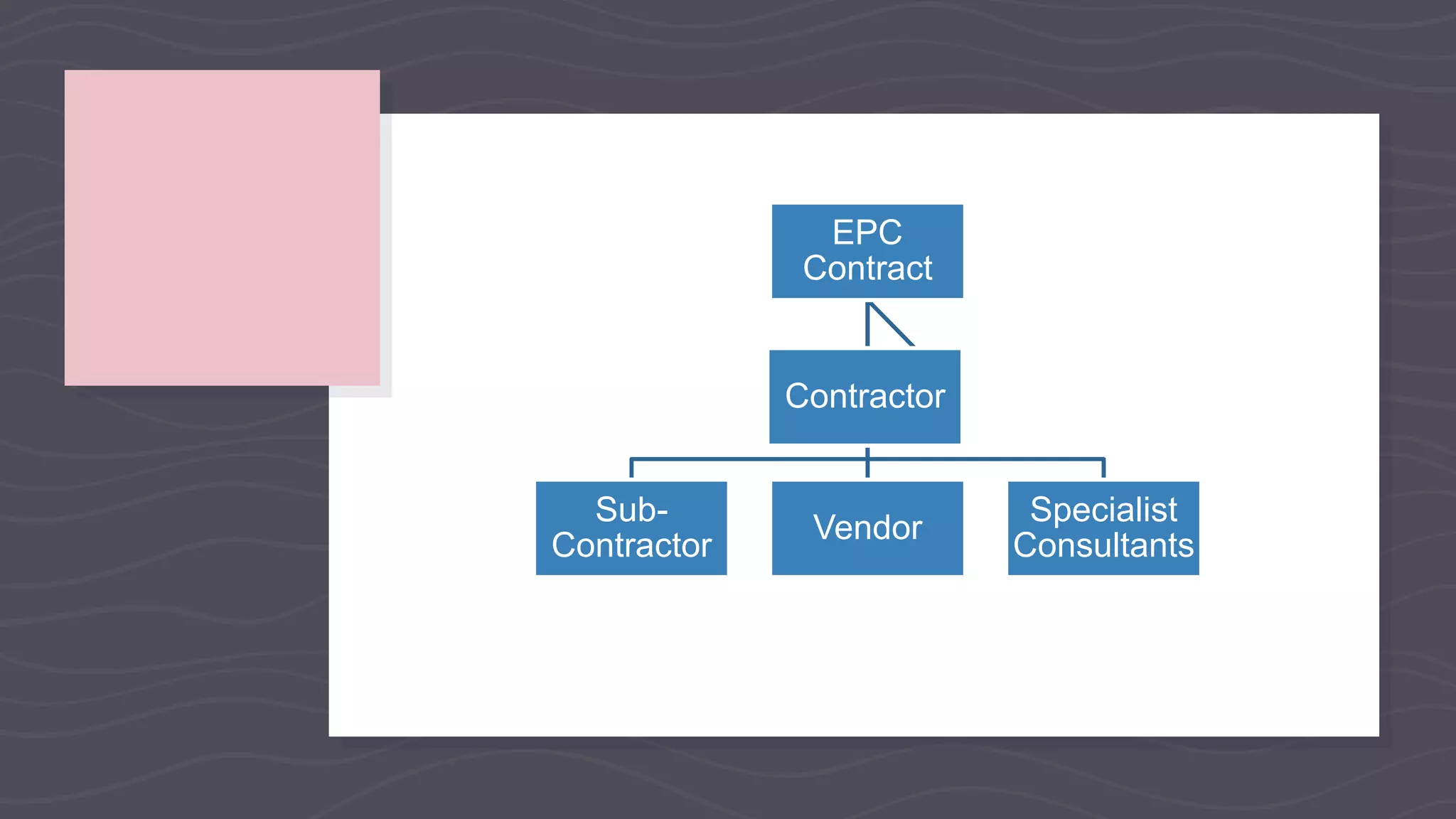
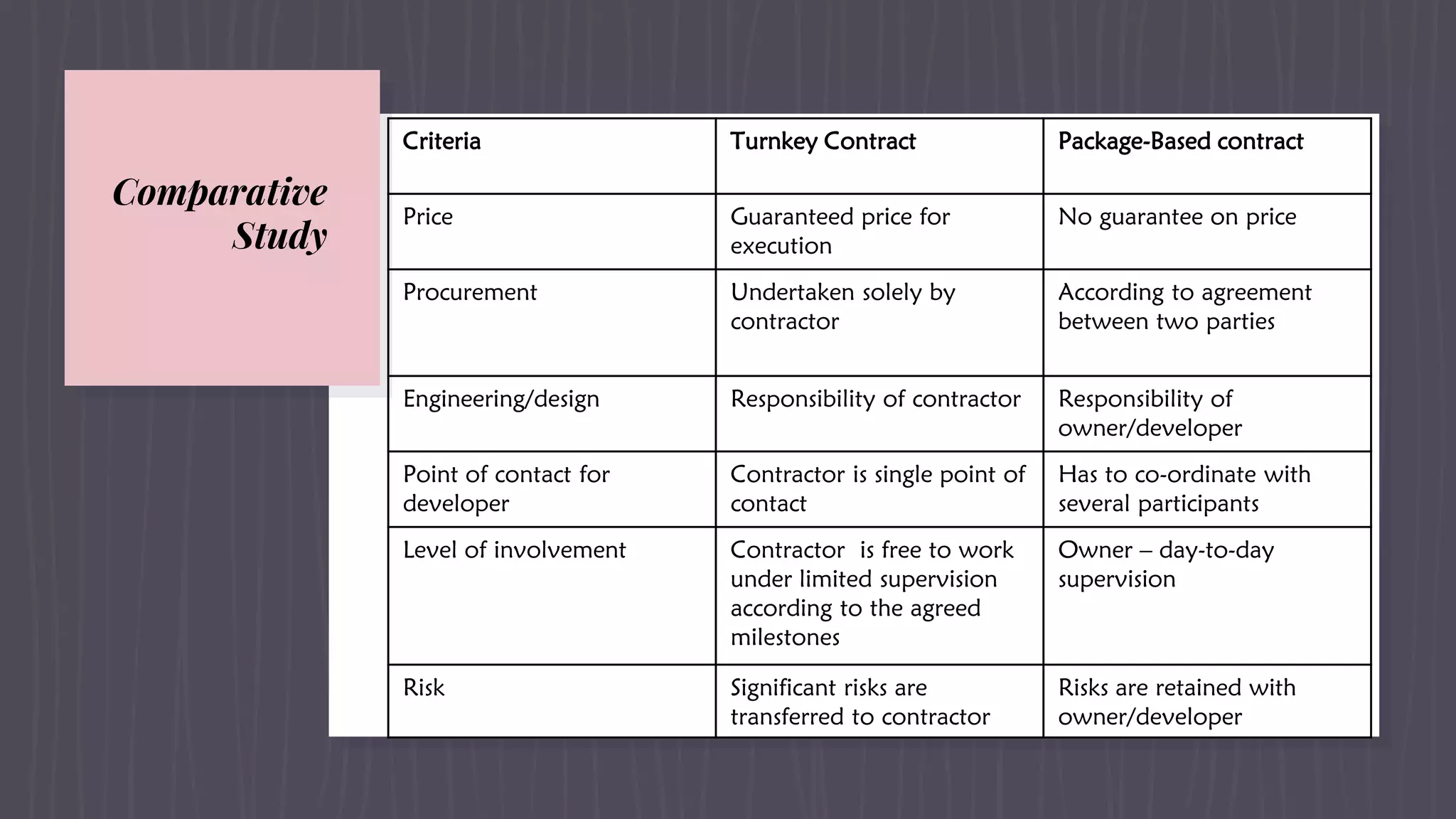
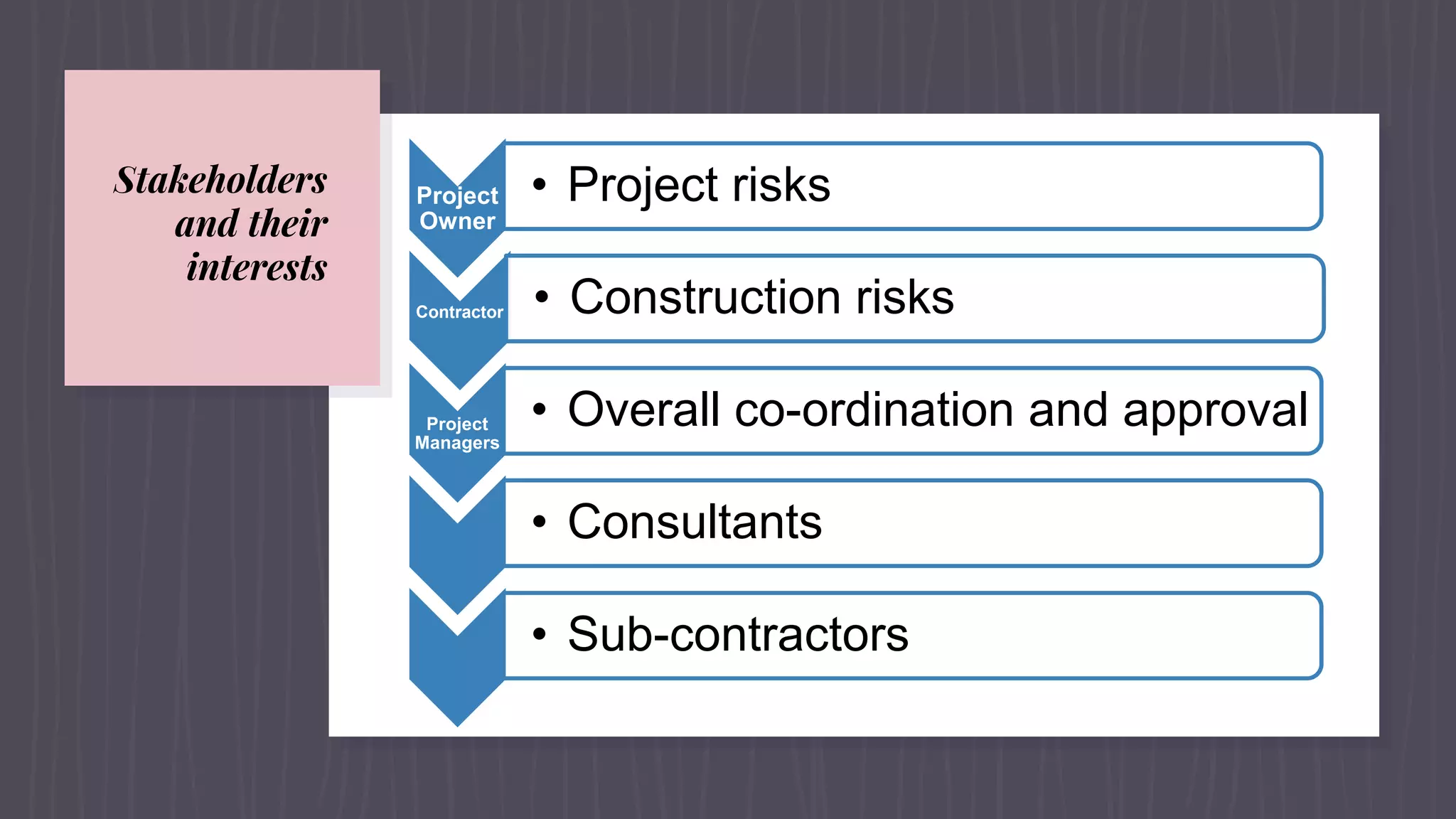
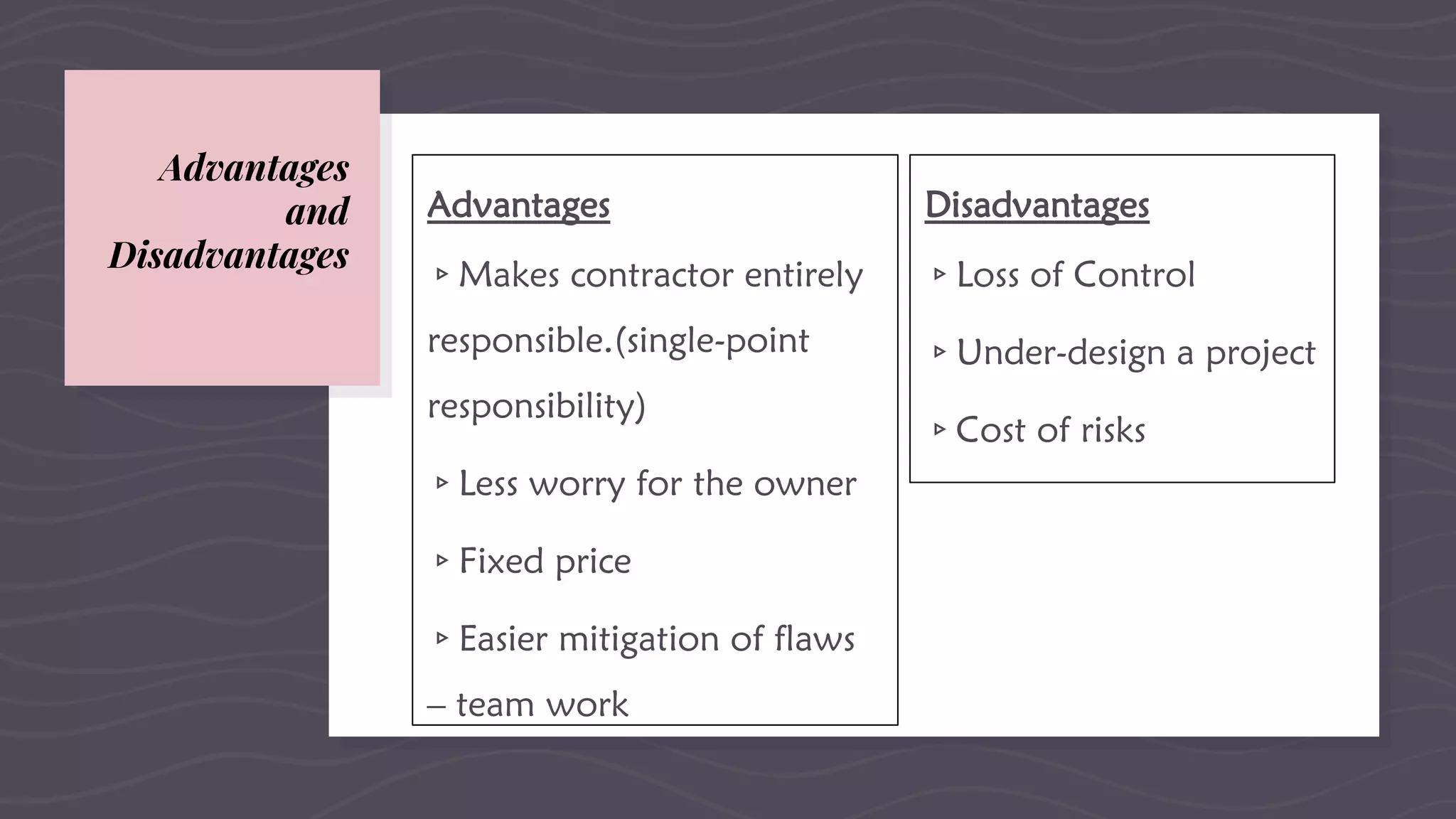
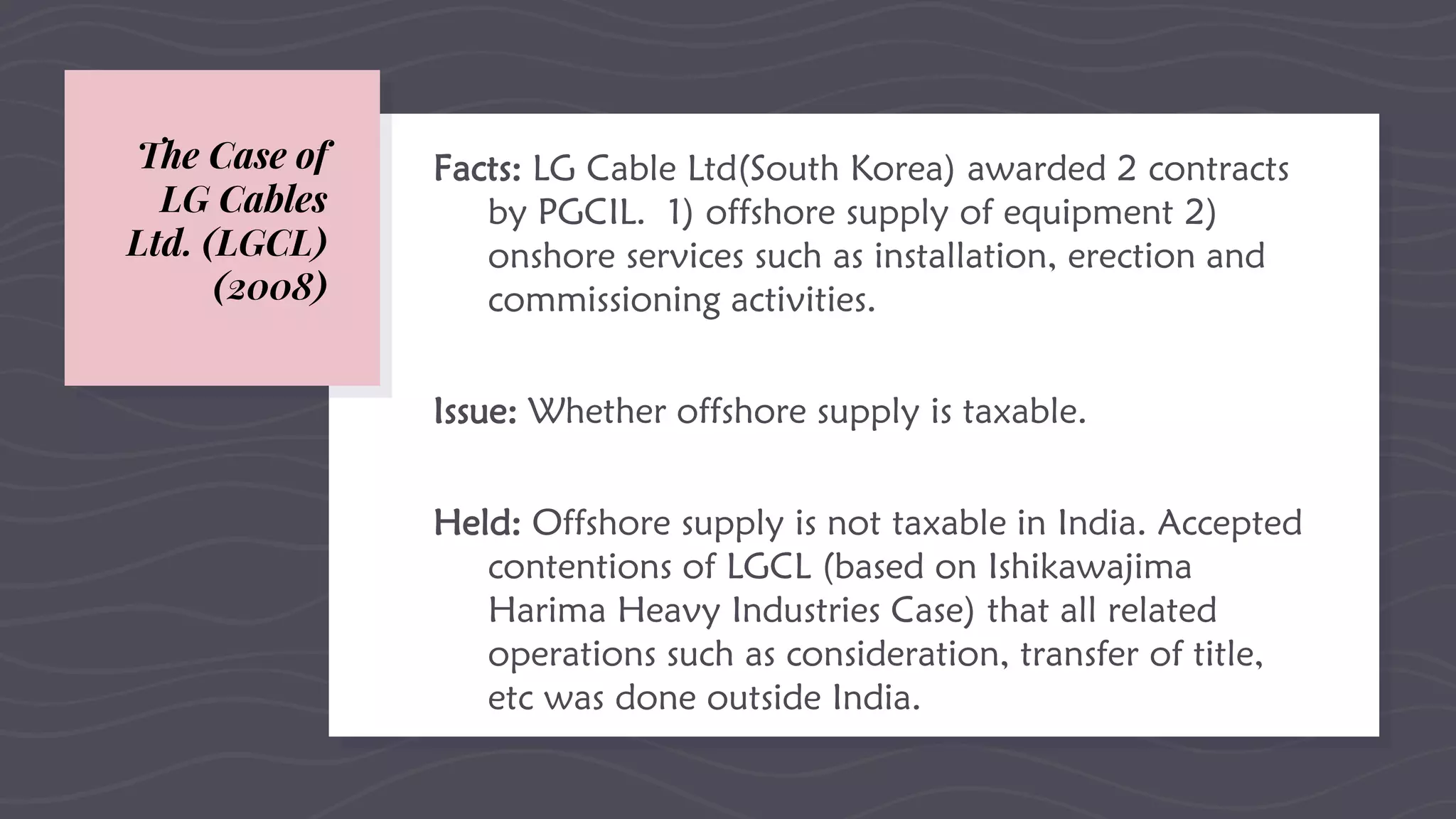
This document provides an overview of EPC (engineering, procurement and construction) contracts. It defines EPC contracts and explains that they make the contractor solely responsible for engineering, procurement and construction. The document outlines the key components, features and contractual technicalities of EPC contracts including single-point responsibility, fixed payment terms, and allocation of risks. It also discusses advantages and disadvantages, the bidding process, important contract clauses, and dispute resolution mechanisms for EPC contracts.