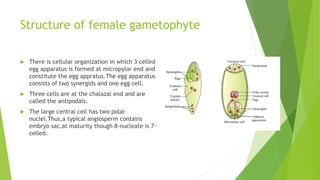
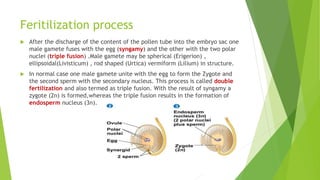
This document summarizes the process of fertilization in angiosperms. It describes the structures involved, including the pollen grain, which contains two cells including the generative cell that divides into two male gametes. The female gamete is contained in the embryo sac, which contains seven cells including an egg cell. Pollination involves the transfer of pollen grains to the stigma. Germination of compatible pollen on the stigma produces a pollen tube that grows down to fertilize the egg cell in a process called double fertilization, where one gamete fuses with the egg and the other with the polar nuclei. This results in the formation of a diploid zygote and triploid endosperm to nourish