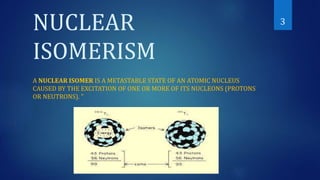
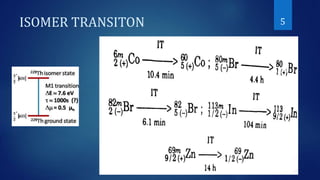
The document covers selective topics in nuclear chemistry, including nuclear isomerism, internal conversion, and the Auger effect. It explains that nuclear isomers are metastable states with relatively long half-lives, and discusses the mechanisms by which nuclei transition to ground states, including the ejection of electrons. The Auger effect is described as the process where the filling of an inner-shell vacancy leads to the emission of an electron from the same atom.