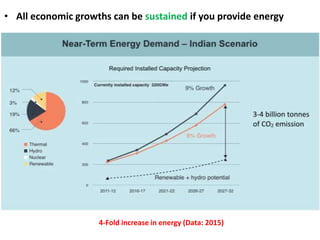
1) Nuclear power provides an emission-free source of energy that can generate electricity as well as steam for industry and potentially hydrogen in the future.
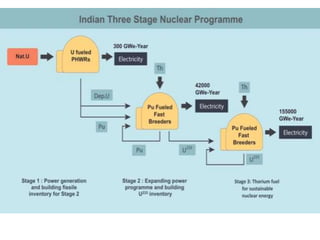
2) Thorium is a more abundant nuclear fuel source than uranium that India has been developing reactor designs to utilize, including accelerator-driven subcritical systems.
3) India has developed a passive nuclear reactor design that can operate on plutonium and thorium or uranium and thorium and avoids situations like Fukushima through inherent safety features requiring no human intervention.