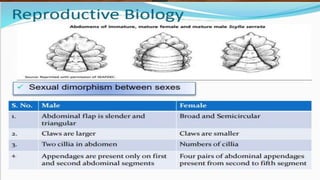
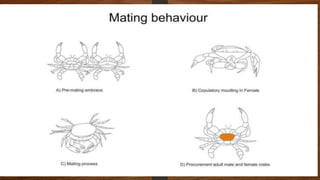
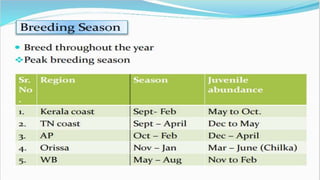
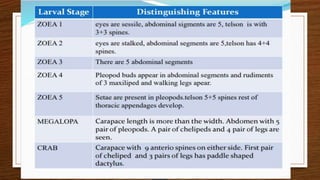
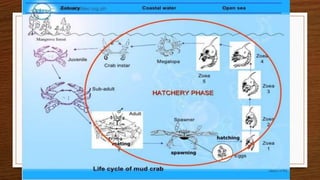
The document provides an overview of crabs, categorizing them within the animal kingdom and detailing their characteristics, reproduction, and importance in the ecosystem. Crabs are decapods with a varied lifespan and can live in both land and water, typically reproducing by laying eggs that have a low survival rate to adulthood. Additionally, crabs serve as a vital food source for marine animals and contribute to climate change mitigation while being nutritionally beneficial for human consumption.



![General characteristics of crabs
Most crabs are decapods meaning that the have one legs
Double antennae most grabs processes a pair of antennae
The move slide way
The live both in land and in water
The are generally made of a thin exoskeleton composed primarily of
chitin with a pair of chelae [claws]
The vary in size from pea crabs ,a few millimeters wide ,and the Japanese
spider crab with a leg span up to 4m
The feed on small fish ,dead animals small clams see weeds and some
algae](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chofor-230123064510-d7788a22/85/chofor-pptx-4-320.jpg)