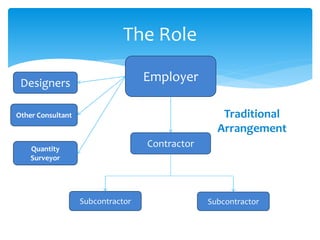
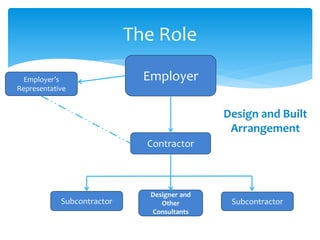
This document provides a presentation on design and build contracts under FIDIC contracts. It discusses what FIDIC is, its origins and vision. It then discusses design and build procurement, highlighting advantages like price certainty and single point responsibility, as well as disadvantages like reduced employer control. It outlines the roles of different parties in traditional vs design and build arrangements. It also summarizes key clauses and details in FIDIC's Orange Book and Yellow Book for design and build and turnkey contracts. Sample questions and answers are provided to illustrate how situations would be addressed under the FIDIC contracts.