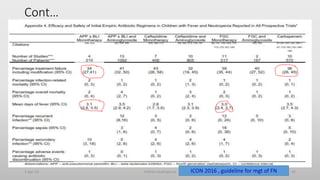
This document provides an overview of the management of neutropenic fever in pediatric patients. It defines febrile neutropenia and outlines the etiology, clinical manifestations, investigations, and risk stratification approach. Common pathogens include gram-negative bacteria like Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli. Investigations include blood cultures, urine analysis and culture if indicated, and chest x-ray only for symptomatic patients. Risk stratification divides patients into high-risk and low-risk categories based on factors like symptoms, anticipated neutropenia duration, and underlying condition. High-risk patients require hospital admission.