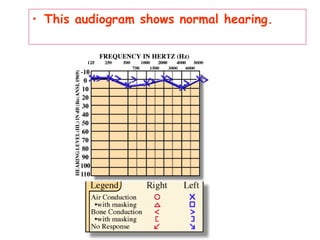
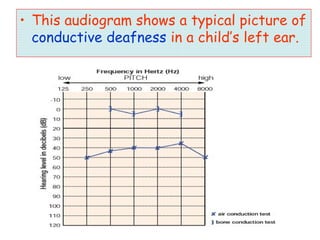
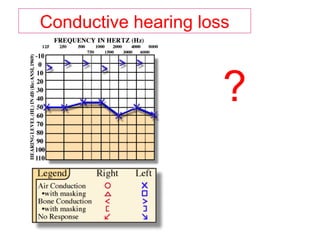
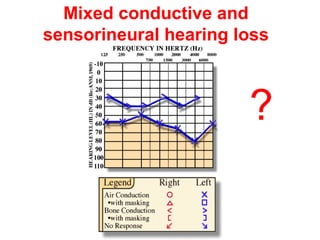
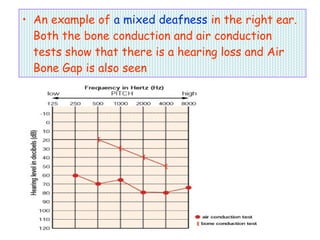
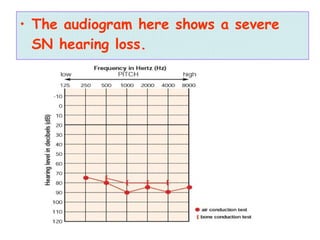
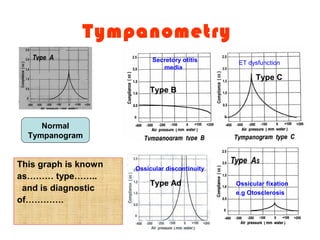
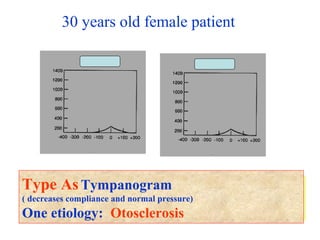
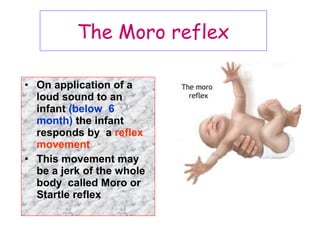
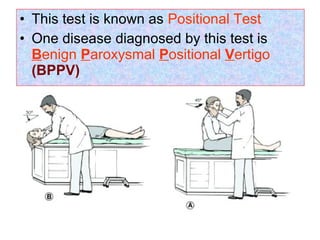
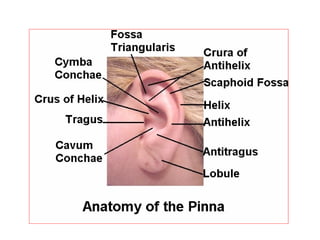
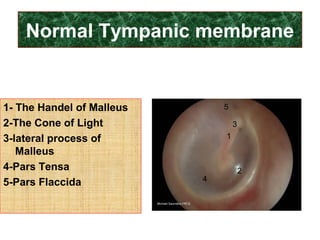
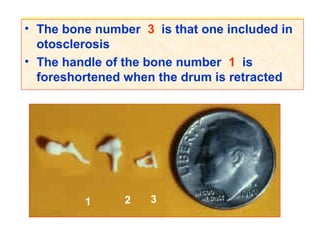
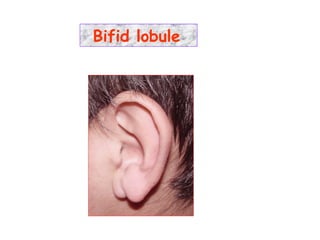
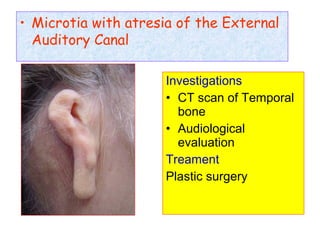
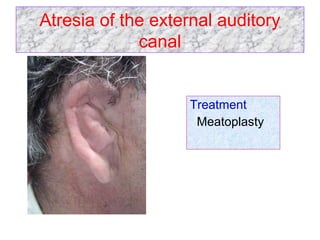
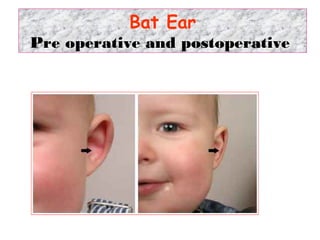
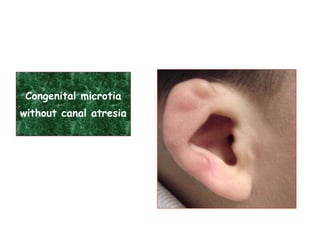
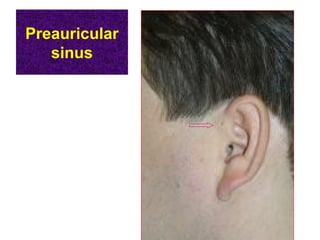
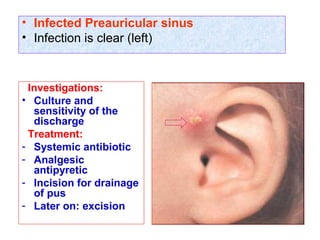
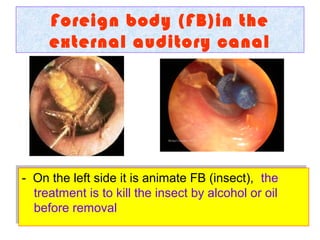
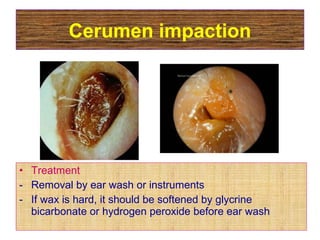
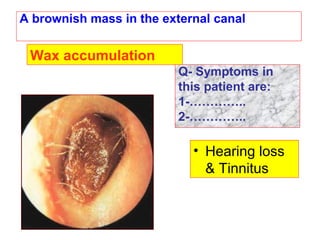
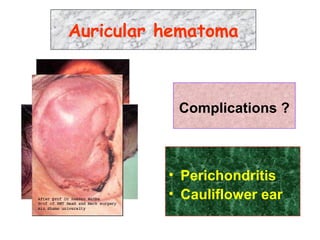
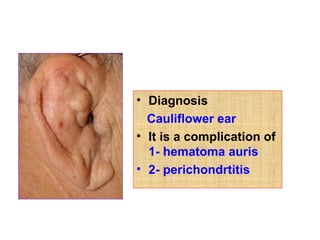
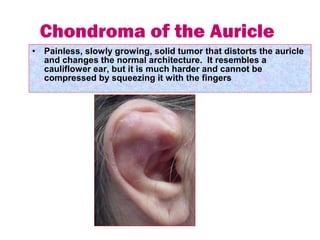
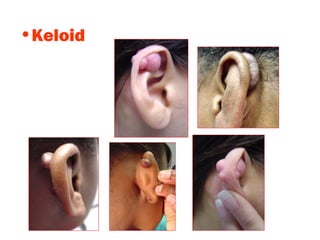
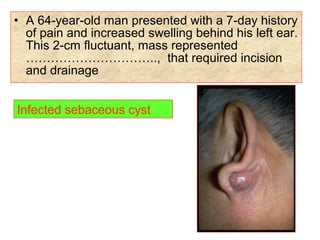
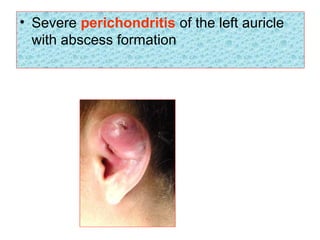
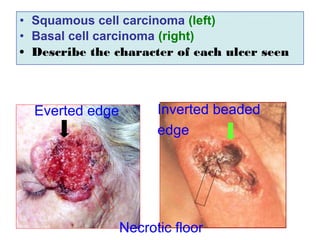
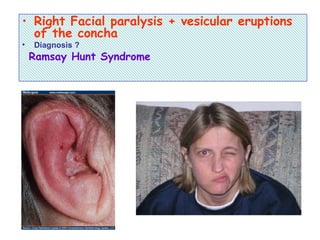
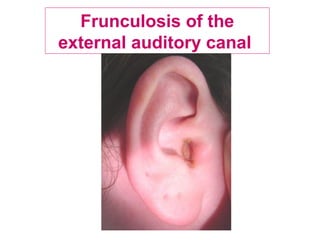
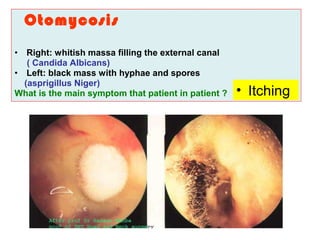
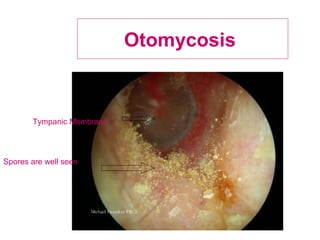
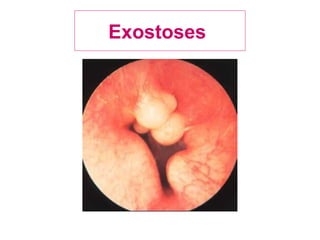
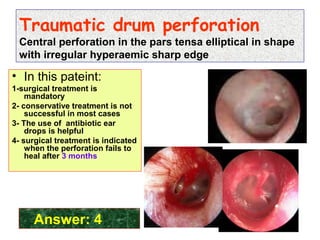
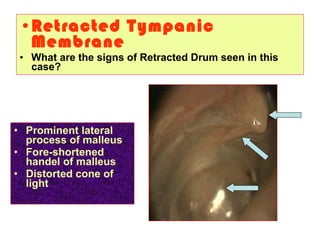
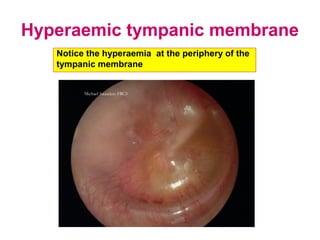
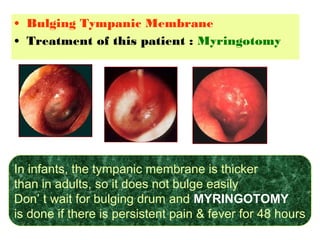
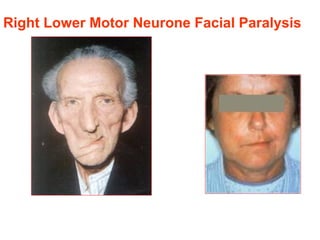
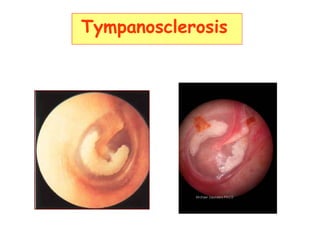
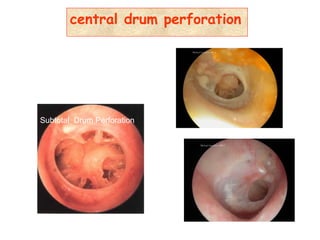
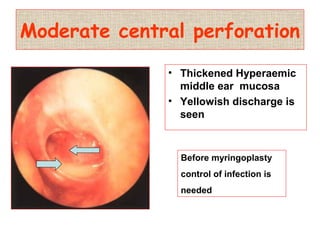
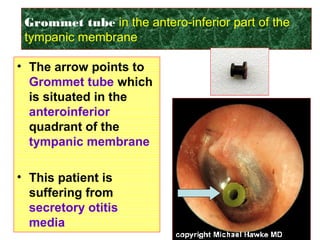
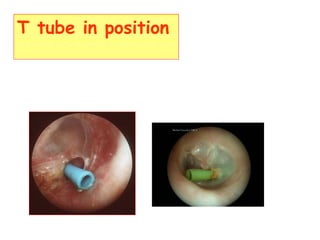
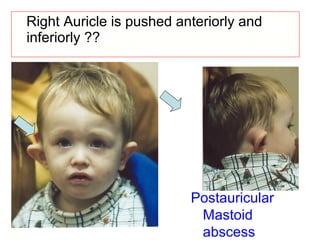
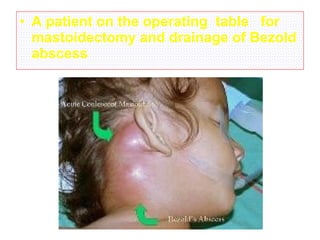
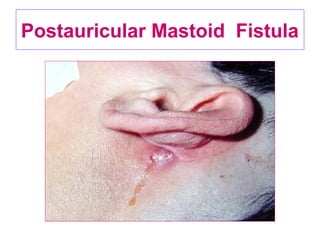
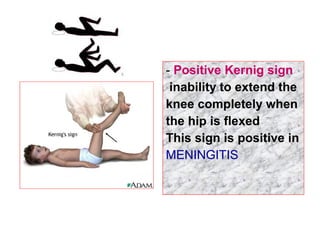
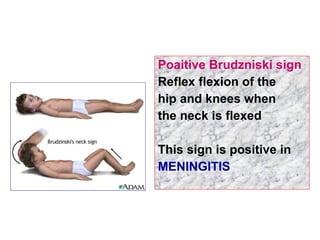
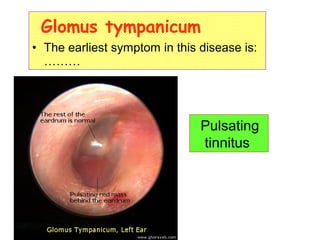
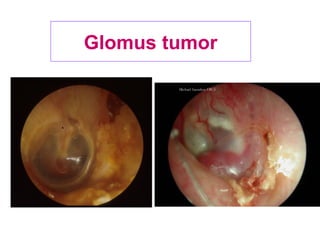
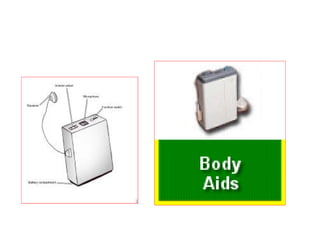
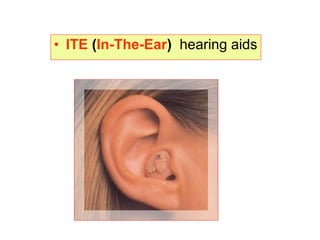
The document describes various equipment, techniques, and procedures used in otolaryngologic examinations. It includes descriptions of:
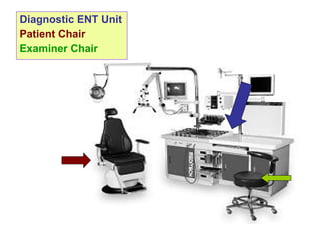
- Examination chairs and mirrors used to examine patients' ears, nose, and throat
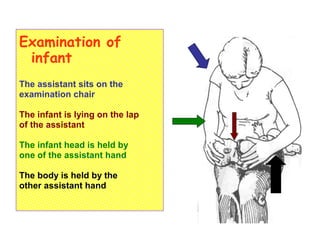
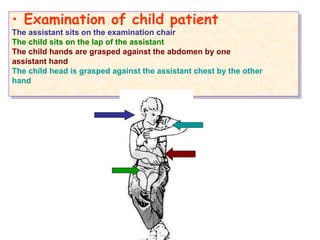
- Techniques for examining infants and children with an assistant's help
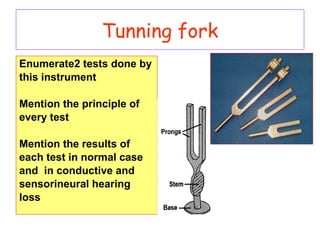
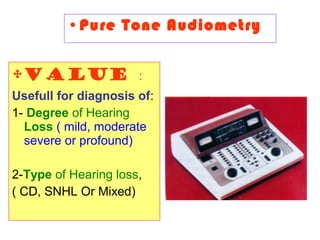
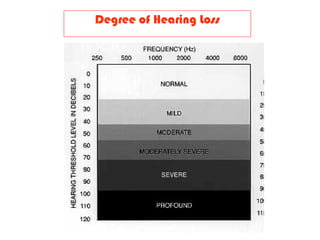
- Common tests performed including tuning fork tests, audiometry, and tympanometry
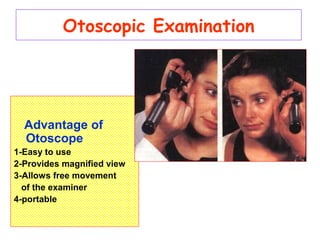
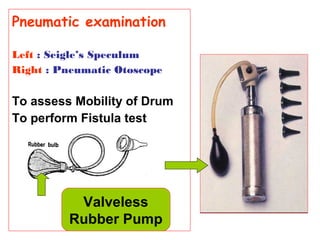
- Otoscopic examination techniques using different specula and equipment
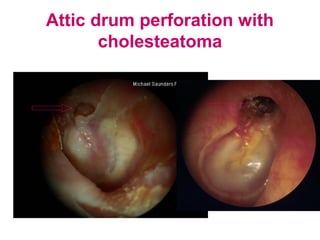
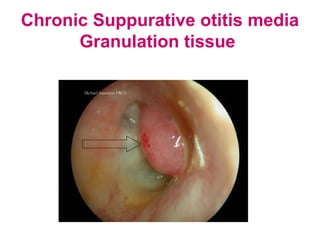
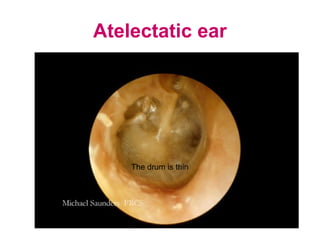
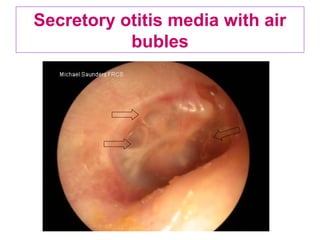
- Examination of the ear drum and conditions that affect its appearance
- Surgical and non-surgical treatment options for various ear conditions