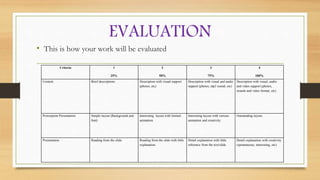
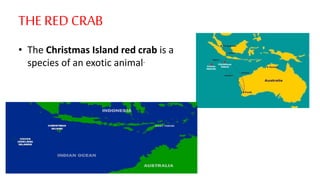
This document outlines a group project focused on exotic animals, emphasizing the use of a flipped classroom approach for learning. Participants are tasked with researching an exotic animal and creating a PowerPoint presentation that includes descriptions, visuals, and creative elements, with evaluation criteria based on content and presentation style. The document provides examples of animals such as the platypus and red crab, detailing their habitats, behaviors, and unique characteristics.