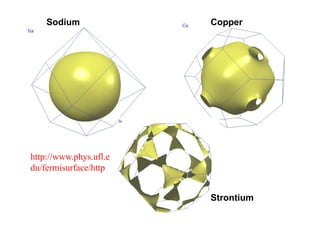
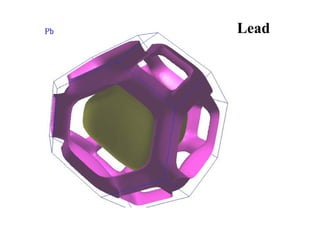
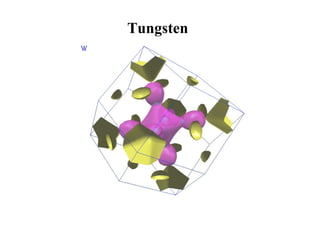
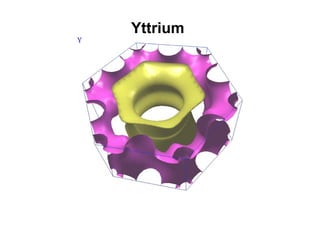
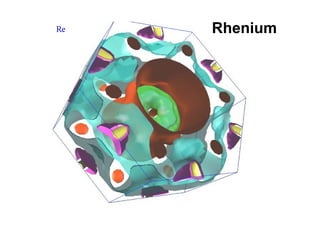
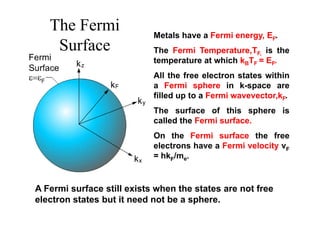
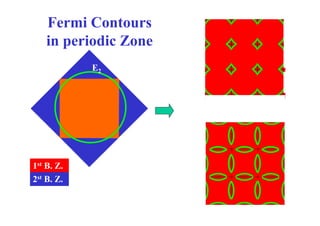
This document discusses Fermi surfaces and band structure calculations in solid state physics. It begins by explaining that band structure calculations give the energy-momentum relationship E(k) for electrons in solids. The dynamics of electrons are determined by E(k), particularly at the Fermi surface. The form and complexity of the Fermi surface depends on factors like overlapping bands. Brillouin zones are constructed to describe the periodic nature of crystal momentum. Metals have a Fermi energy EF, and the Fermi surface is the surface in k-space enclosing states below EF. The Fermi surface need not be a sphere when states are not free electrons. Examples of Fermi surfaces for different materials like sodium, copper, and palladium


![Brillouin Zones and Fermi Surfaces
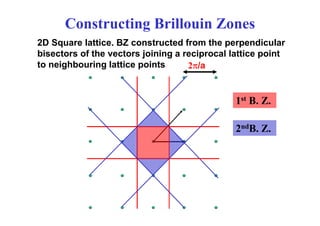
Empty Lattice model (limit of weak
Empty Lattice model (limit of weak
lattice potential):
States are Bloch states.Independent
E E2
States are Bloch states.Independent
states have k-vectors in first BZ.
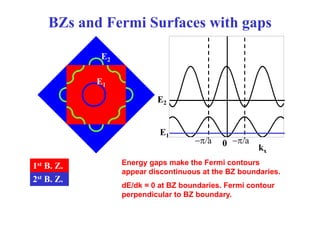
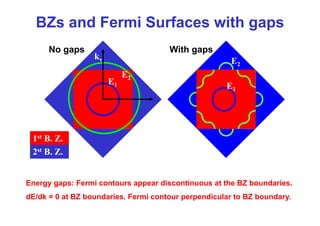
No energy gaps at the BZ boundaries.
E1
kx π/a
−π/a 0
ky
[100]
kx = ky
E1
E2
y
E2
1
E1
1st B Z
k
−21/2π/a 0 21/2π/a
[110]
2st B. Z.
1st B. Z.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fermi-surfaces-240408065406-4e2230a0/85/fermi-surfaces-sperficies-de-fermi-slide-pdf-5-320.jpg)
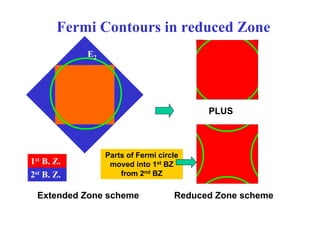
![E = -α –γ( Cos[kx x] - Cos[ky y]),
2D simple square
Lattice tight binding
Lattice tight binding
model.
Changing Fermi
Changing Fermi
Contour with
I i F i
Increasing Fermi
Energy.
http://dept.physics.upenn.edu/~mele/phys518/anims/Kronig/FermiSurf1.gif](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fermi-surfaces-240408065406-4e2230a0/85/fermi-surfaces-sperficies-de-fermi-slide-pdf-8-320.jpg)


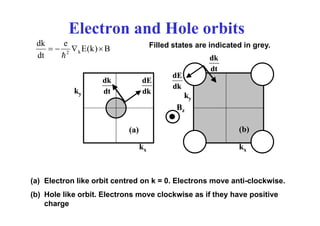
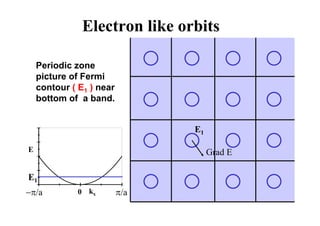
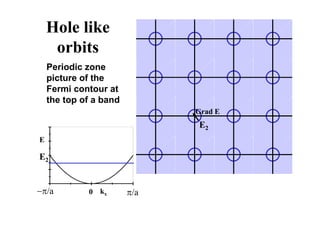
![Tight binding simple cubic
d l F i S f
model:Fermi Surfaces
-α – γ(Cos[kx x] - Cos[ky y] - Cos[kz z]
Increasing Fermi Energy
h //h i b / l l /f i i l h l
http://home.cc.umanitoba.ca/~loly/fermiarticle.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fermi-surfaces-240408065406-4e2230a0/85/fermi-surfaces-sperficies-de-fermi-slide-pdf-17-320.jpg)