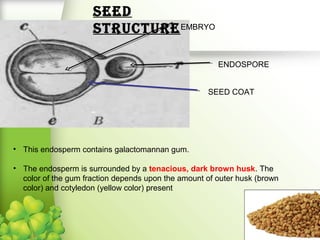
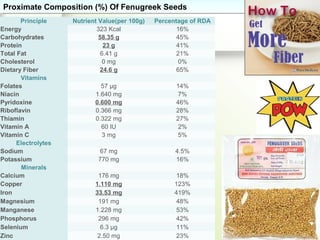
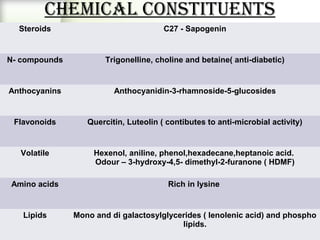
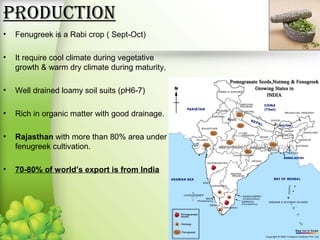
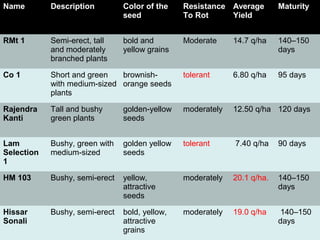
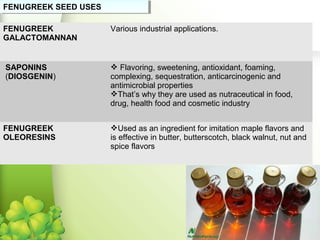
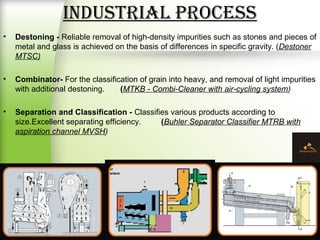
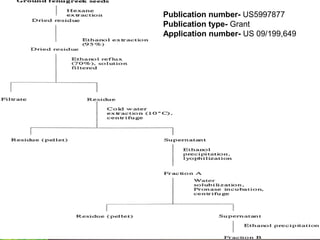
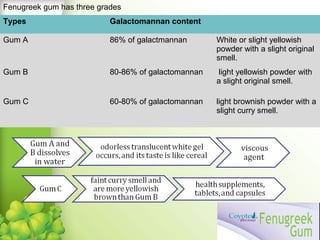
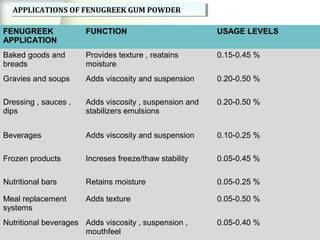
Fenugreek is an annual herb that has been used medicinally and in cooking for thousands of years. The seeds are the main part used and contain compounds like fiber, proteins, vitamins, and minerals. Fenugreek seeds are commonly used as a spice and also have a variety of traditional medicinal uses due to their anti-diabetic, anti-inflammatory, and cholesterol-lowering properties. The seeds contain galactomannan gum which has various industrial applications as a thickening, stabilizing, and emulsifying agent. Fenugreek is widely cultivated in parts of India and its seeds are an important crop and commodity.