Embed presentation




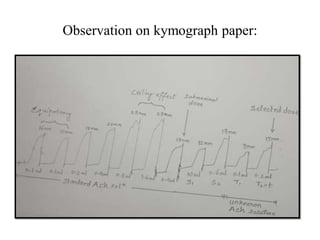

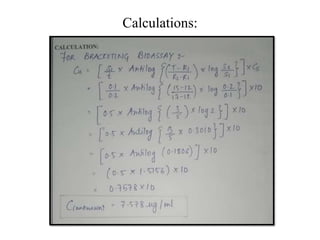



This document describes an experiment to estimate the unknown concentration of an acetylcholine solution using a bracketing bioassay with hen's ileum tissue. The experiment involves determining the dose-response curve for a standard acetylcholine solution and then bracketing responses to the unknown solution with responses to the standard. Close bracketing of the unknown response between two standard responses allows the concentration of the unknown to be accurately calculated using the formula provided. The aim is to present the methodology for using a bracketing bioassay to estimate an unknown drug concentration.









