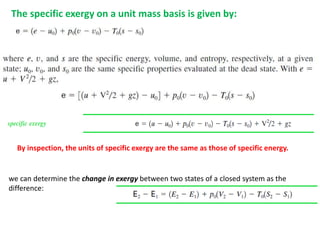
The document discusses exergy analysis of thermal systems. Exergy analysis is based on the conservation of mass, conservation of energy, and the second law of thermodynamics. Exergy analysis can be used to design thermal systems, reduce inefficiencies in existing systems, and evaluate system economics. Exergy, unlike energy, is not conserved and can be destroyed by irreversibilities as a system approaches equilibrium with its environment. The document provides examples of calculating the specific exergy of systems.