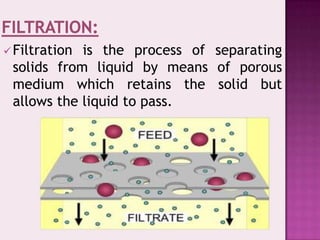
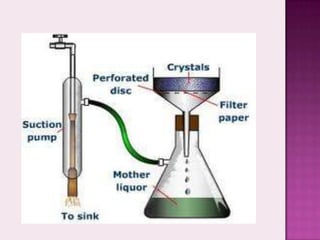
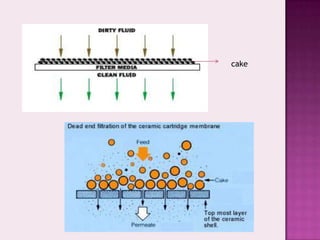
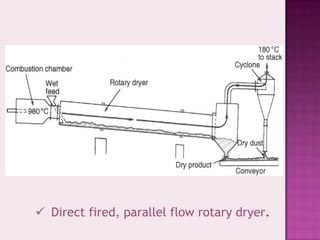
The document discusses various aspects of filtration and drying processes used in mineral processing. It describes how filtration separates solids from liquids using a porous medium, and identifies some key factors that affect filtration like pressure difference, pore size, and filter cake thickness. It also outlines different types of filters like pressure filters, suction filters, and cake filters. The document then covers common drying methods like rotary dryers, and whether heating is done directly or indirectly. The overall content provides an overview of solid-liquid separation and moisture removal techniques for mineral processing applications.