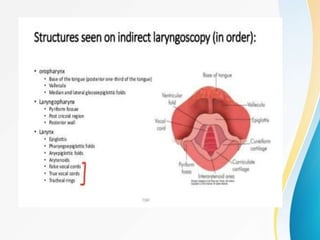
This document provides guidance on examining the nose and sinuses. It discusses examining the external nose, nasal cavities, and paranasal sinuses. Examination of the nose involves inspection, palpation, anterior and posterior rhinoscopy, and functional tests. Specific points of examination include the nasal vestibule, turbinates, septum, sinuses, and lymph nodes. Examination techniques are modified for children.