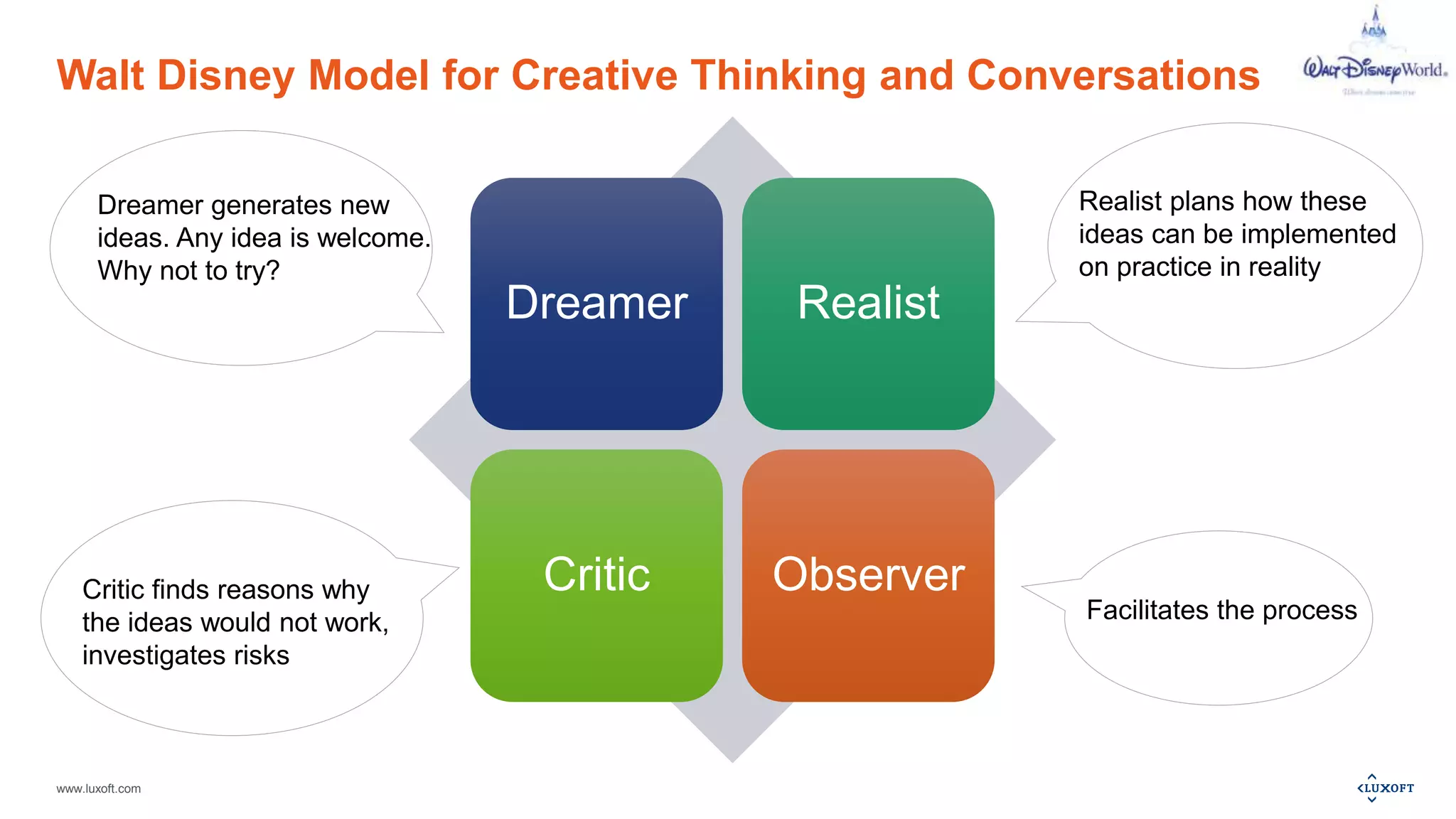
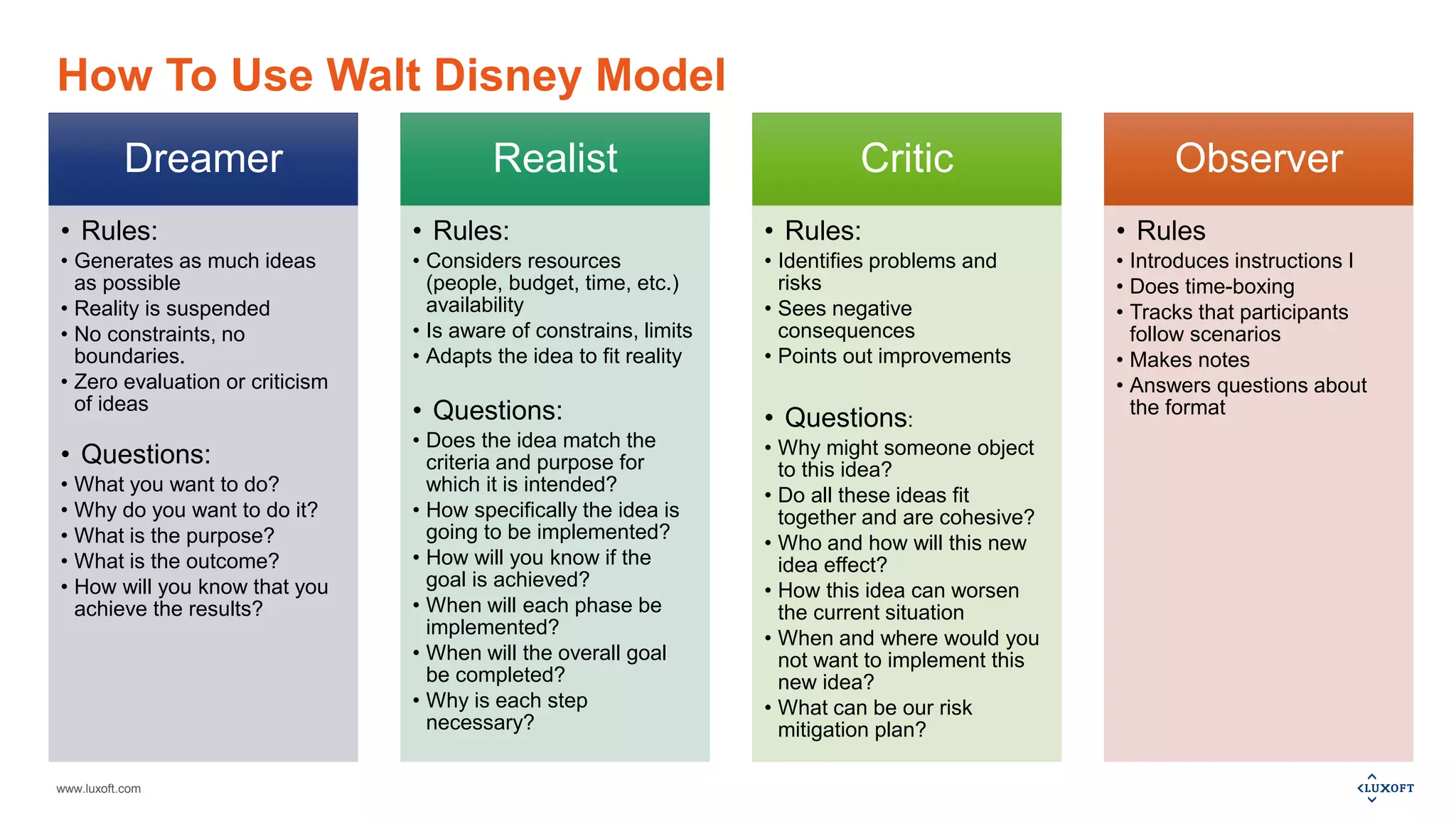
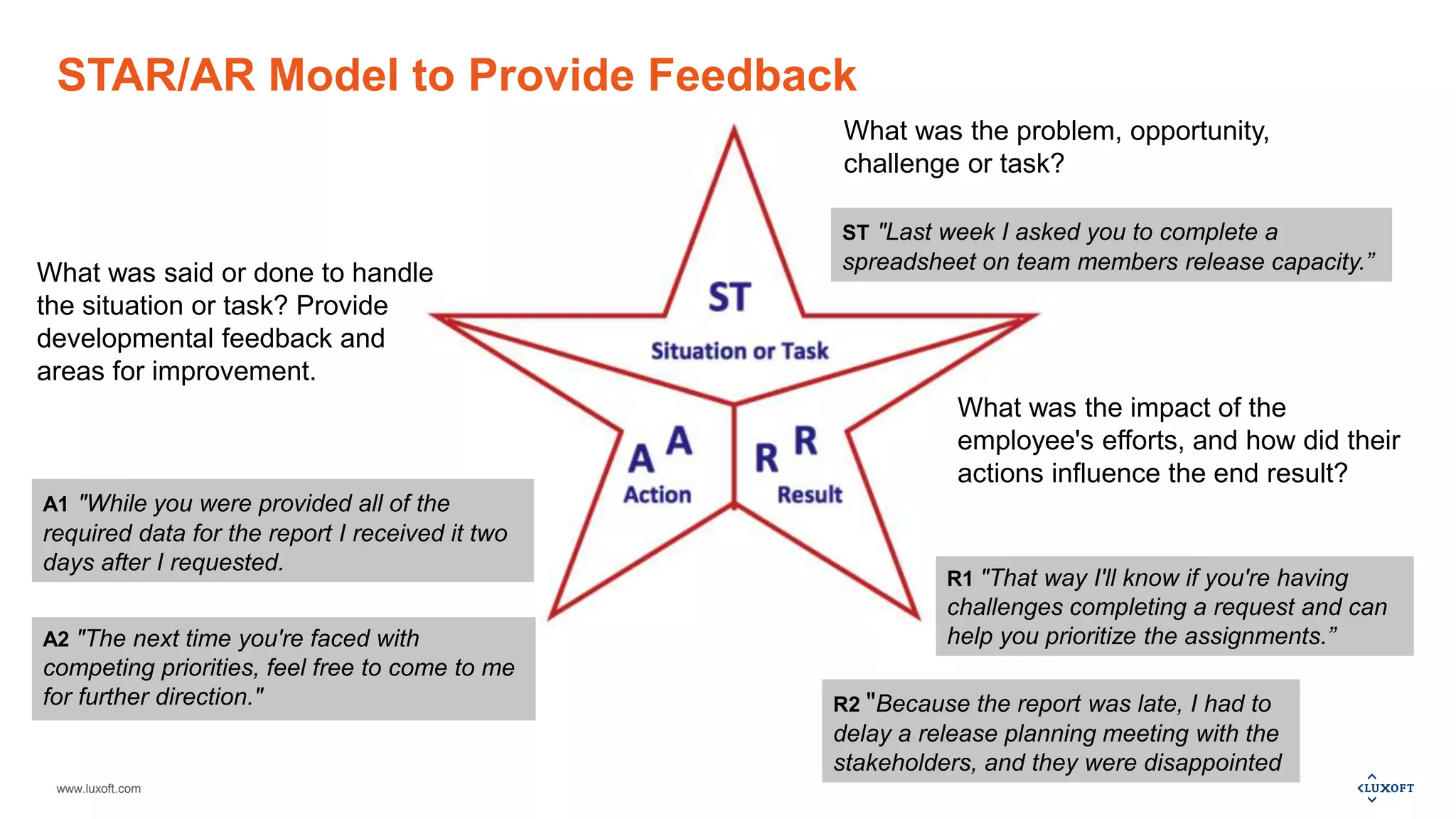
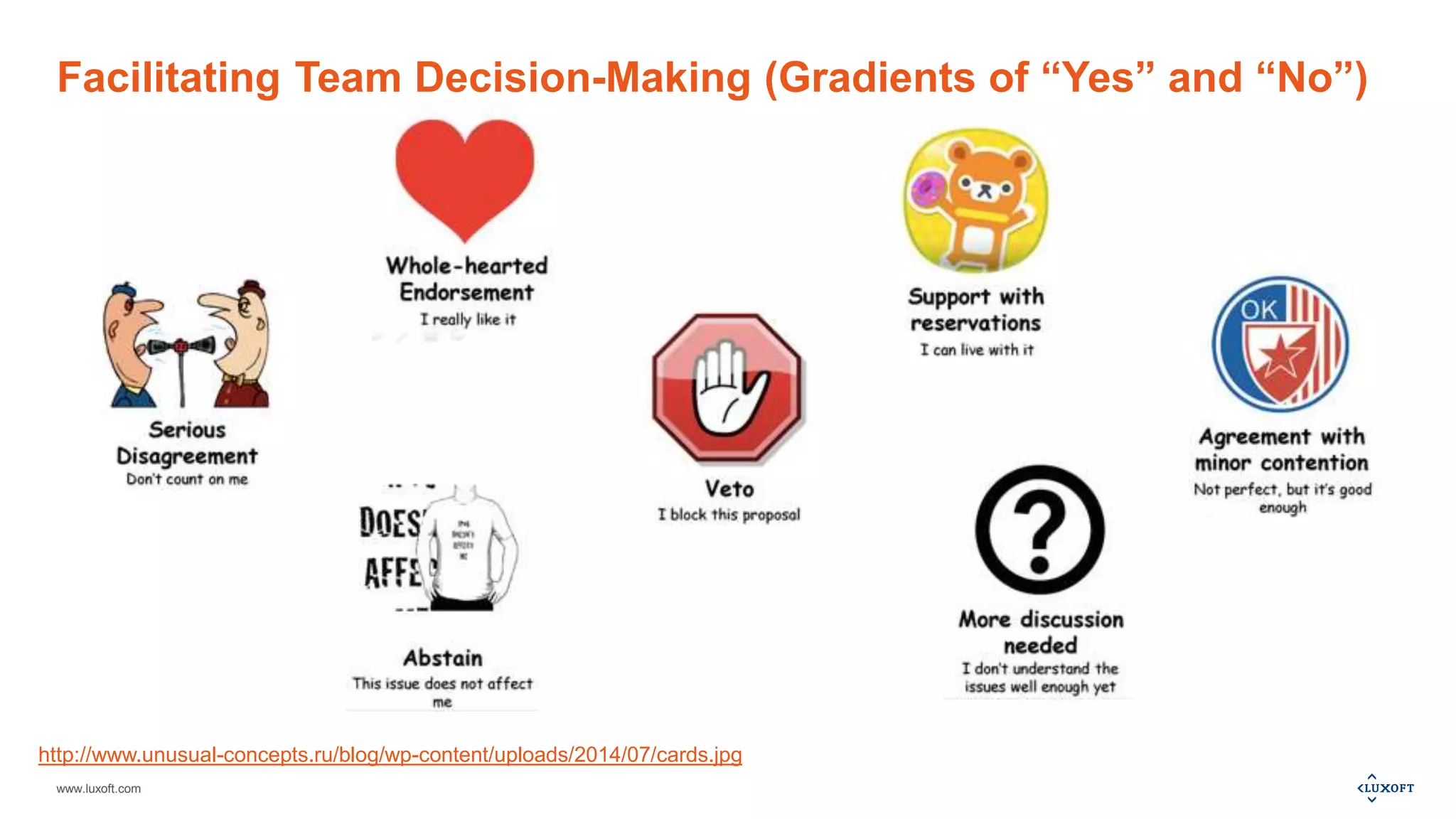
The document outlines a webinar session plan from Luxoft focused on creative thinking and decision-making techniques, including the Walt Disney model, Cartesian coordinates, pro-con analysis, and various feedback models. It details how these techniques facilitate idea generation, planning, and risk assessment through structured methodologies. Additionally, it provides recommended materials for further learning and available services related to agile practices and training.





![www.luxoft.com
Recommended Materials
Greatest book on facilitation, applicable not only for Agile team, it’s #1 to read for any facilitator -
http://www.amazon.com/Facilitators-Guide-Participatory-Decision-Making-Kaner/dp/0787982660
Retromat – cookbook on Retro facilitation, they provide step-by-step scenarios for Retros facilitation -
http://plans-for-retrospectives.com/
Video to learn graphic facilitation - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=S5DJC6LaOCI
Post about tools (not techniques) for distributed teams
facilitation http://www.luxoft.com/blog/smukhina/tools-for-collaboration-in-distributed-teams/
Video on empathy that is one of the Servant Leader qualities -
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1Evwgu369Jw
Face2Face training ICAgile Certified Professional - Agile Team Facilitation, apply to it by sending me
email smukhina@luxoft.com [title “Facilitation training”, body “I wish to participate” or/and any
questions ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015-150703204355-lva1-app6891/75/Facilitating-Conversations-and-Decision-making-11-2048.jpg)


![www.luxoft.com
How-to-apply for Face-to-Face Trainings and Workshops
Specify request for Agile Education
Learning objectives
Time period
Location
Send the request to Agile Practice [smukhina@luxoft.com]
Follow the instructions provided by Agile Practice on response to your request](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015-150703204355-lva1-app6891/75/Facilitating-Conversations-and-Decision-making-14-2048.jpg)