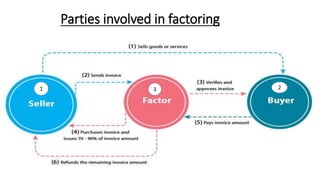
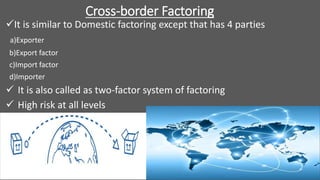
Factoring is a financial transaction where businesses sell their accounts receivable to third parties at a discount, providing a fast way to raise money and shorten collections processes. There are several types of factoring, including recourse, non-recourse, maturity, and cross-border factoring, each carrying its own risk and benefits. While factoring offers advantages like liquidity and cost savings, it also comes with disadvantages such as high costs and potential buyer refusal to pay.