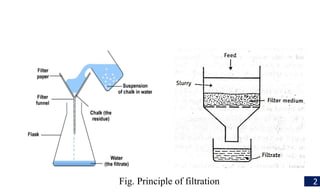
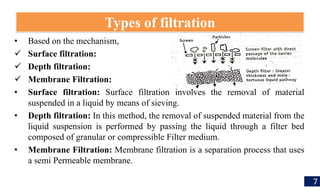
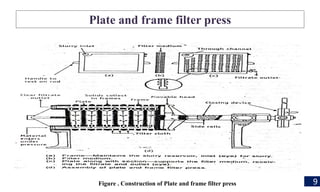
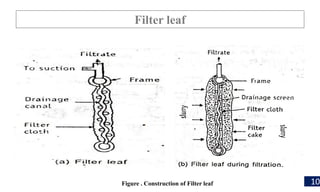
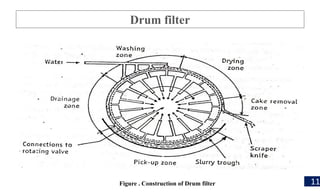
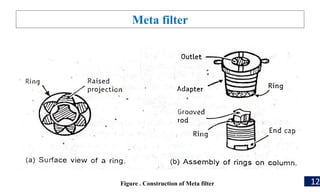
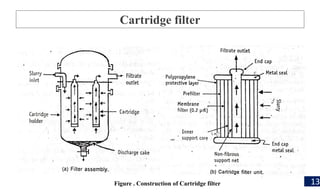
Filtration is a process used to separate solid particles from a liquid by passing it through a porous medium, resulting in a clear liquid called filtrate. The document discusses various types of filtration, mechanisms involved, and its applications in different fields, including water treatment and pharmaceutical manufacturing. It also outlines the importance of filtration in obtaining sterile products and the equipment used in the process.