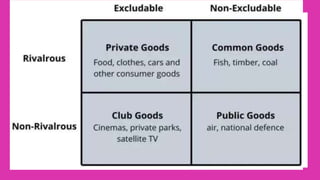
Public goods are goods that are non-rival and non-excludable, meaning one person's use does not reduce availability to others and people cannot be prevented from using them. Examples include clean air, water quality, national defense, and open spaces. Environmental goods like air and water quality are also typically public goods. However, sometimes environmental goods are questioned as being pure public goods. Externalities occur when the production or consumption of a good impacts a third party not involved in the transaction, creating costs or benefits not reflected in the market price. Externalities can be positive or negative.