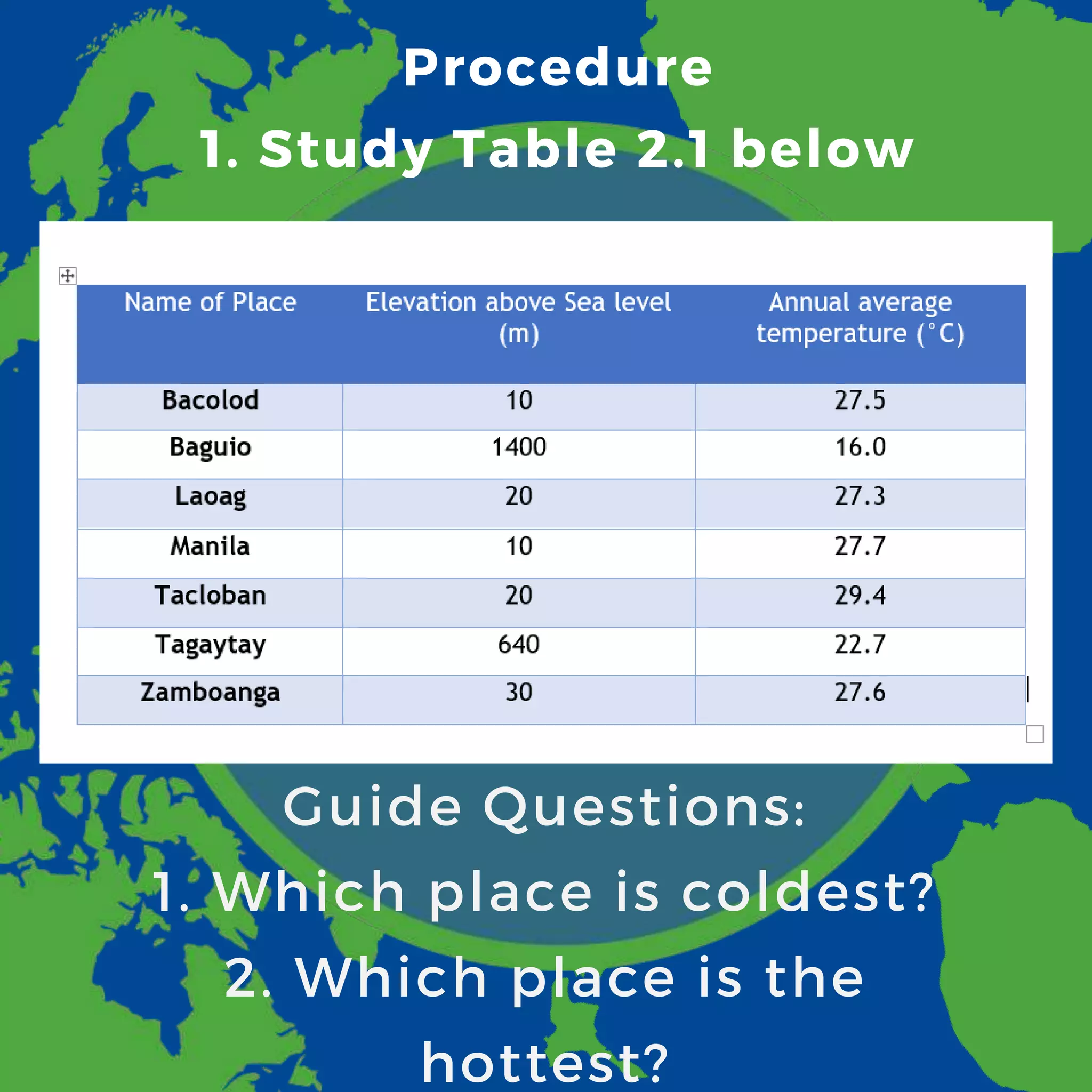
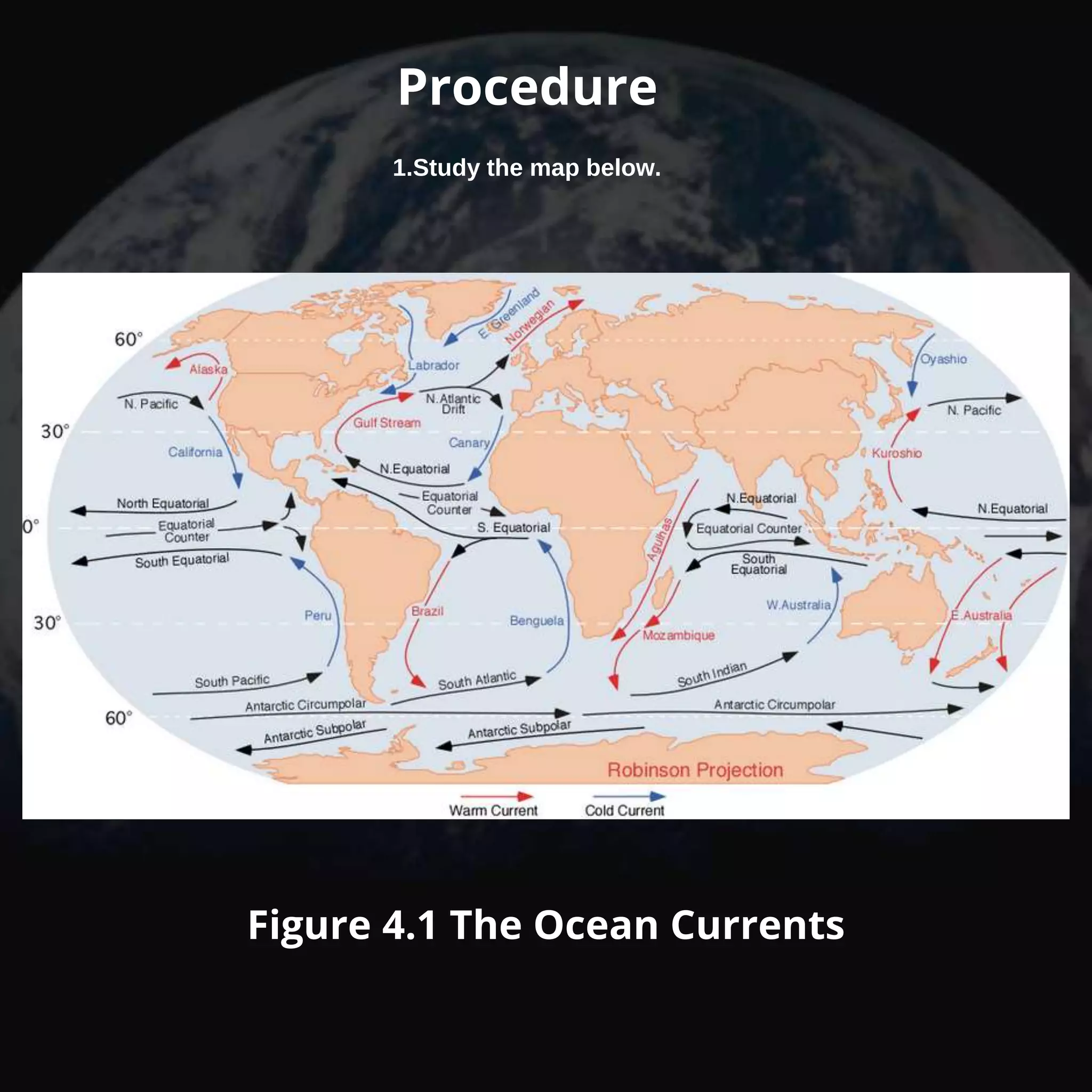
This document contains information about various climate factors and a series of assessment questions. It discusses how latitude, altitude, distance from bodies of water, air pressure systems, mountain barriers, elevation, continental location, wind belts, ocean currents, and storms can all impact the climate of a given region. Several diagrams and tables are included to illustrate these concepts. Students are asked to identify which cities would have the highest and lowest recorded temperatures based on their locations, and to explain how ocean currents can influence climate conditions.