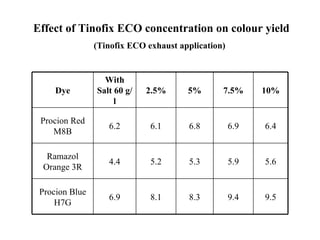
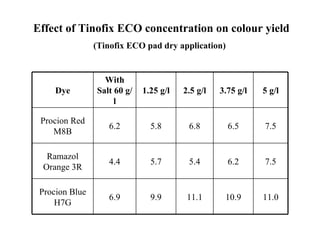
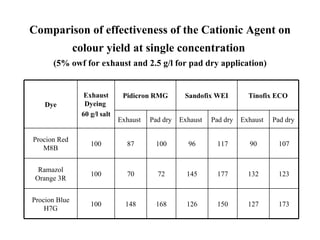
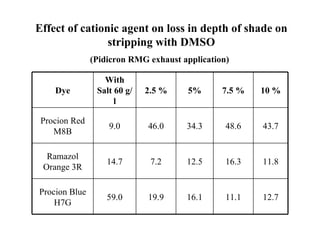
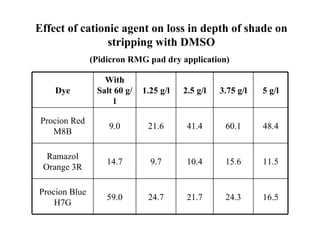
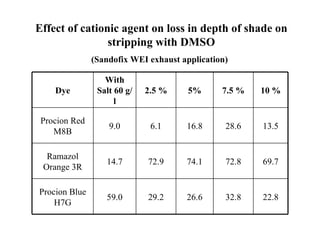
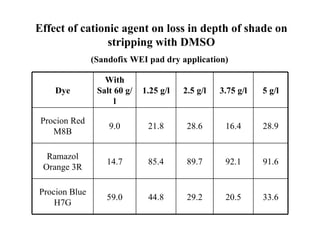
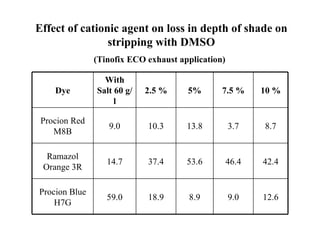
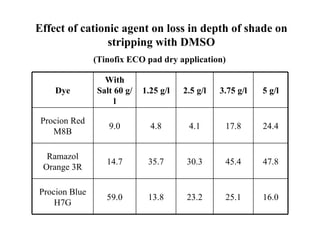
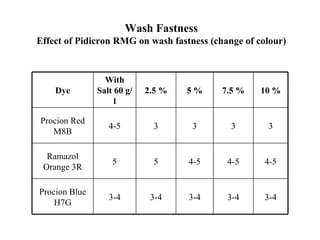
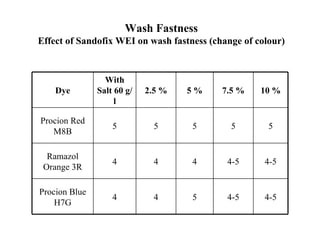
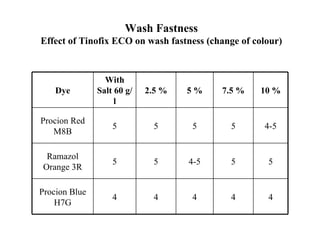
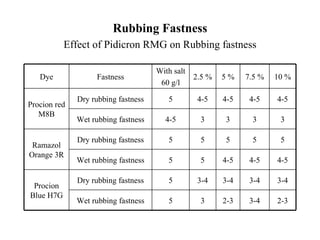
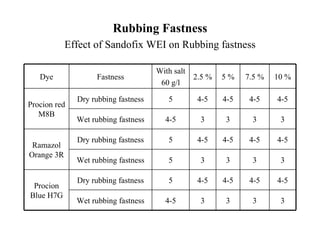
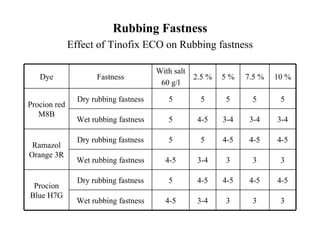
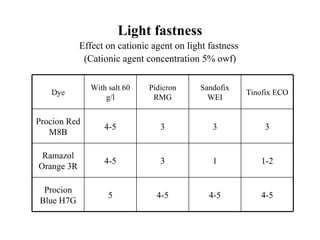
The document discusses salt-free dyeing of cotton with reactive dyes using cationic agents. It aims to study the feasibility of using cationic agents instead of salt for dyeing cotton with reactive dyes. Various cationic agents are used to pretreat cotton via exhaust and pad-dry methods, followed by exhaust dyeing without salt. Dye exhaustion and color yield are compared for different cationic agents and pretreatment methods. Results show that pretreatment with cationic agents increases dye exhaustion and color yield compared to dyeing with salt. Tinofix ECO gives the highest dye exhaustion and color yield for most dyes tested. The study suggests cationic agents can enable salt-free dyeing of cotton with reactive