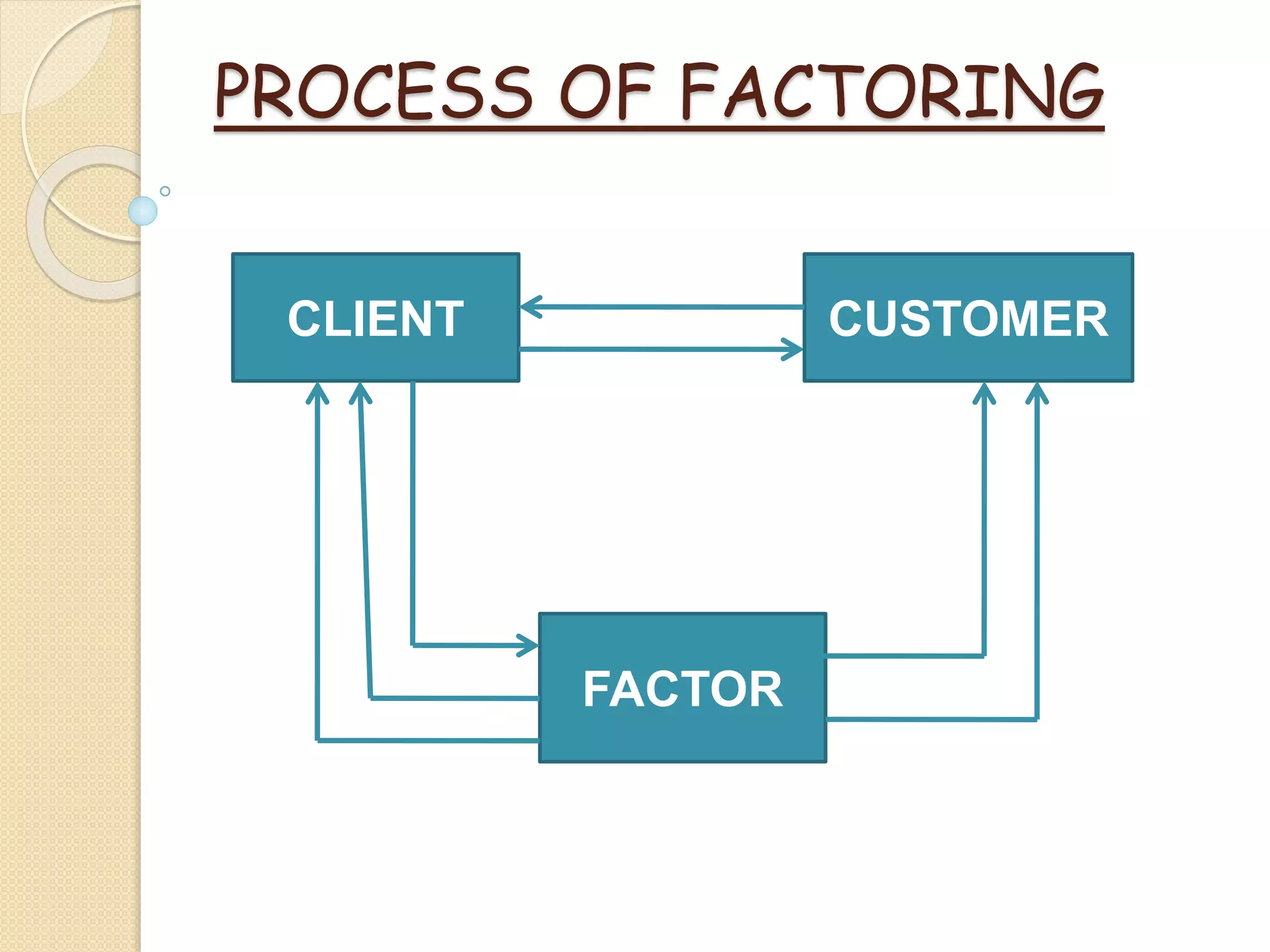
Factoring involves an agreement between a seller and a financial institution (factor) that purchases the seller's receivables, assuming the risk of collection. Factors offer various financing types, including recourse and non-recourse factoring, and can help businesses manage cash flow and credit risks. The document outlines the process, characteristics, and legal framework governing factoring in India.