The document discusses instructional modeling and its benefits. It provides several key points:
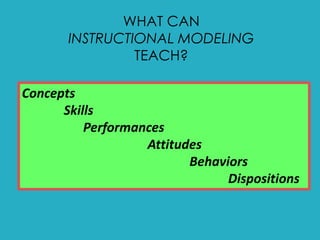
1. Modeling is an effective instructional method where teachers demonstrate concepts, skills, procedures and thinking processes for students to observe.
2. There are various modeling techniques including think-alouds, worked examples, demonstrations and cognitive apprenticeships.
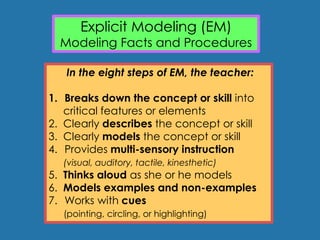
3. To successfully model, teachers must carefully plan demonstrations by identifying areas students may struggle with and breaking down complex skills into steps. They should also check for student understanding.
4. After modeling, teachers should provide guided and independent practice for students to apply their new learning with support and on their own. Comparing their work to the teacher's model can also help learning