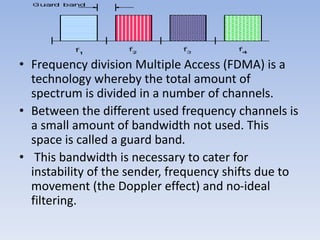
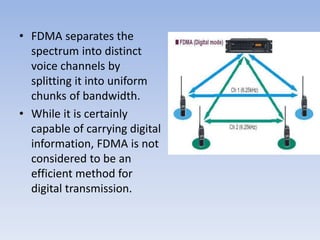
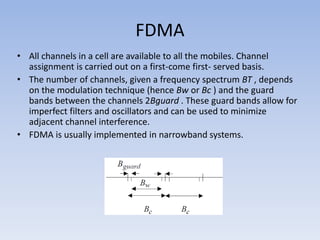
FDMA (frequency division multiple access) is a technology that divides the frequency band allocated for wireless communication into multiple channels, with each channel assigned to a single user. It allows more than one user to share the radio frequency spectrum by allocating different frequency channels. In FDMA, each call is placed on a separate frequency channel. It separates the spectrum into uniform chunks of bandwidth for voice channels. While capable of digital transmission, FDMA is not efficient for digital transmission.