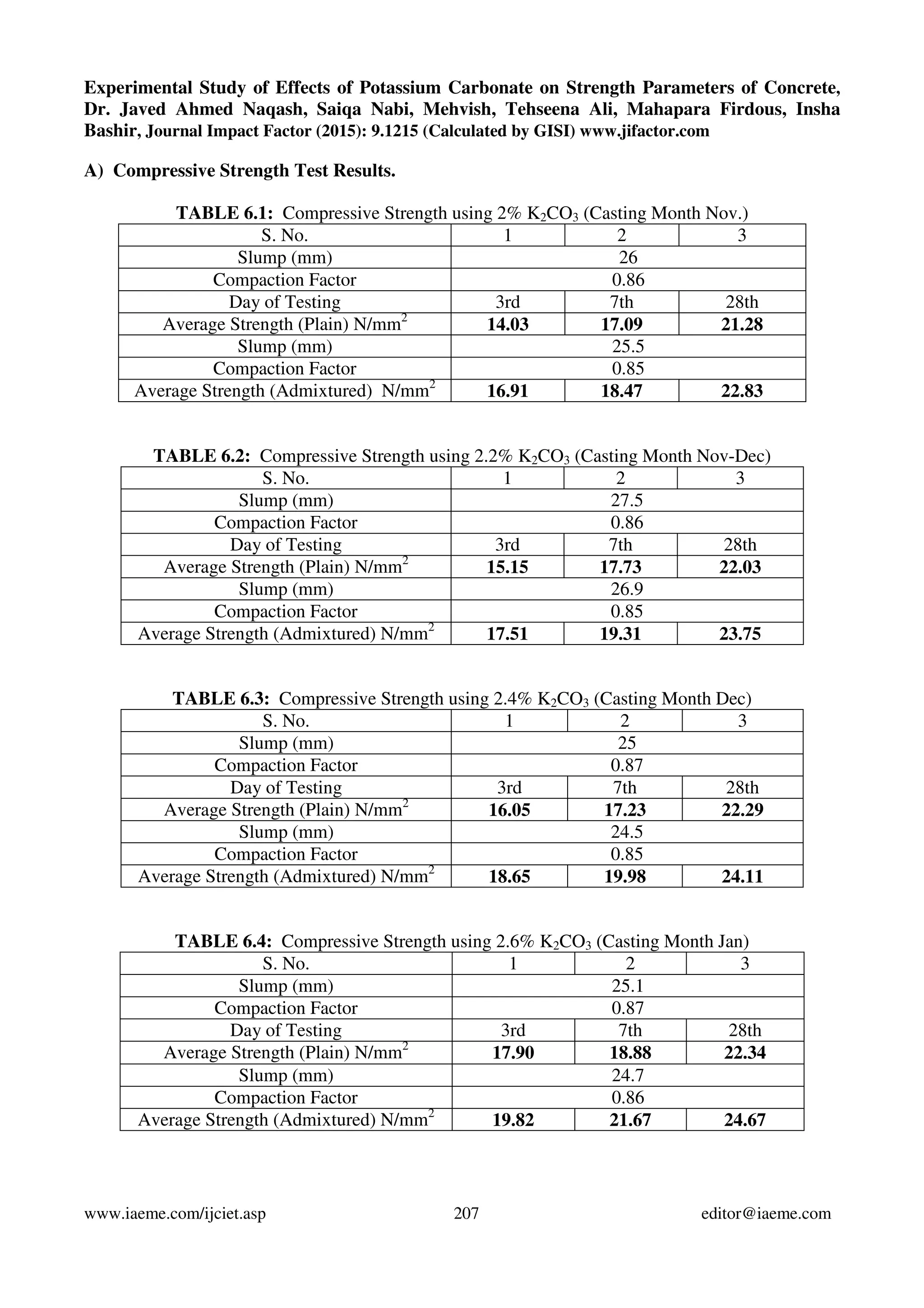
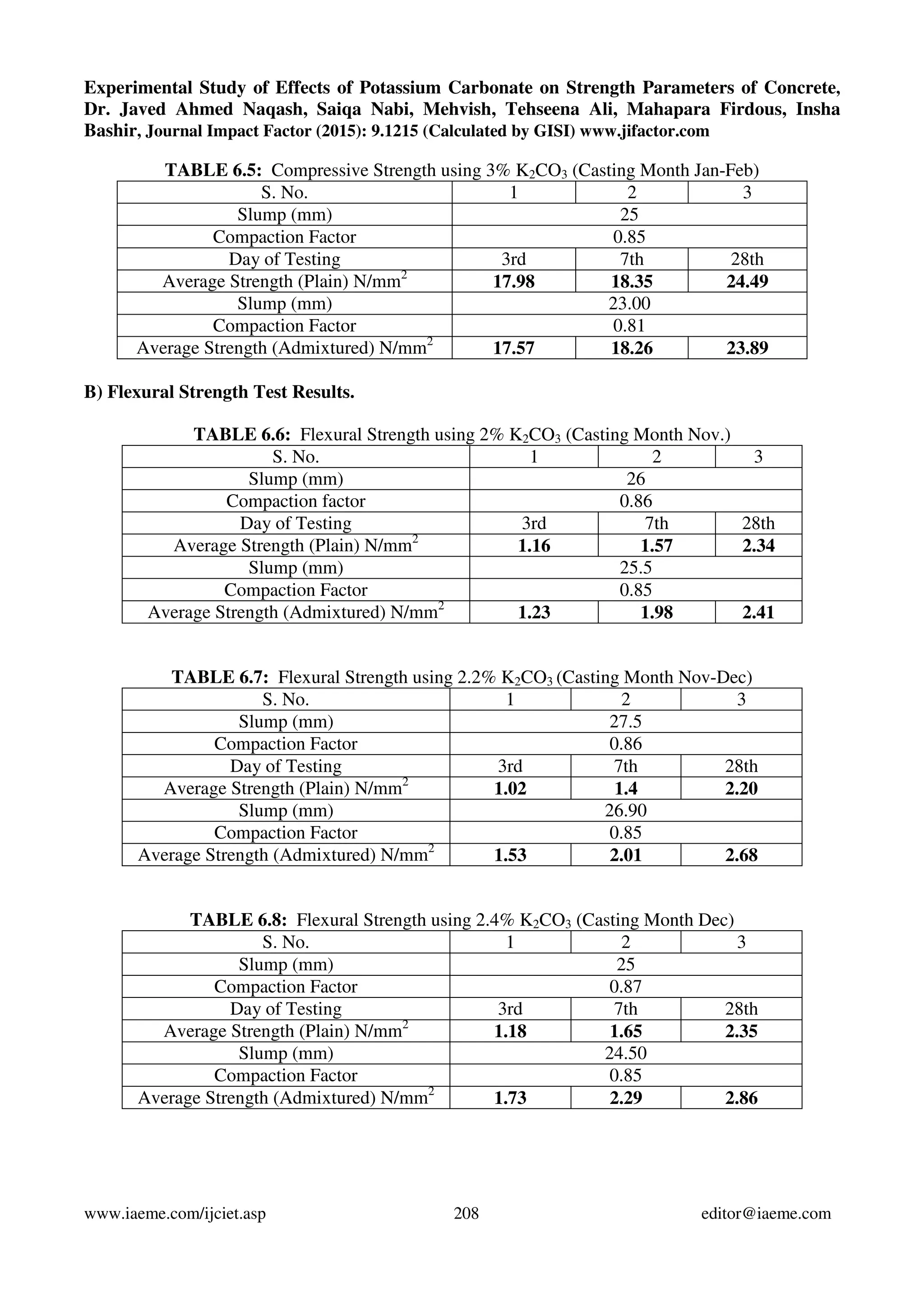
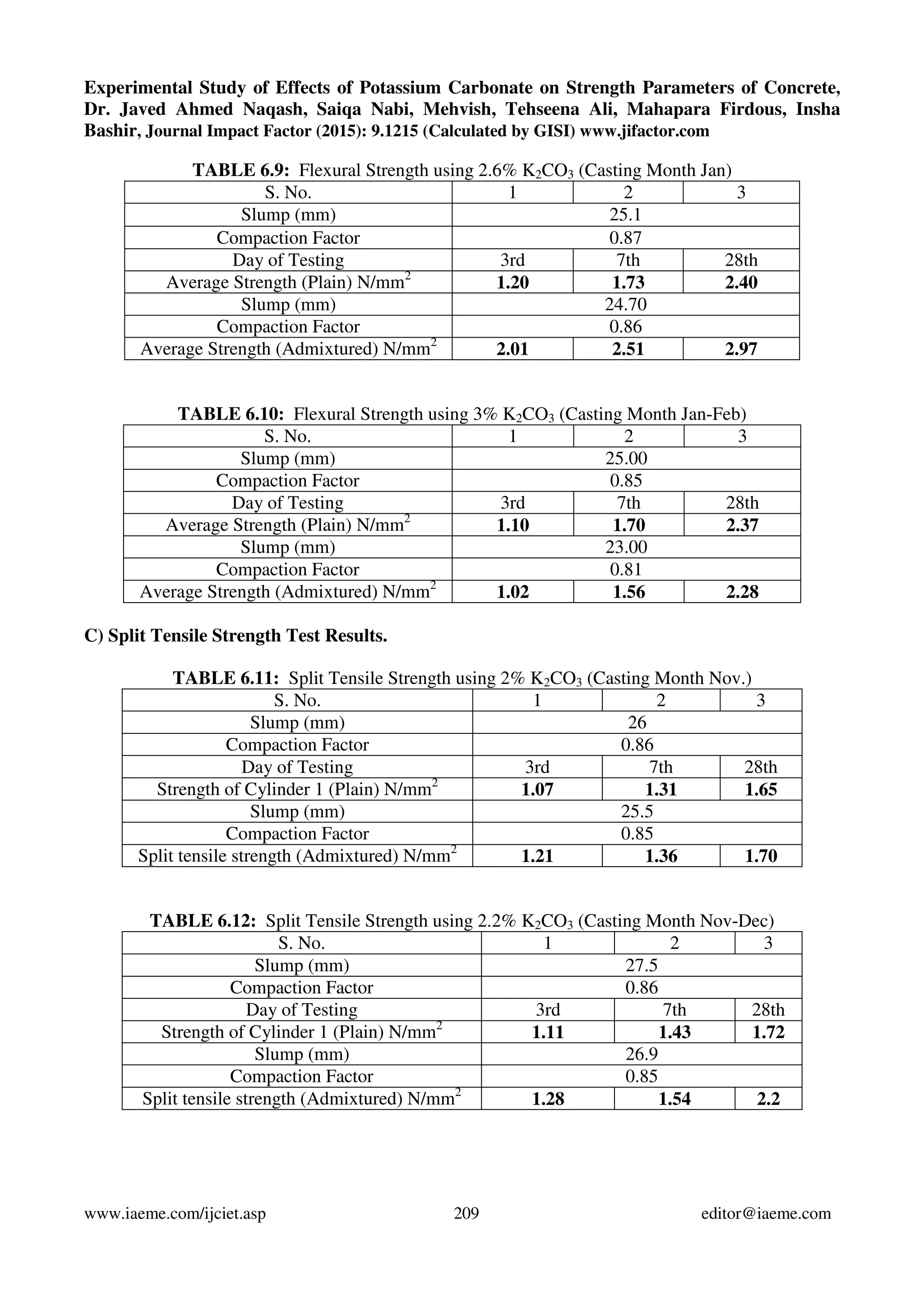
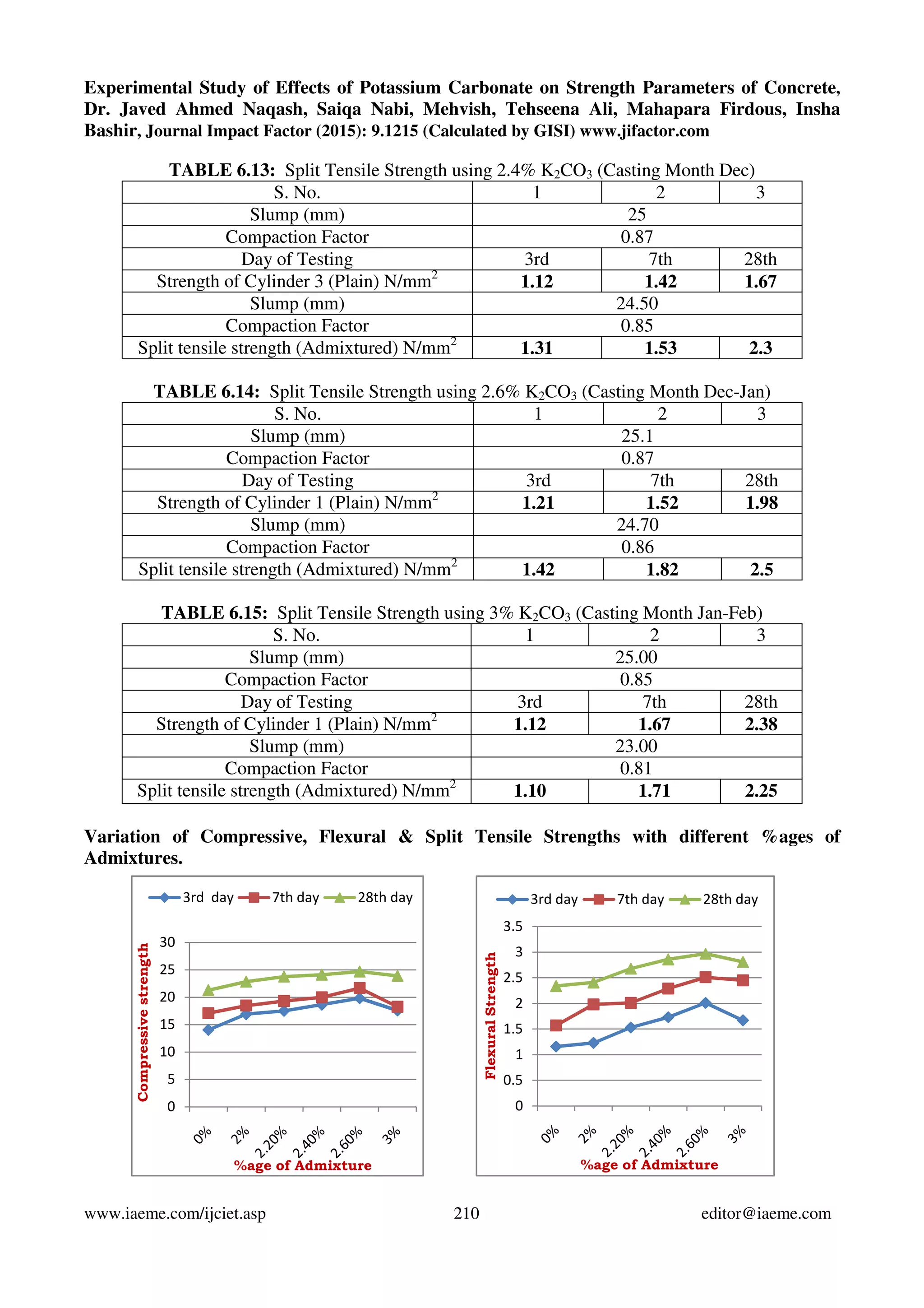
This study examines the effects of potassium carbonate (K2CO3) on the strength properties of plain concrete. Concrete specimens were produced with K2CO3 added at different percentages by weight of cement (2%, 2.2%, 2.4%, 2.6%, and 3%). The specimens were tested for compressive, flexural, and split tensile strengths at various ages. Results showed strengths increased up to 2.6% K2CO3 addition, but decreased with 3% addition. The optimum K2CO3 percentage was found to be 2.6%, as it improved strengths without harming concrete properties.
![Experimental Study of Effects of Potassium Carbonate on Strength Parameters of Concrete,
Dr. Javed Ahmed Naqash, Saiqa Nabi, Mehvish, Tehseena Ali, Mahapara Firdous, Insha
Bashir, Journal Impact Factor (2015): 9.1215 (Calculated by GISI) www.jifactor.com
www.iaeme.com/ijciet.asp 204 editor@iaeme.com
1
Associate Professor National Institute of Technology Srinagar, J&K, India
2,3,4,5,6
UG Students, Department of Civil Engineering, S S M College of Engineering & Technology,
J&K, India
ABSTRACT
This study presents the effects of Potassium Carbonate (K2CO3) on plain concrete. Potassium
carbonate as depressant admixture was added in different percentages by weight of cement. The
concrete specimens were tested for compressive, flexural and split tensile strengths and the results
obtained were compared with those of normal concrete. The optimum percentage of admixture that
could be used without harming the properties of concrete was also assessed. The results concluded
permissibility of using admixture (K2CO3) up to 2.6% by weight of cement.
Key words: Potassium Carbonate, Workability, Compressive Strength, Flexural Strength, Split
Tensile Strength.
I. INTRODUCTION
Winter has some peculiarities that affect construction in general and concreting in particular.
Its duration is different in different parts of globe, but cold weather with white frosts may also
happen in spring and autumn- not just in winter only. In central part of Russia, the cold period
including winter early spring and late autumn may be as long as five to six months reaching eight to
ten months in north. The situation is same in Canada, Alaska, Northern China, Finland, Sweden and
Norway. Kashmir is also a cold region and cold weather conditions prevail over a period of about
four months.
The cold weather conditions warrant special precautions to be taken while placing, finishing
and curing of concrete, so as to protect concrete against the effects of cold weather. Concrete has to
be protected from freezing until it reaches a minimum strength of 3.5 Mpa. If concrete freezes while
it is still fresh or before it has developed sufficient strength to resist the expansive forces associated
with the freezing water, ice formation results in the disruption of the cement paste matrix causing an
irreparable loss in strength. Once the concrete has attained a compressive strength of around 3.5
MPa, it is generally considered to have sufficient strength to resist significant expansion and damage
if frozen [2].
Concreting in winter conditions is quite difficult. It is possible to create favourable conditions
for concrete to harden when the ambient air temperature is below 00
C but that requires additional
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF EFFECTS OF POTASSIUM CARBONATE
ON STRENGTH PARAMETERS OF CONCRETE
1
Dr. Javed Ahmed Naqash, 2
Saiqa Nabi, 3
Mehvish, 4
Tehseena Ali, 5
Mahapara Firdous,
6
Insha Bashir
Volume 6, Issue 6, June (2015), pp. 204-212
Article Id: 20320150606021
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET)
© IAEME: www.iaeme.com/Ijciet.asp
ISSN 0976 – 6308 (Print)
ISSN 0976 – 6316(Online)
IJCIET
© I A E M E](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/experimentalstudyofeffectsofpotassiumcarbonateonstrengthparametersofconcrete-150820073657-lva1-app6892/75/Experimental-study-of-effects-of-potassium-carbonate-on-strength-parameters-of-concrete-1-2048.jpg)
![Experimental Study of Effects of Potassium Carbonate on Strength Parameters of Concrete,
Dr. Javed Ahmed Naqash, Saiqa Nabi, Mehvish, Tehseena Ali, Mahapara Firdous, Insha
Bashir, Journal Impact Factor (2015): 9.1215 (Calculated by GISI) www.jifactor.com
www.iaeme.com/ijciet.asp 205 editor@iaeme.com
energy, material and labour. The energy cost for thermal protection is estimated to be 800 million
dollar in US alone. So, it is not only a technical problem but a problem of cost effectiveness.
Stopping the process of concreting in winter is uneconomical due to long downtimes of
equipment and workers. It is better to bear additional costs and trying to minimize them as much as
possible. In some cases when construction schedule is very tight and project is to be completed in
winter, the additional costs are inevitable. The simplest and the least expensive way is to use a
chemical depressant like potassium carbonate.
In order to study the effects of K2CO3 on properties of concrete, to get the optimum
percentage of the chemical and to compare the various properties of concrete; a number of castings
were done with varying percentages i.e., 2%, 2.2%, 2.4%, 2.6% and 3% by weight of cement. Also
cost analysis reveals that cold weather concreting using chemical depressants is cost effective and
economical than any other conventional methods.
II. MATERIALS USED
2.1) Cement: Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) 43 Grade (Khyber cement) confining to IS: 4031[4]
has been used for this Work. The properties of the used cement are shown in Table 1.
2.2) Aggregates: Fine aggregates used throughout the work comprised of clean river sand with
maximum size of 4.75mm conforming to zone II as per IS:383-1970 [5] with specific gravity of 2.6
and Fineness Modulus of 2.6. Coarse aggregates used consisted of machine crushed stone angular in
shape passing through 20mm I S sieve and retained on 4.75mm I S sieve with specific gravity of 2.7
and Fineness Modulus of 6.18.
2.3) Potassium Carbonate: K2CO3 was used as depressant admixture and was obtained from local
market. Potassium Carbonate was in white fine powder form so it was easy to add it in mix. Fig. 1
shows Potassium carbonate.
Function of Potassium Carbonate as Admixture: When K2CO3 is added as admixture, it depresses
the freezing point of water by increasing the ions in the water. Also it accelerates the initial setting of
concrete. It allows concrete to gain early strength at sub-freezing temperature.
III. EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION
3.1) Mix Proportion: The concrete mix design was proposed by using IS 10262 [6]. The grade of
concrete used was M20 with water to cement ratio of 0.45.The ratio obtained from mix design was
1:1.6:3.2.
3.2) Tests on Fresh Concrete: The workability of all concrete mixtures was determined through
Slump test and Compaction factor test. The slump tests were performed according to IS: 1199-
1959[9]. Compaction factor test works on the principle of determining the degree of compaction
achieved by a standard amount of work done by allowing the concrete to fall from a standard height.
The degree of compaction, called the Compaction Factor is measured by the density ratio i.e., the
ratio of the density actually achieved in the test to density of same concrete fully compacted.
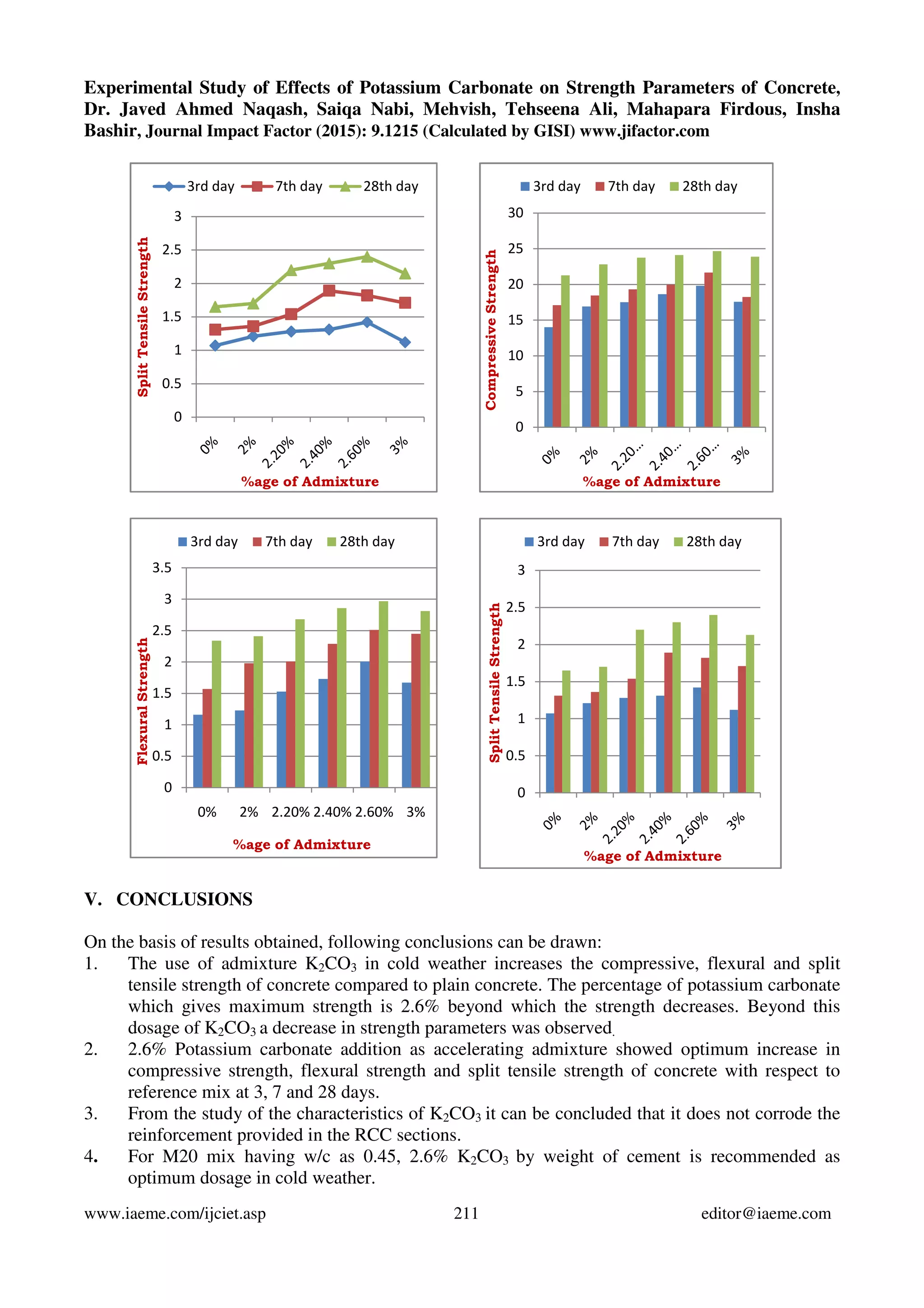
3.3) Tests on hardened concrete: From each concrete mixture, cubes of size 150mm x 150mm x
150mm, 150mm dia. 300mm cylinders and 500mm x 100mm x 100mm beams were cast for the
determination of compressive strength, split tensile strength and flexural strength respectively. The
concrete specimens were cured under normal conditions as per IS:516-1959 [10] and were tested at 3
days, 7 days and 28days for determining compressive strength as per IS:516-1959 [11], split tensile
strength as per IS:5816-1999 [12] and flexural strength as per IS:516-1959 [13].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/experimentalstudyofeffectsofpotassiumcarbonateonstrengthparametersofconcrete-150820073657-lva1-app6892/75/Experimental-study-of-effects-of-potassium-carbonate-on-strength-parameters-of-concrete-2-2048.jpg)