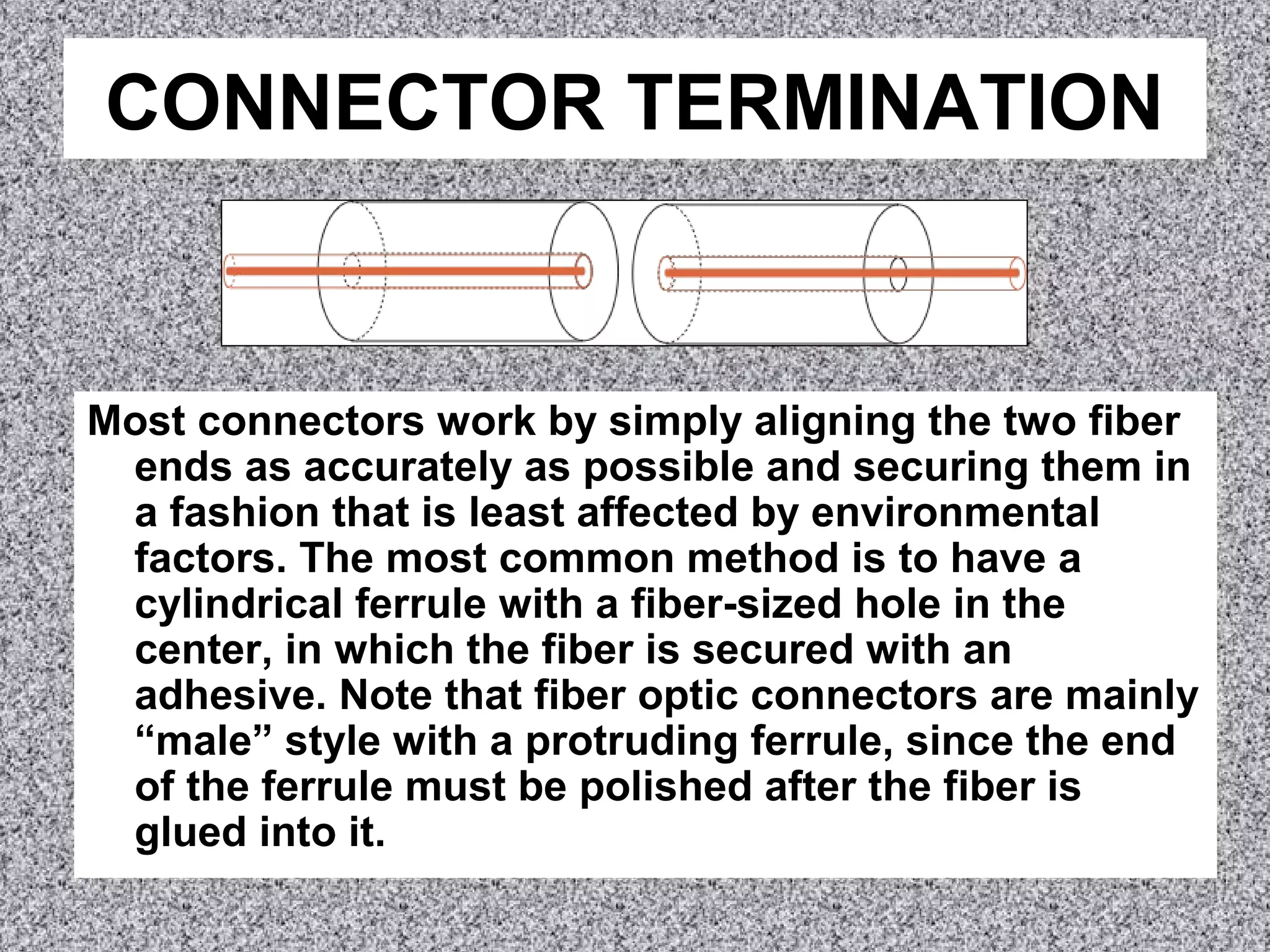
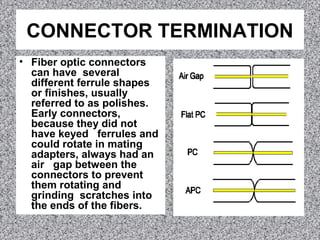
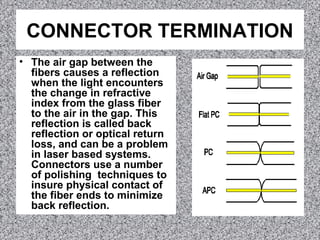
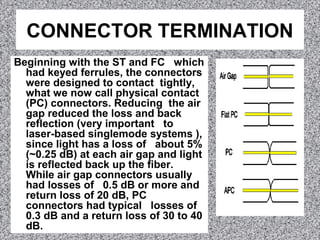
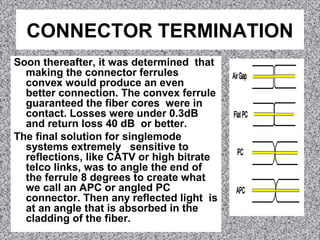
Most fiber optic connectors work by aligning the two fiber ends and securing them in a way that is resistant to environmental factors. The most common method uses a cylindrical ferrule with a fiber-sized hole to secure the fiber with adhesive. Connector ferrules are often made of ceramic because it is environmentally stable and easy to polish. Proper termination involves stripping the fiber, applying adhesive to the ferrule, inserting and cleaving the fiber, and polishing the end to minimize back reflection.