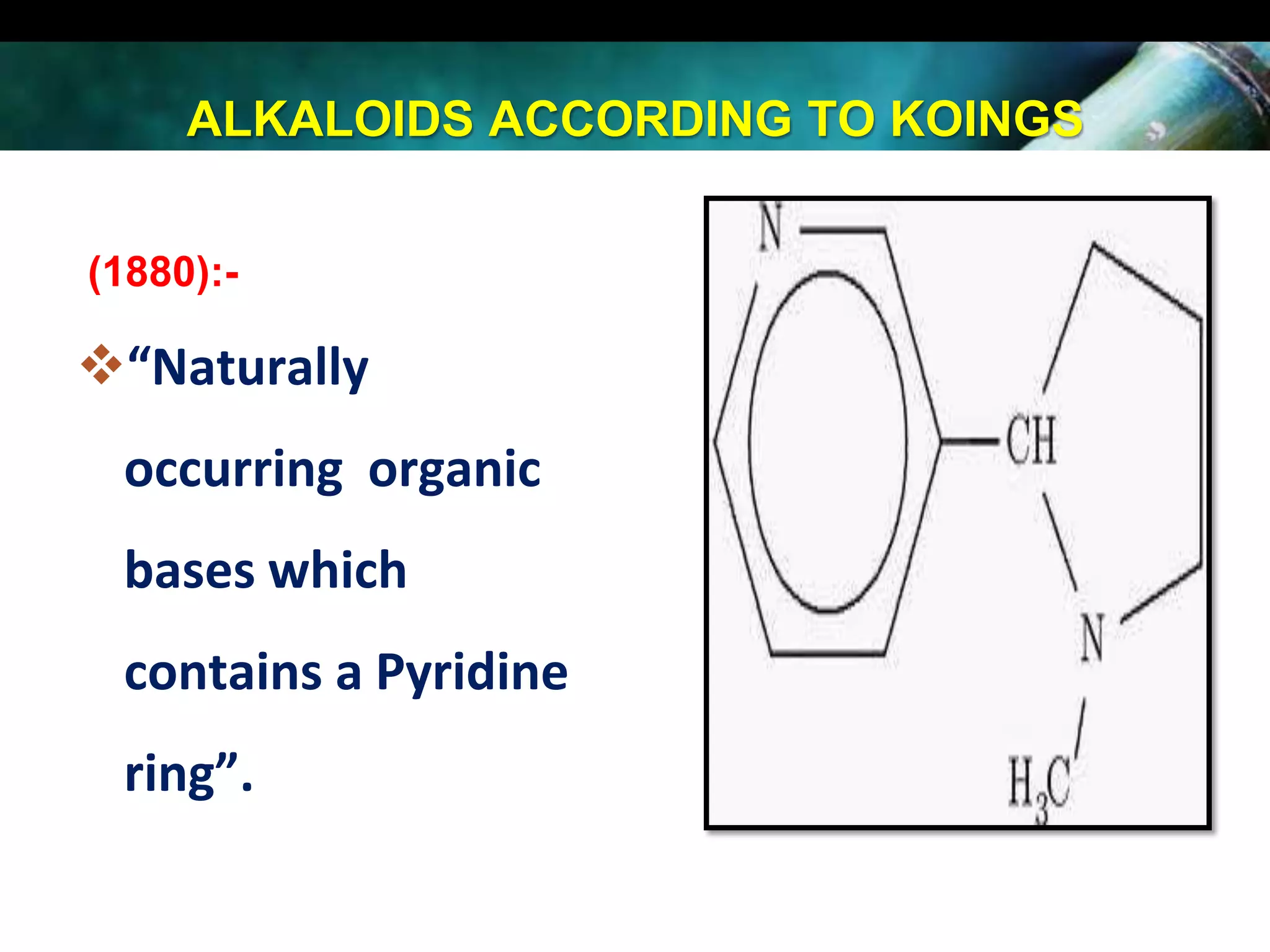
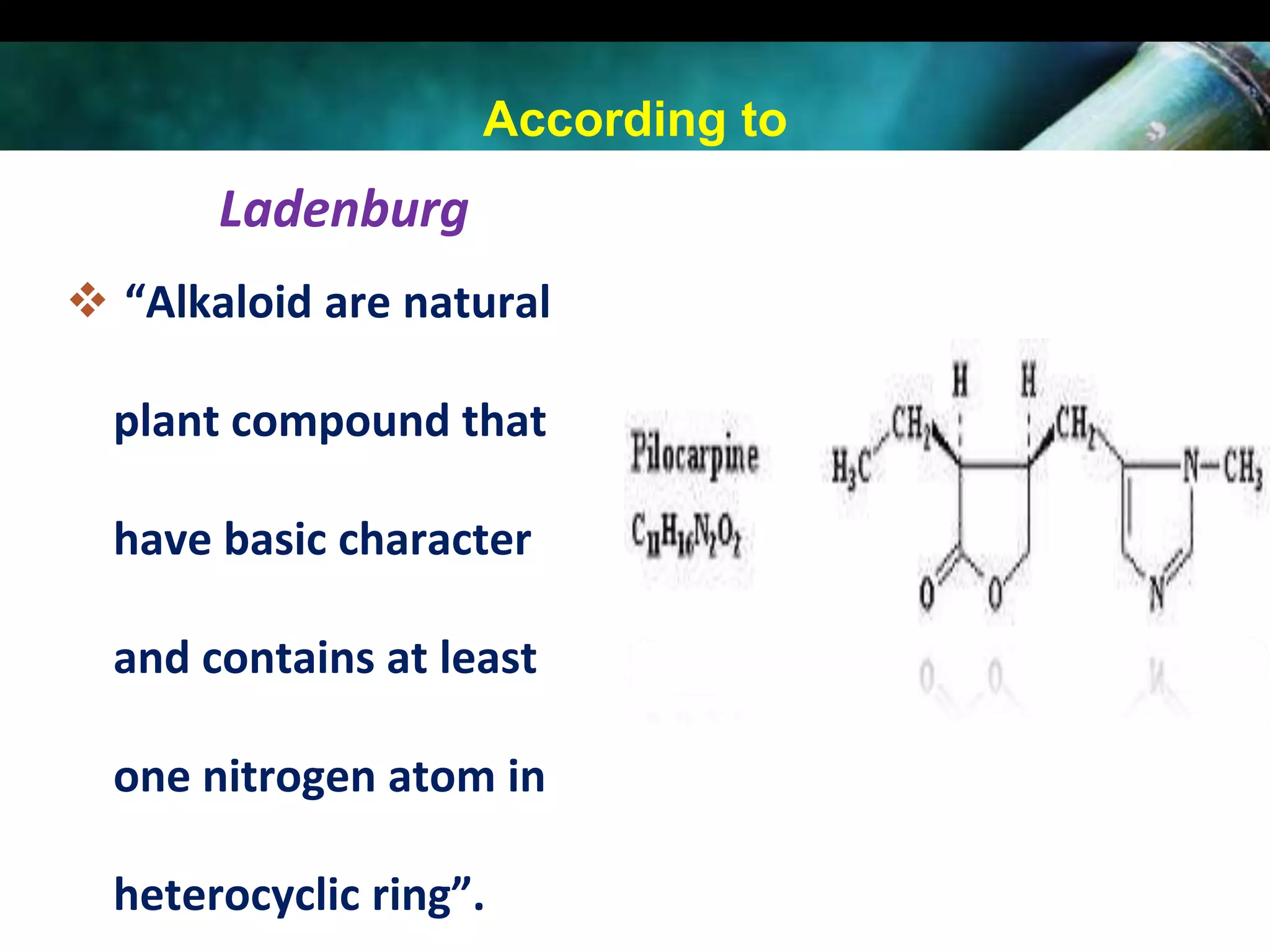
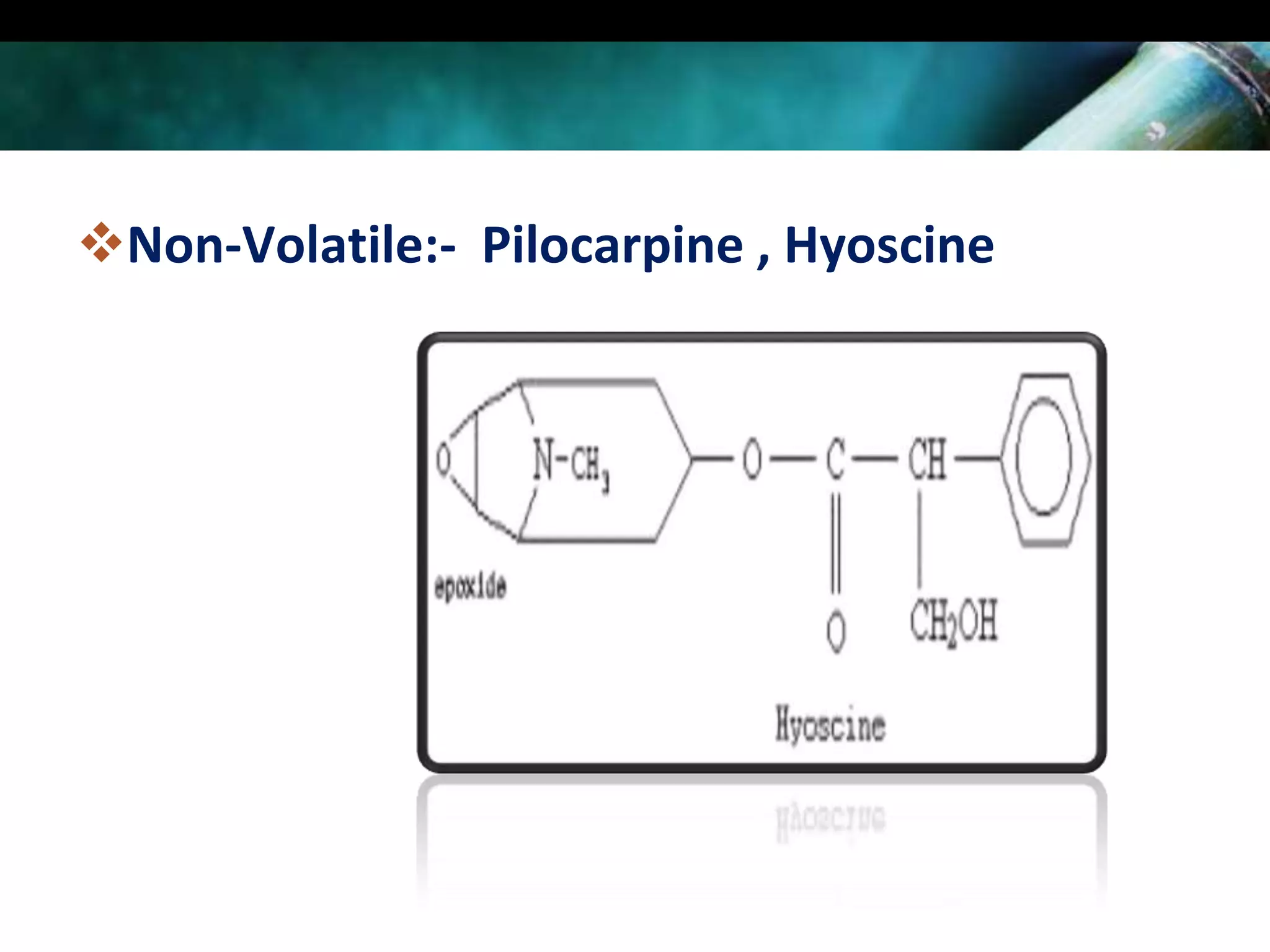
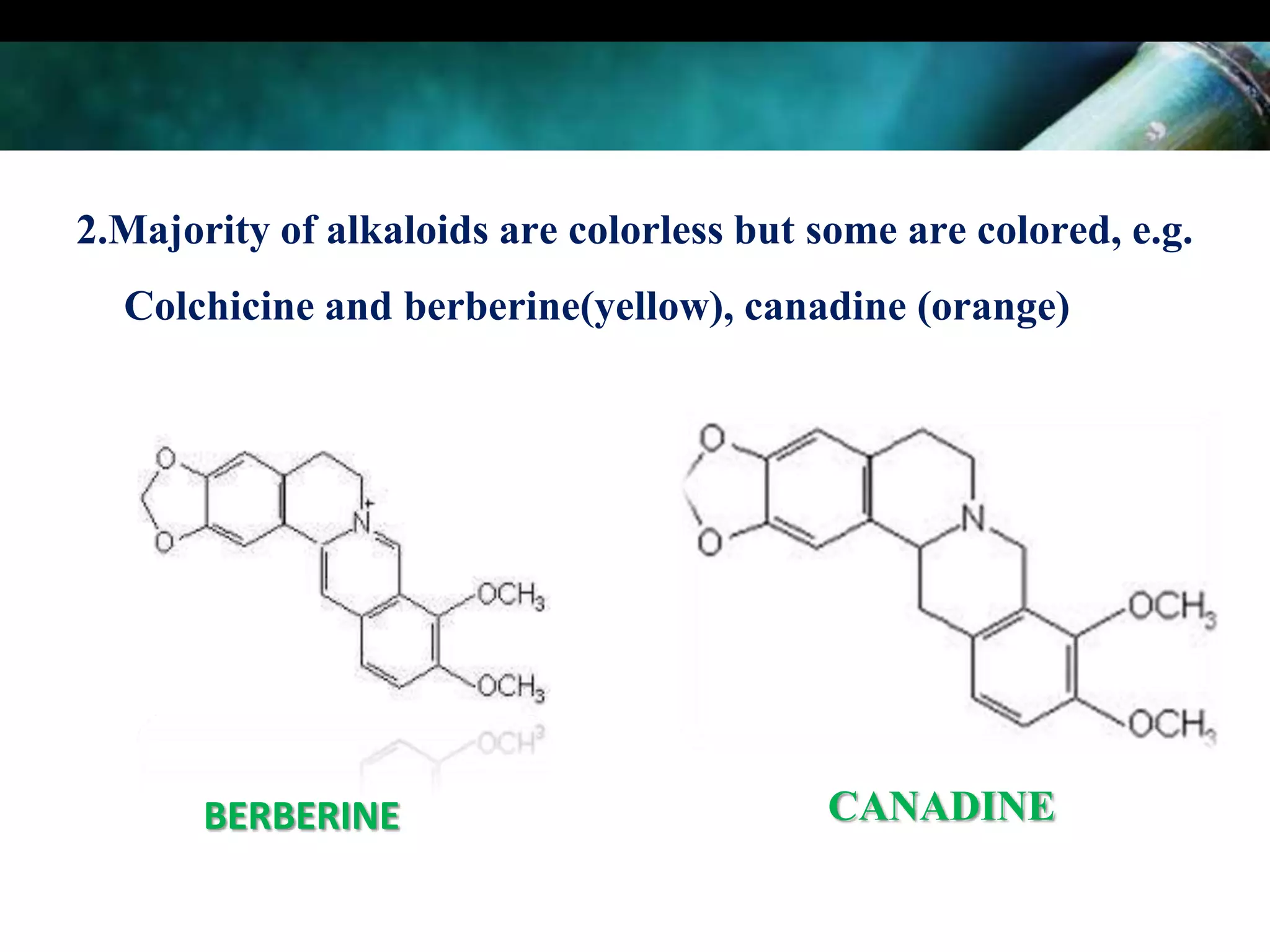
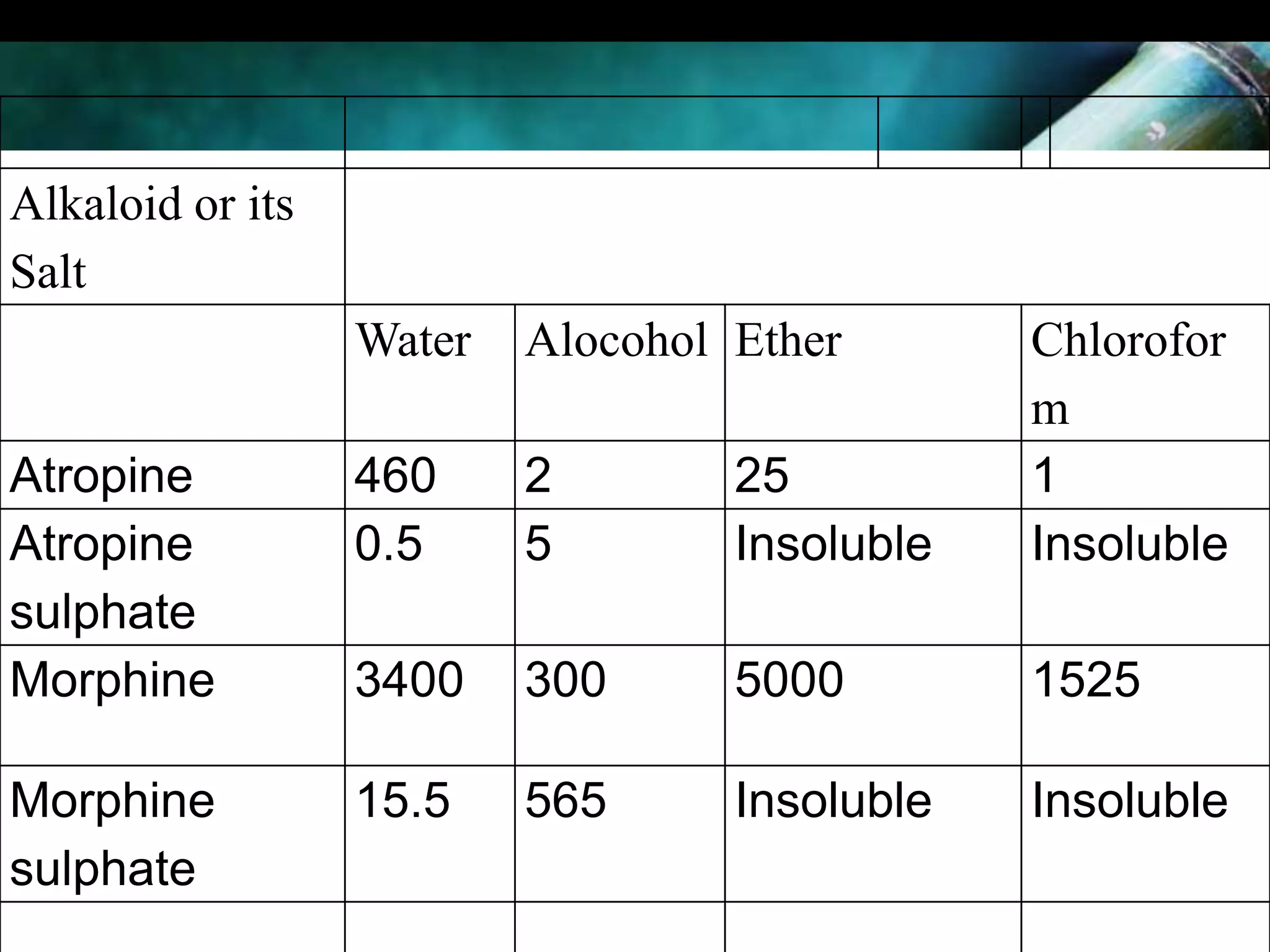
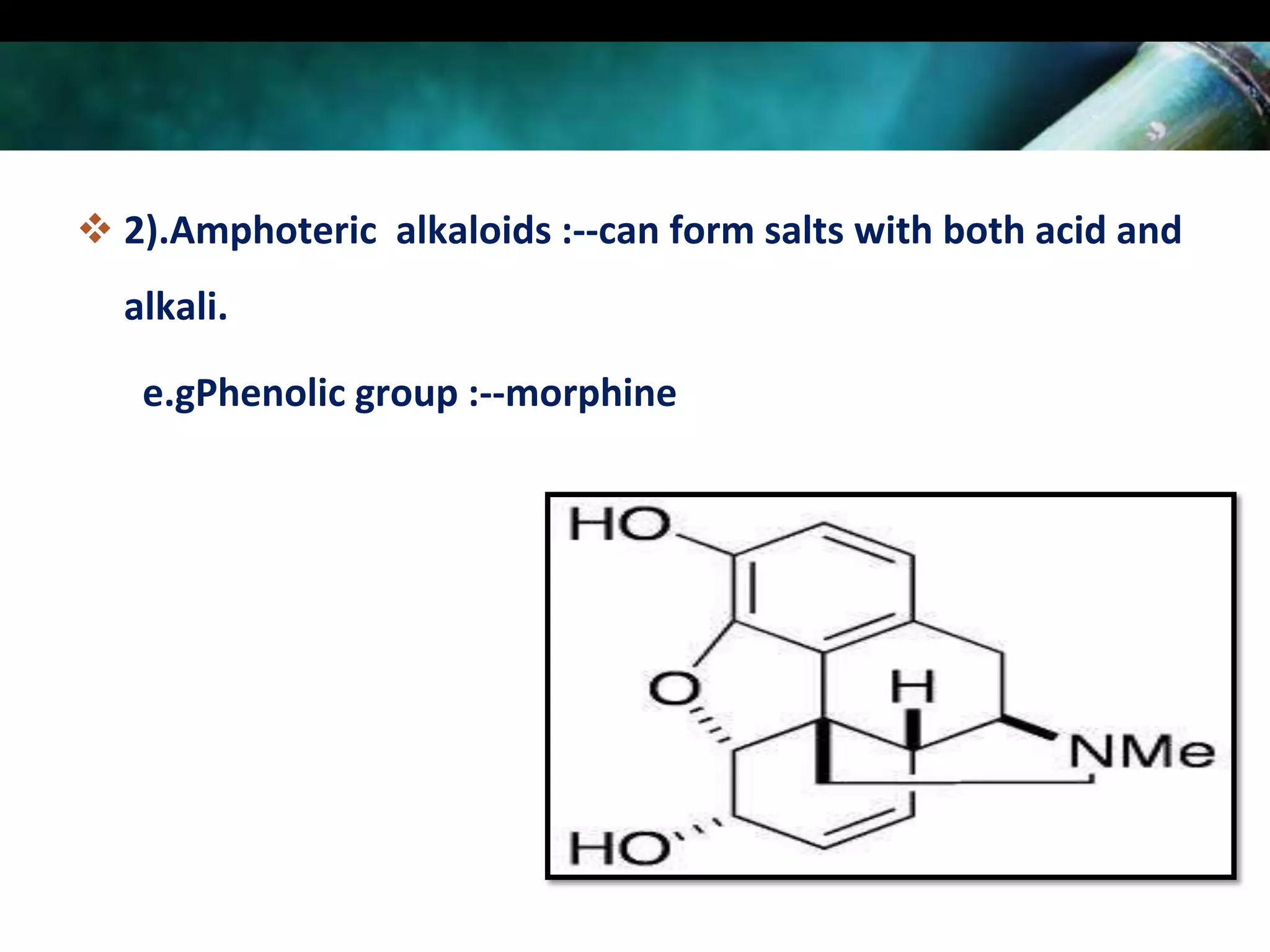
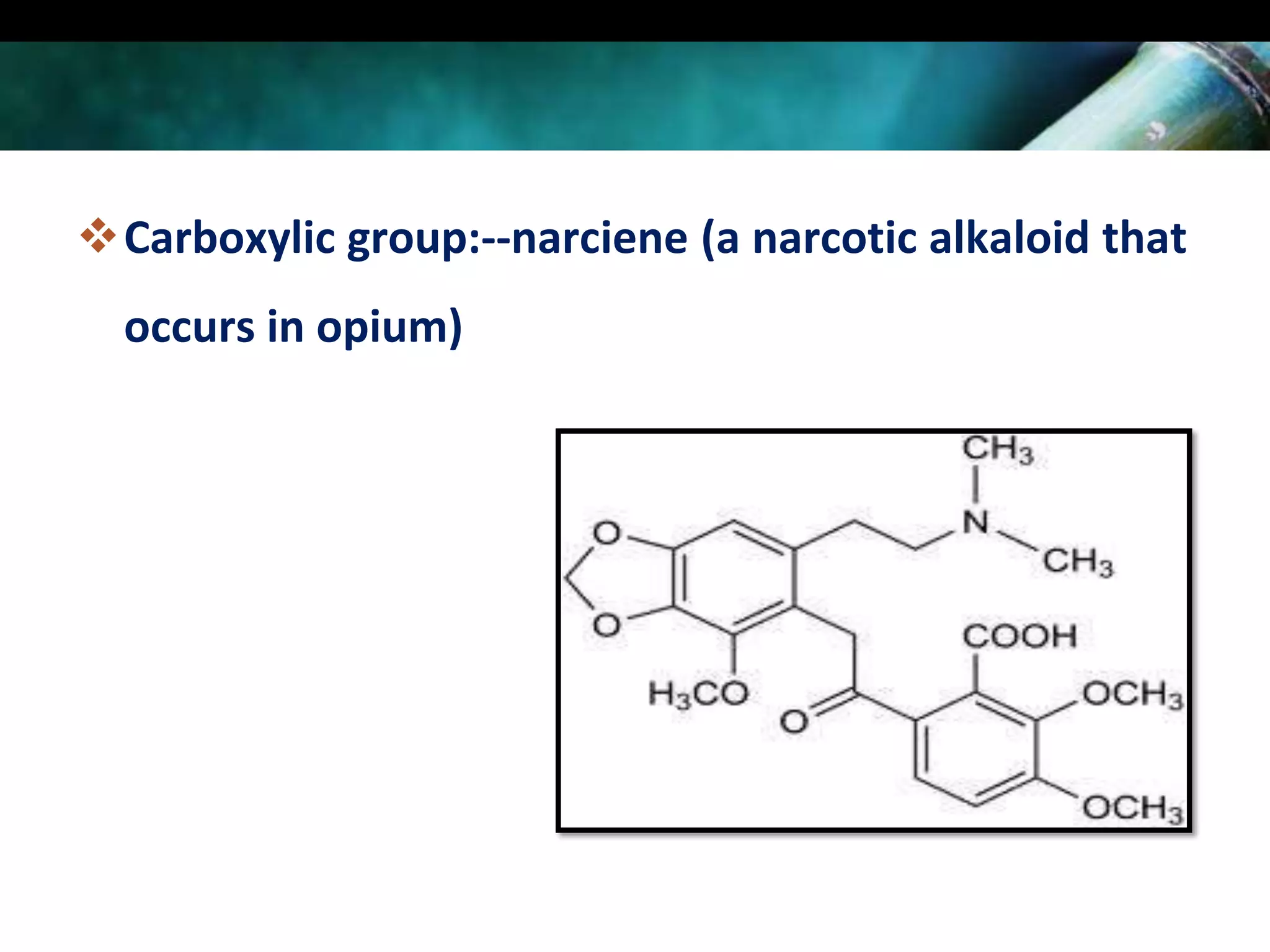
This document discusses the extraction of alkaloids from plant materials. It describes the Stas-Otto method, which involves distributing alkaloidal bases between an acid or aqueous solution and an immiscible organic solvent. The method involves rendering the plant material alkaline, extracting with an organic solvent, shaking with dilute sulfuric acid to form alkaloidal salts, making the solution alkaline to precipitate the free alkaloidal bases. The Stas-Otto method allows for the separation and isolation of alkaloids from other plant compounds.