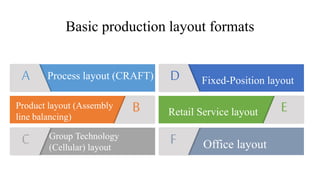
This document discusses different facility layout types including process, product, group technology, fixed-position, office, and retail service layouts. It describes the objectives and factors to consider for an efficient layout. Process layout is suitable for standard products produced in large volumes, while product layout arranges machines in a line based on sequence of operations. Group technology layout groups machines into cells that function like smaller production lines. Fixed-position layout keeps products stationary while moving labor and equipment.