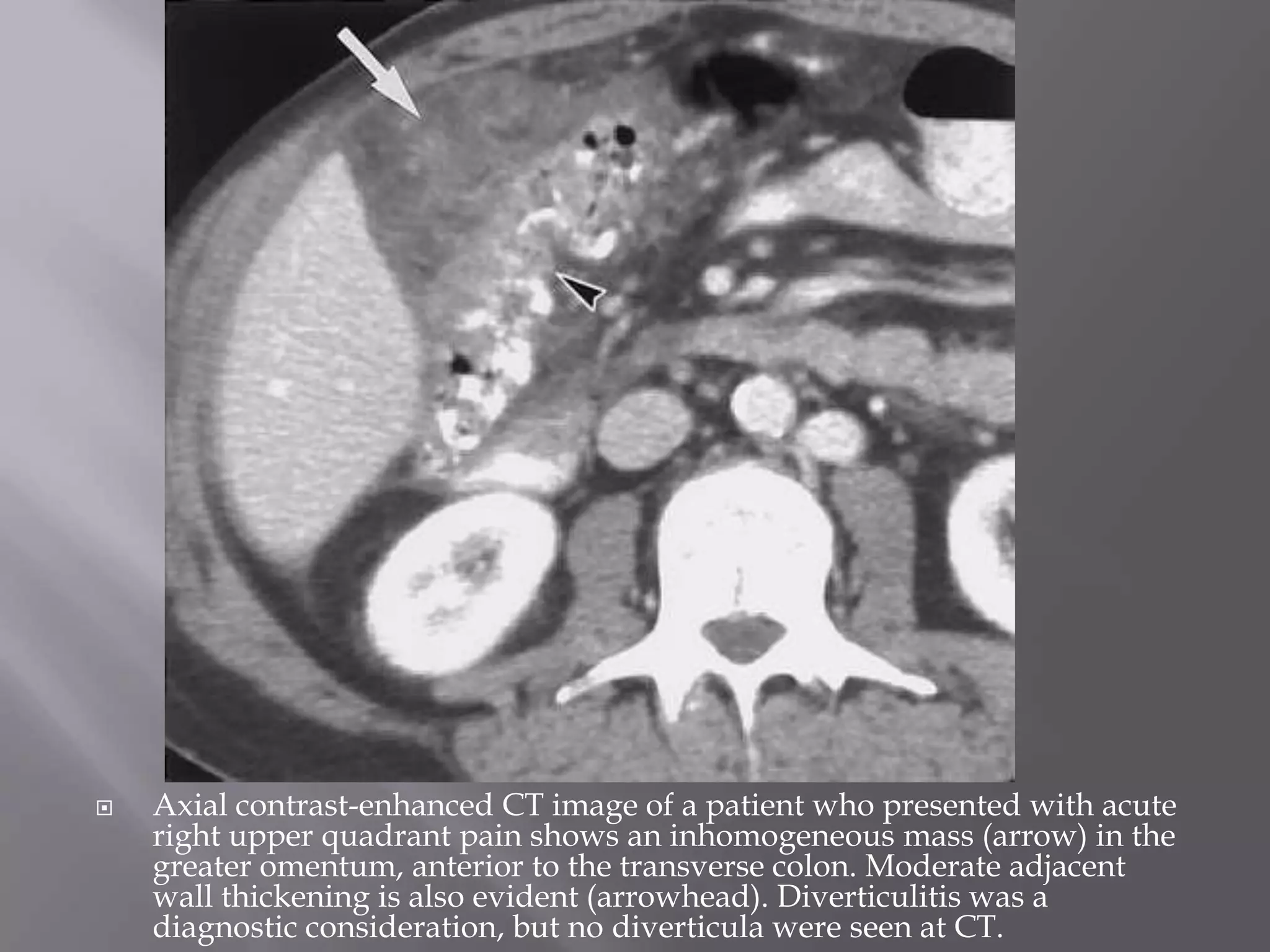
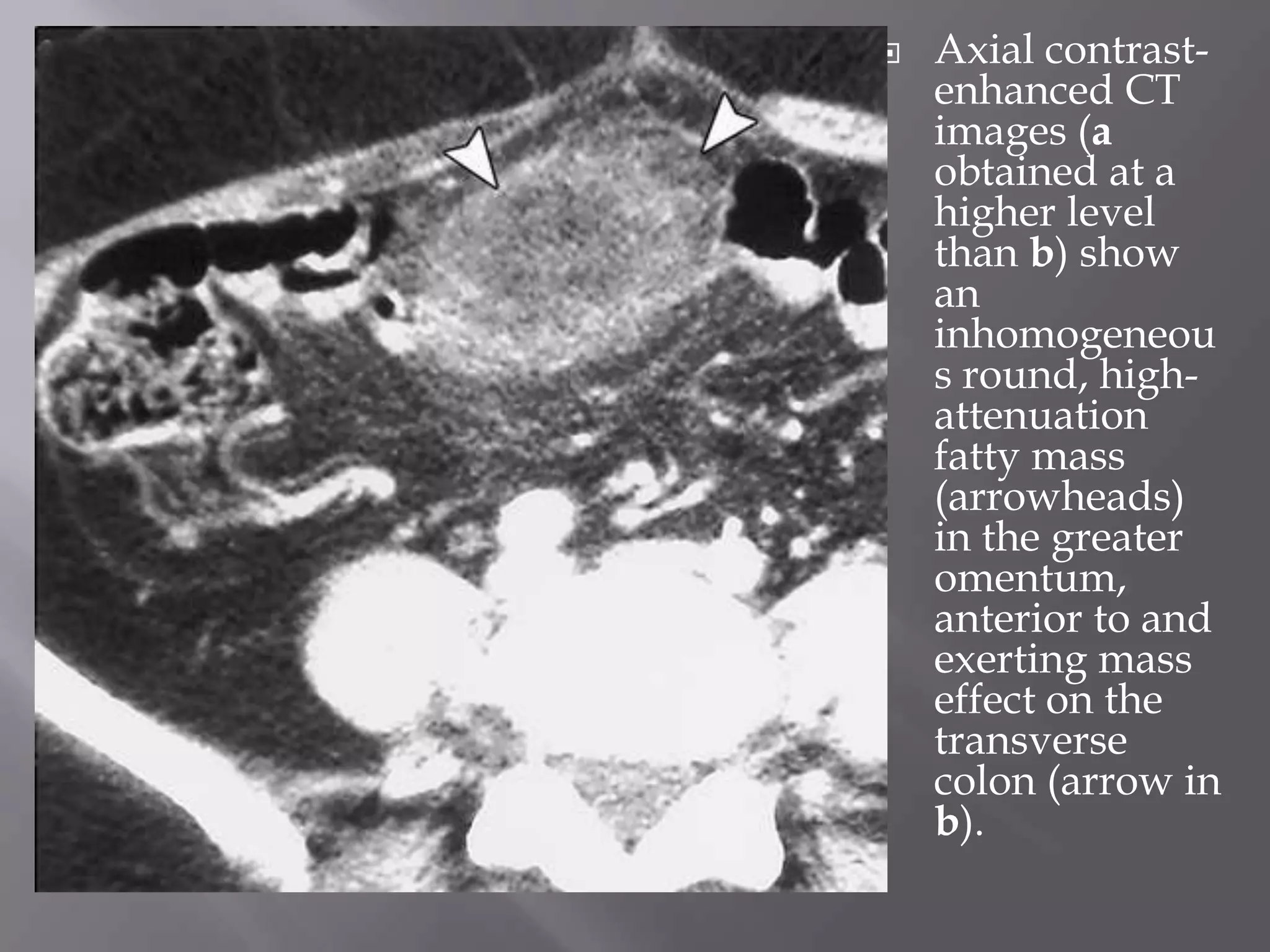
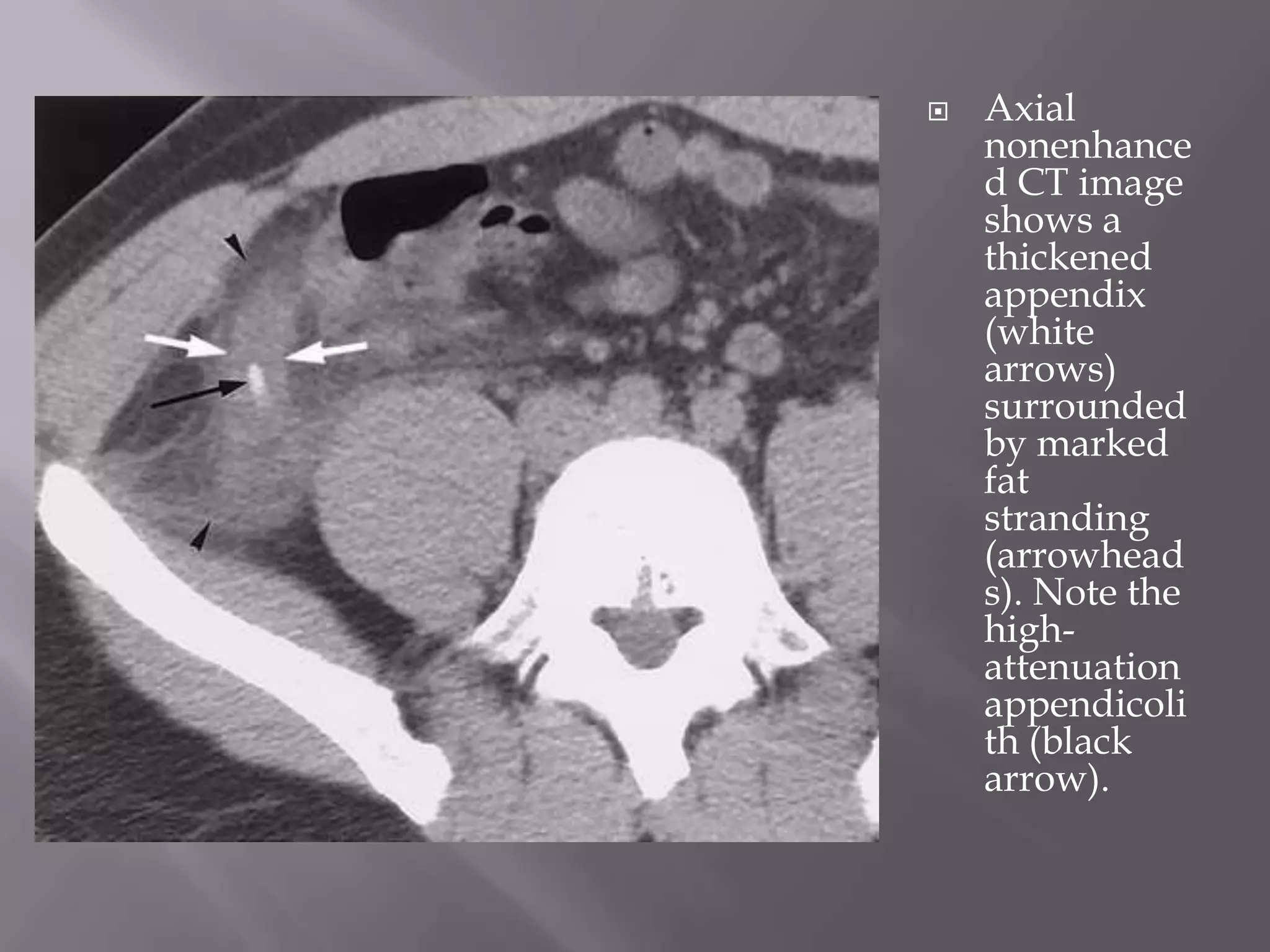
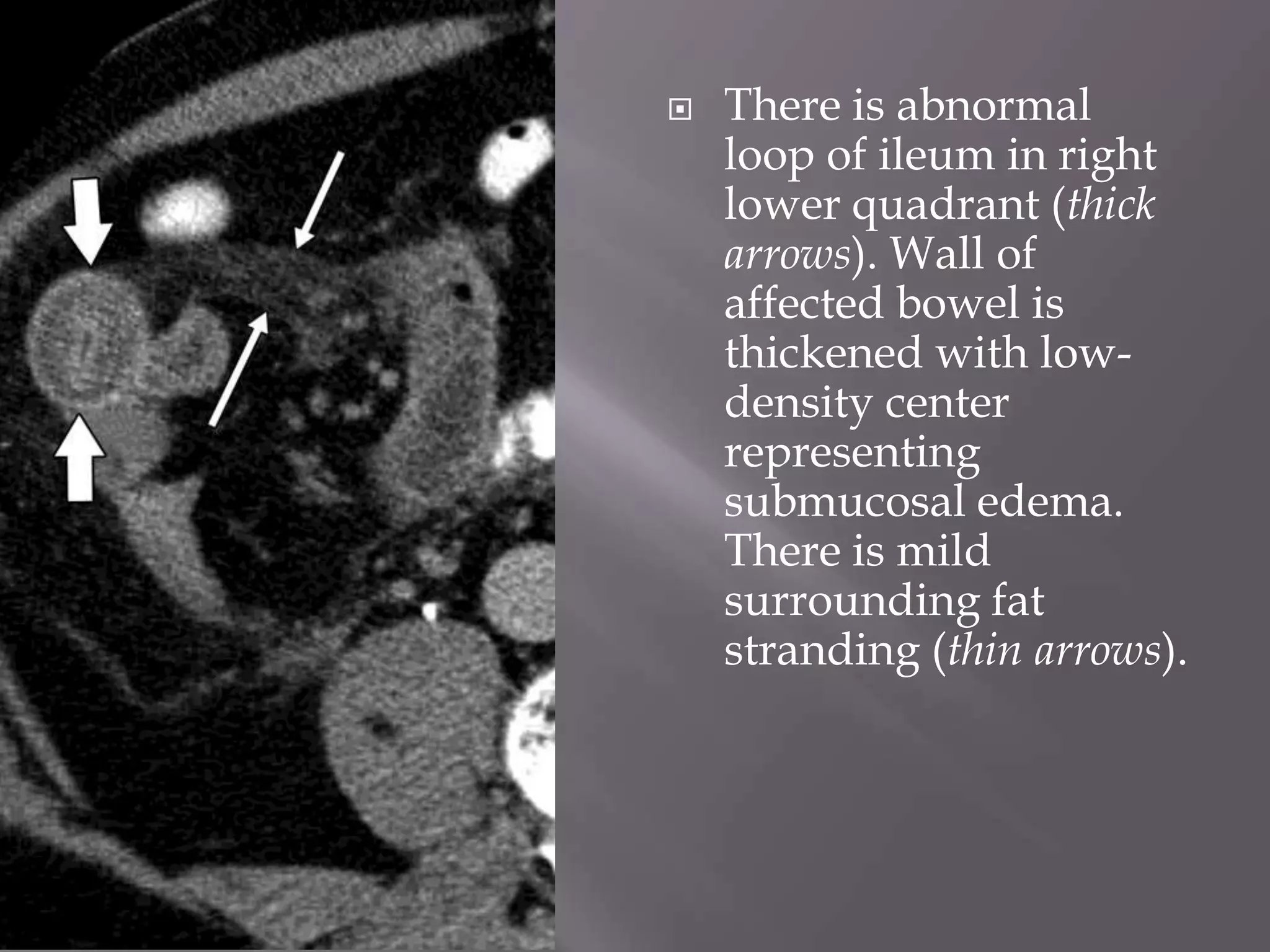
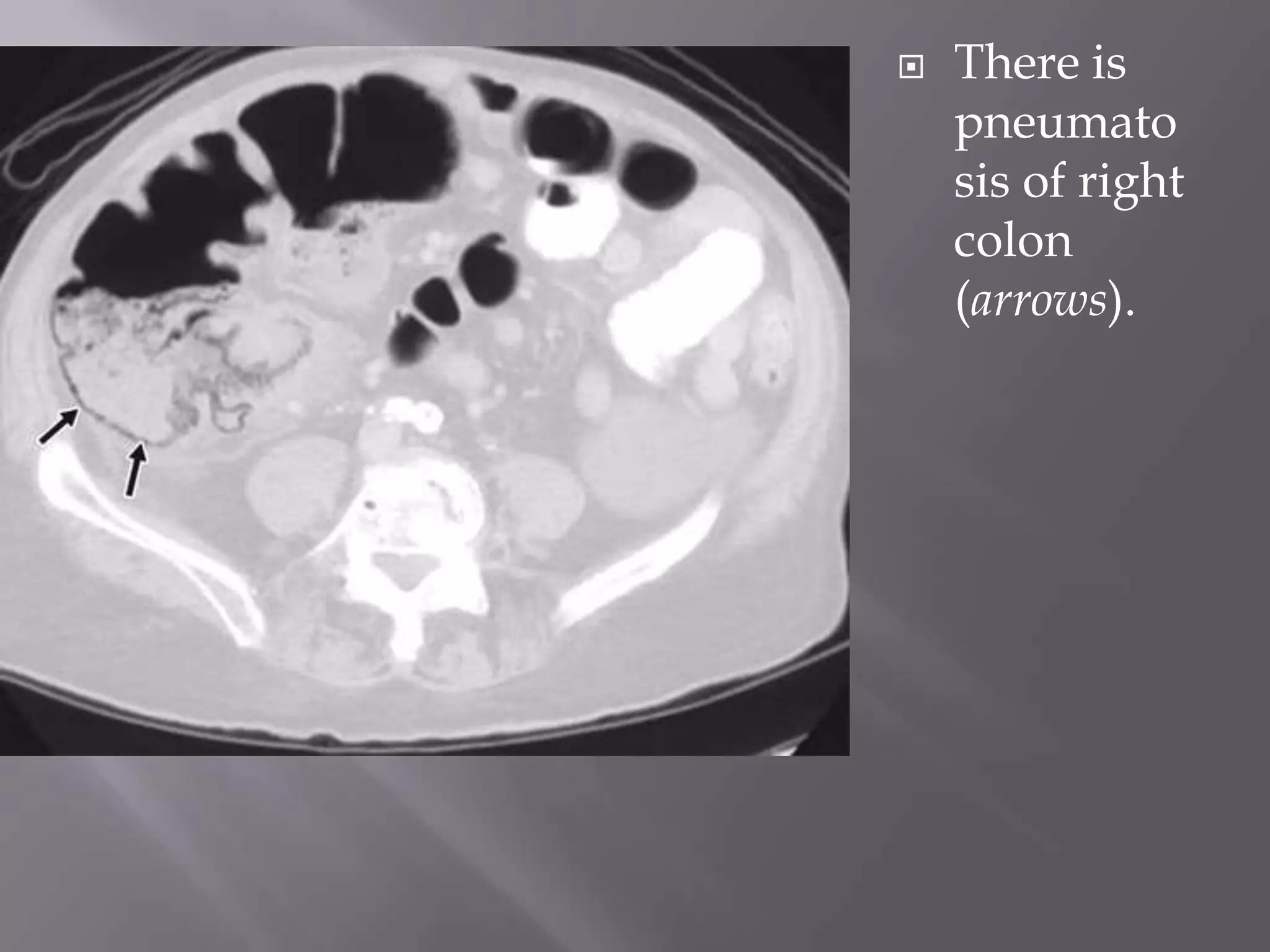
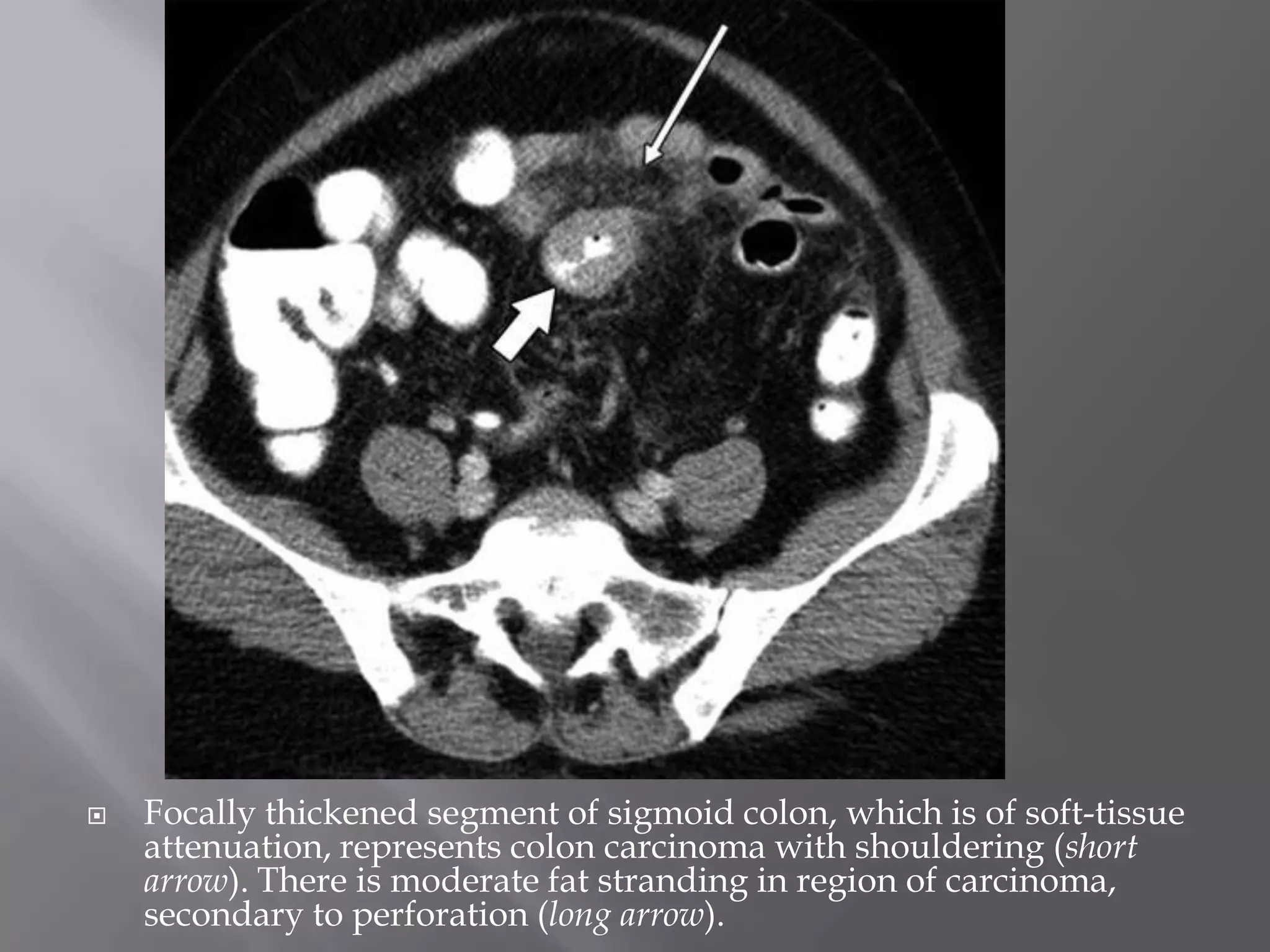
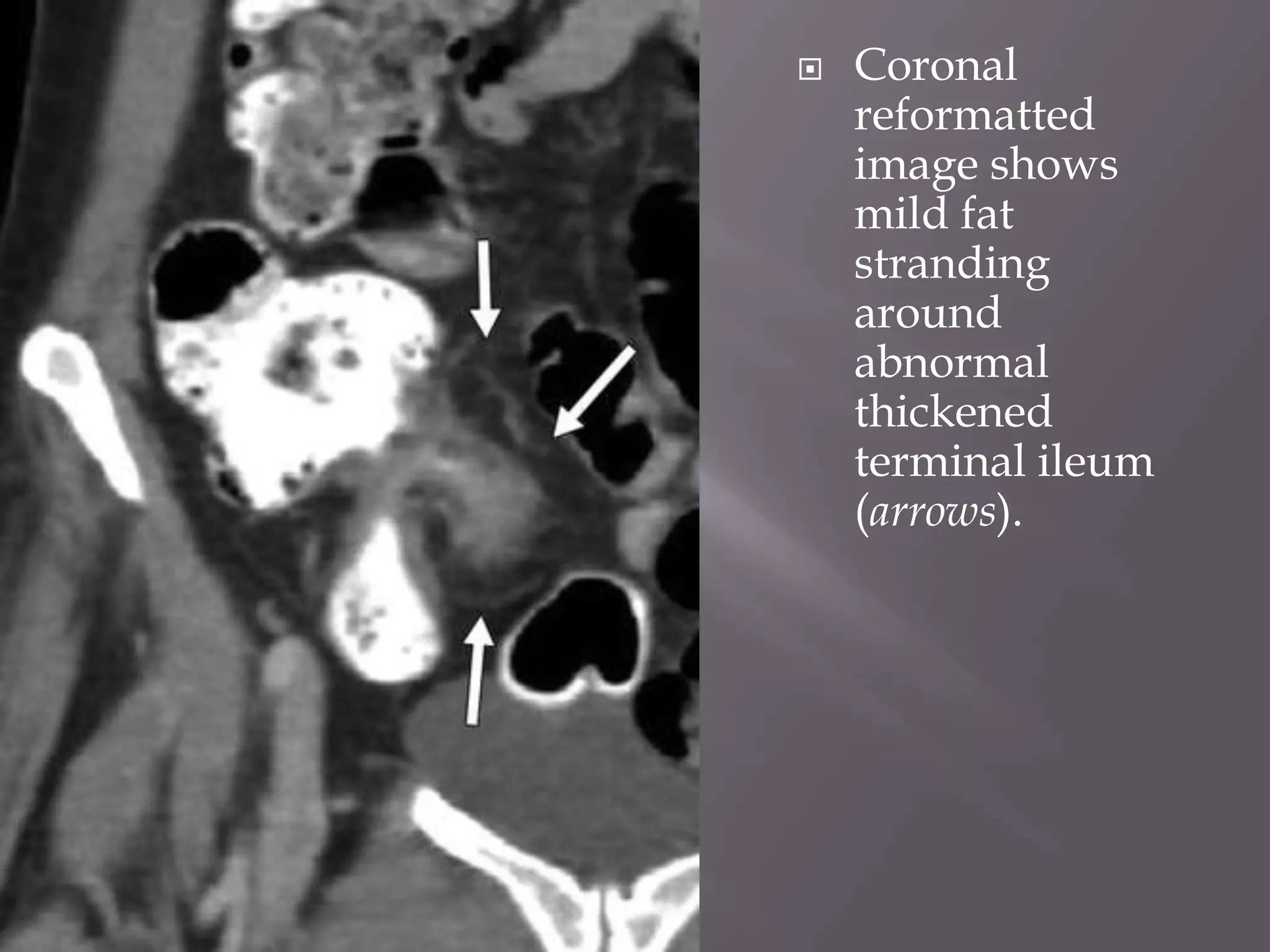
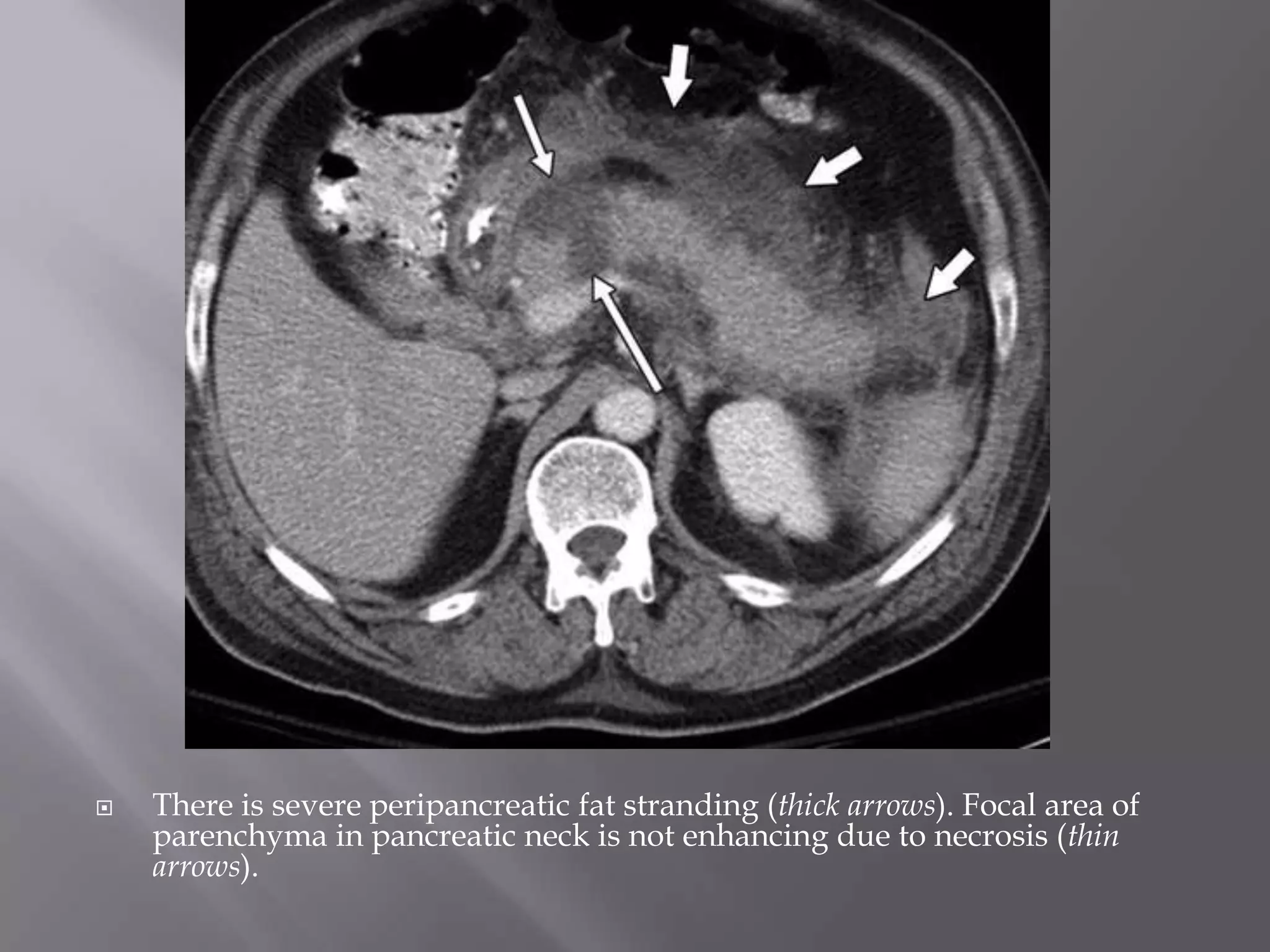
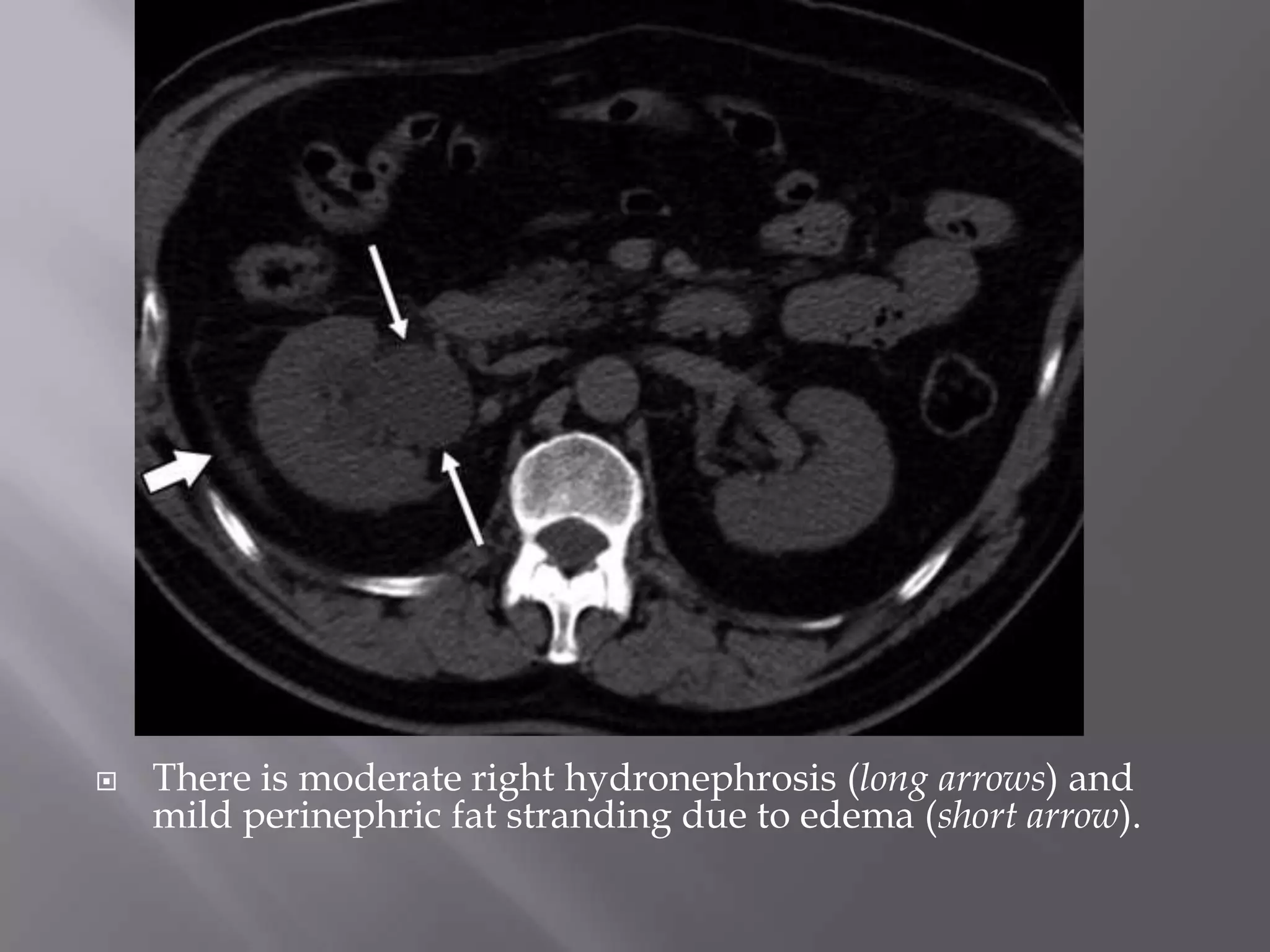
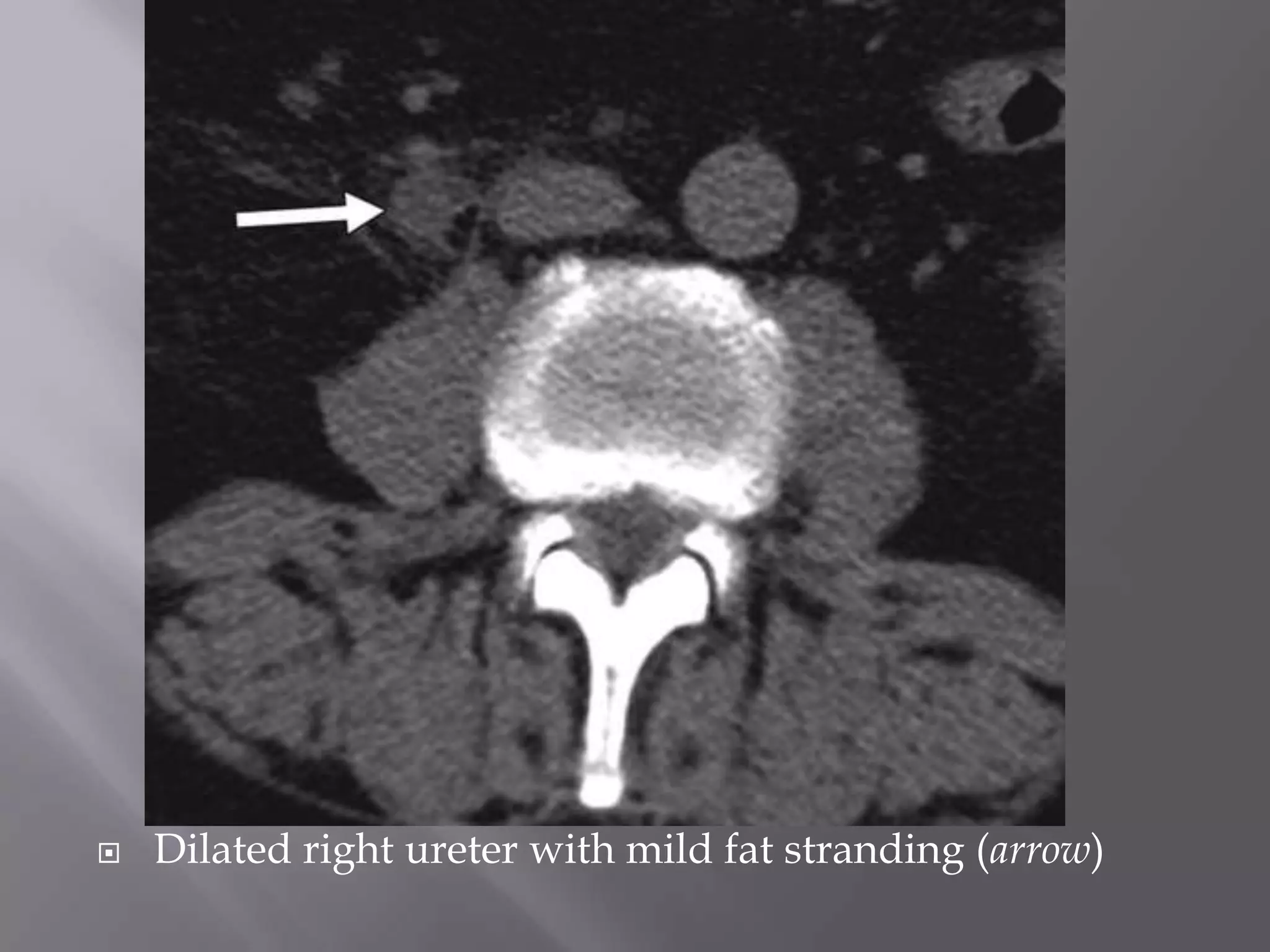
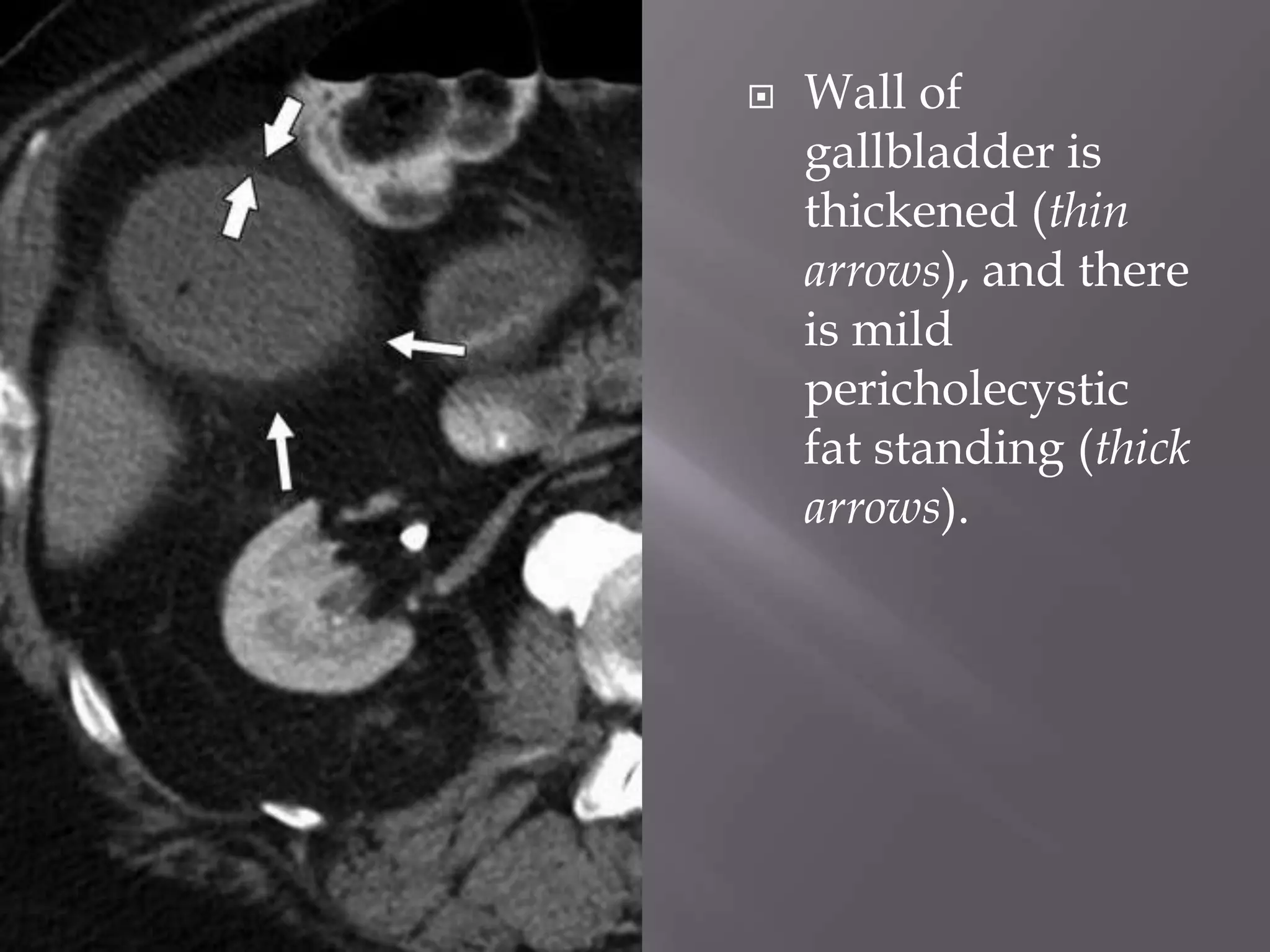
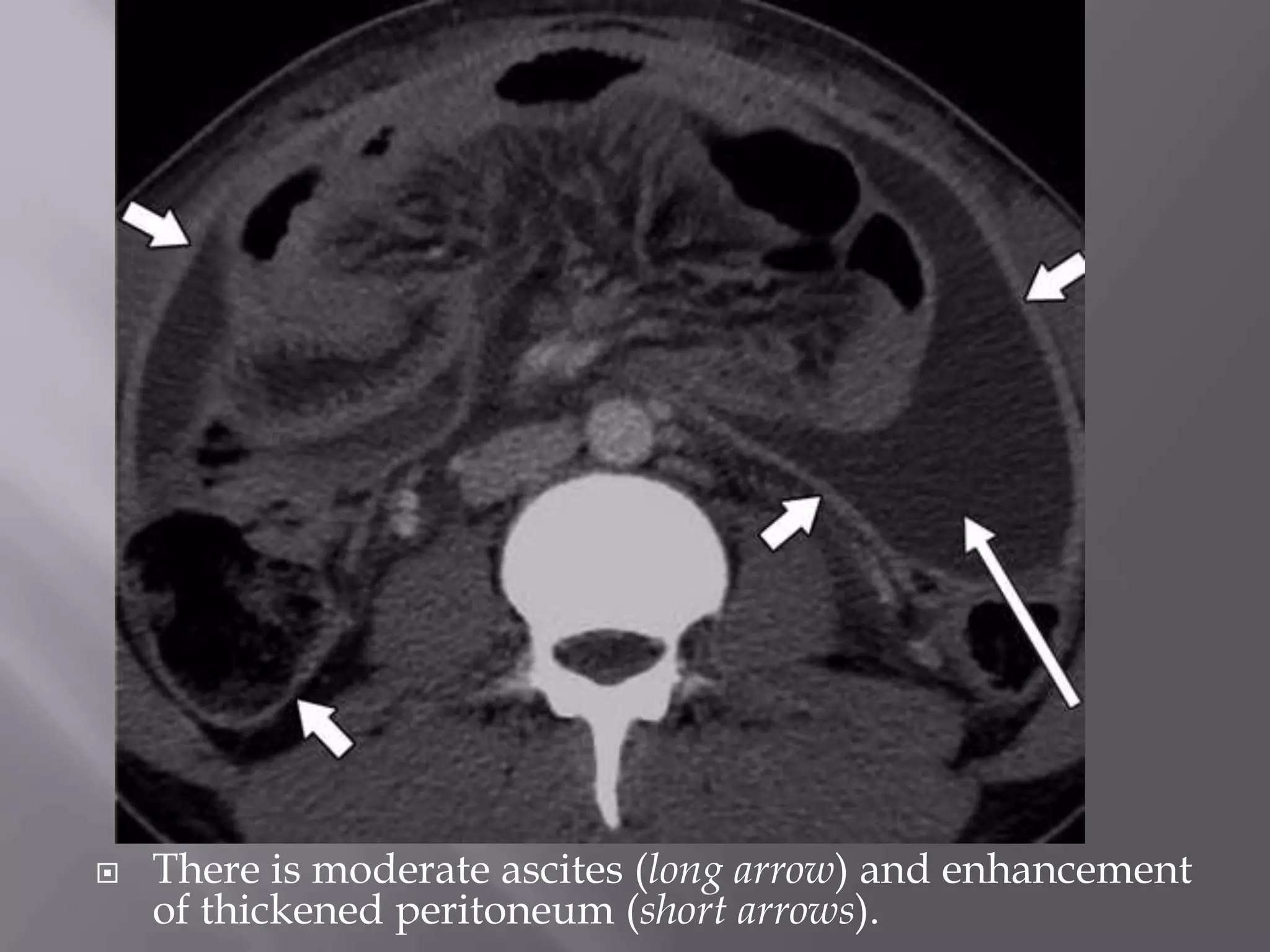
1. Fat stranding refers to abnormal increased attenuation of fat seen on CT scans that is caused by edema and engorgement of lymphatics due to inflammation.
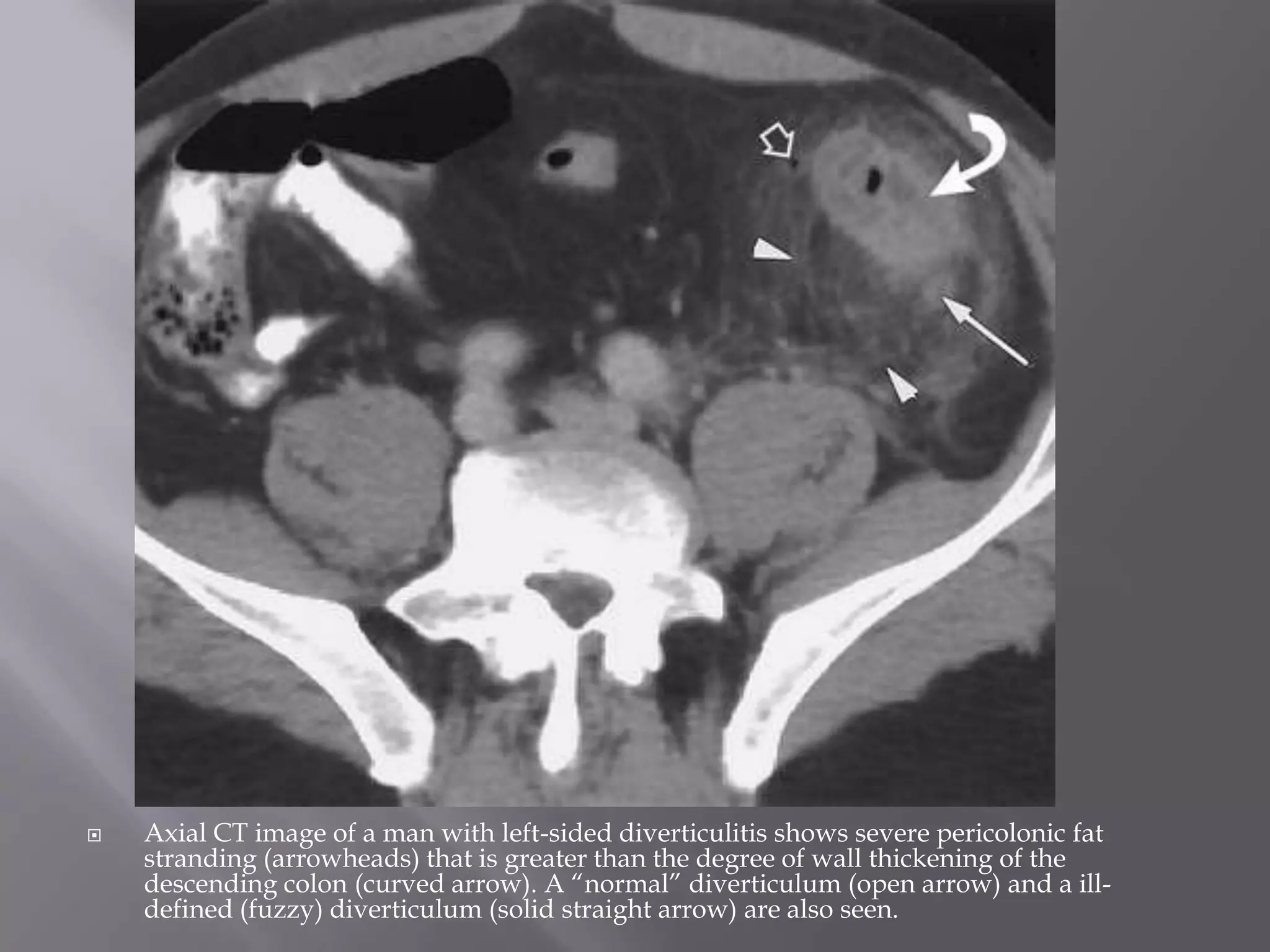
2. Common causes of fat stranding include diverticulitis, epiploic appendagitis, omental infarction, appendicitis, bowel ischemia, and malignancy. Diverticulitis is suggested by disproportionate fat stranding greater than bowel wall thickening.
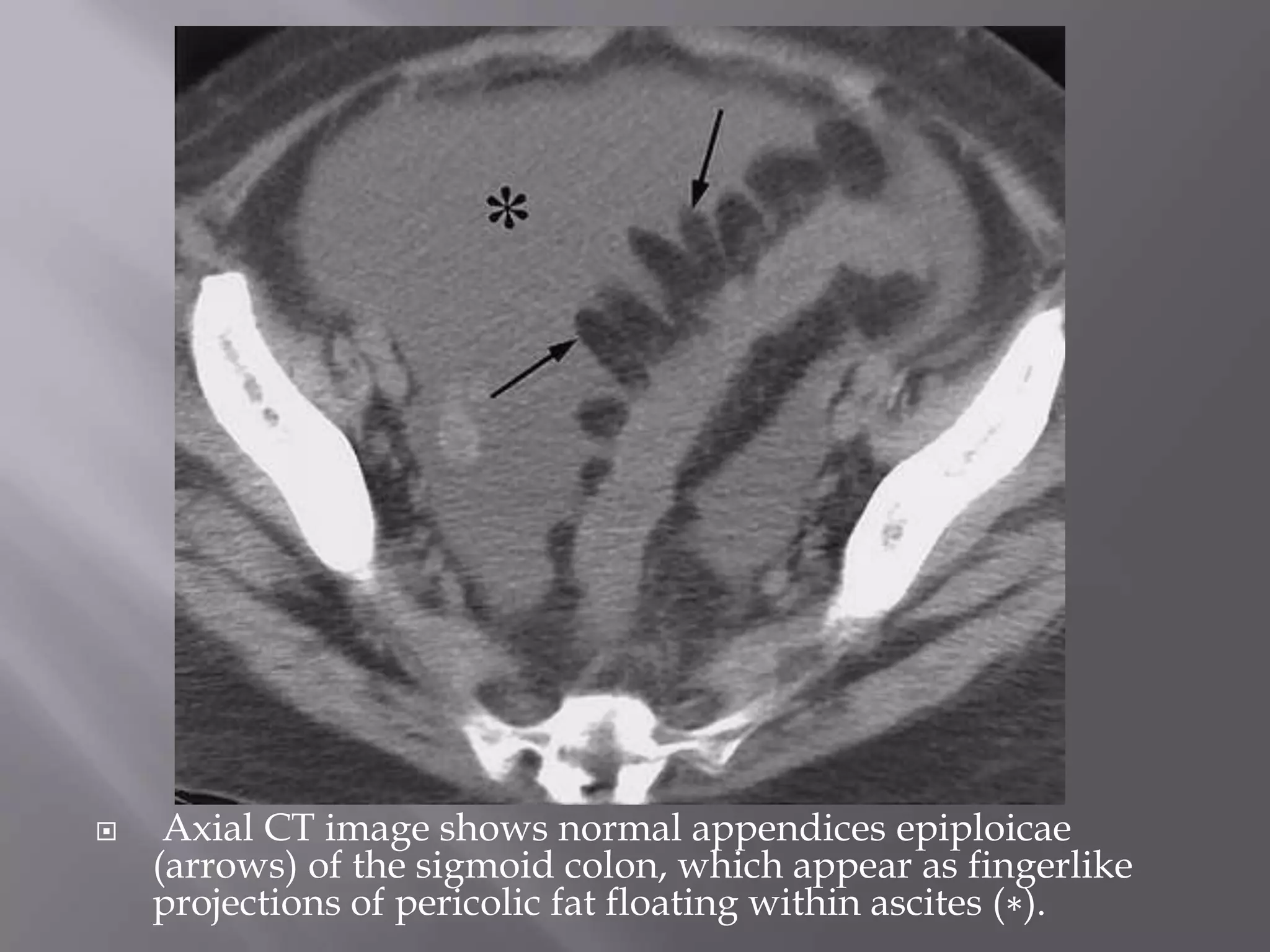
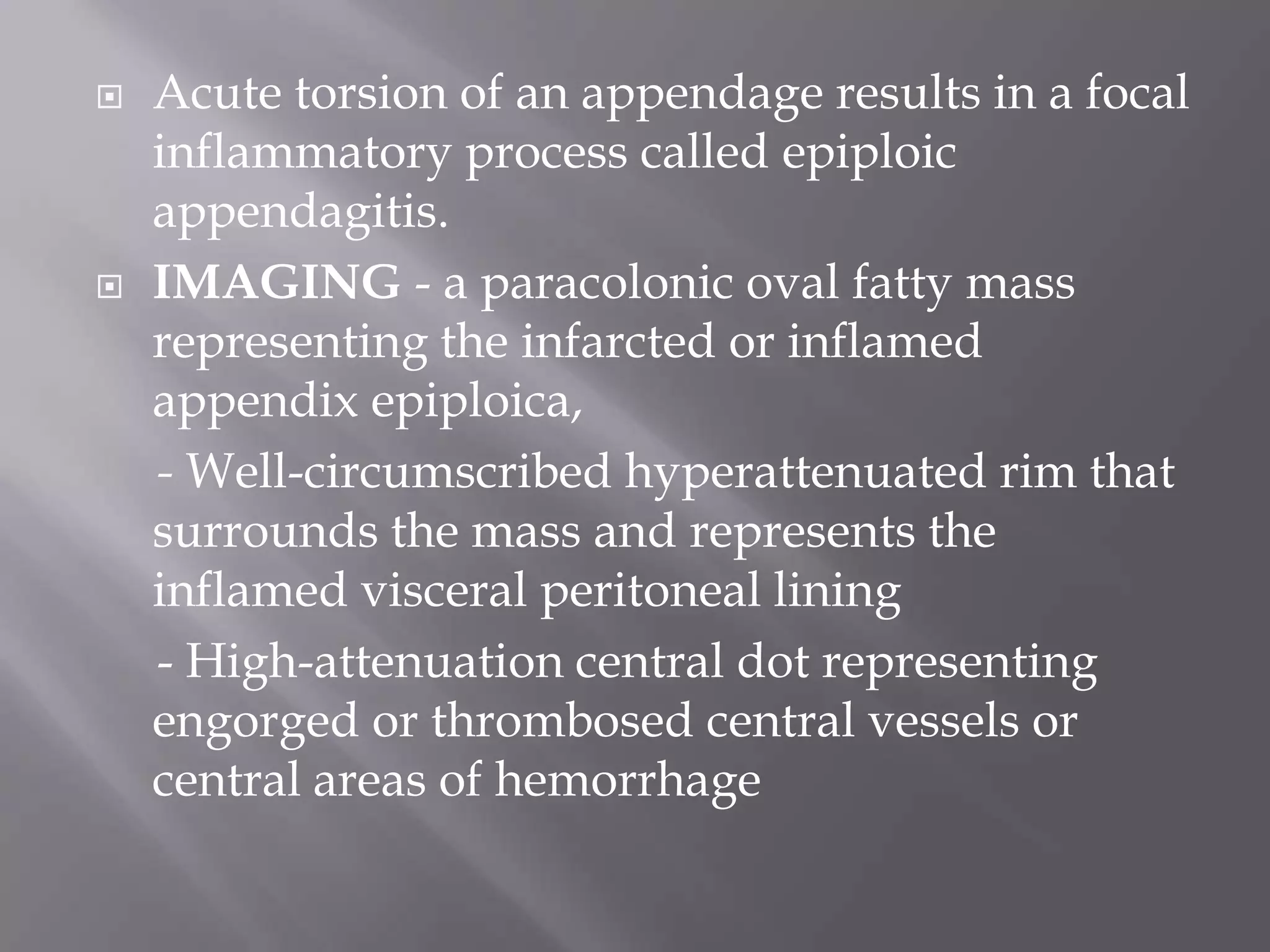
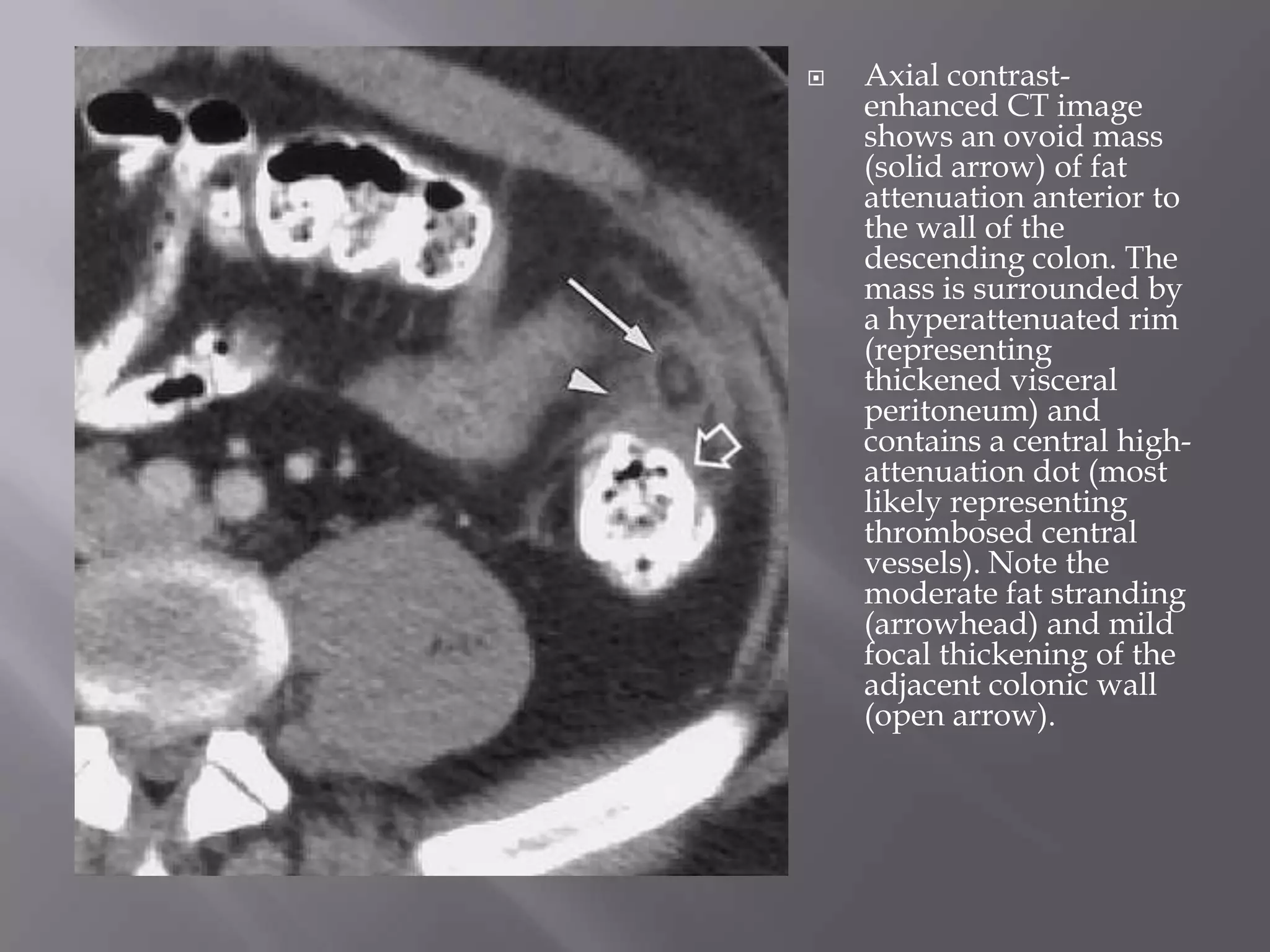
3. CT findings help differentiate the causes, such as seeing the characteristic appearances of epiploic appendagitis, omental infarction, and appendicitis that include focal fatty masses and central dots.