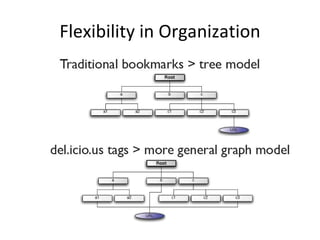
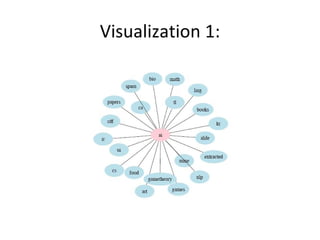
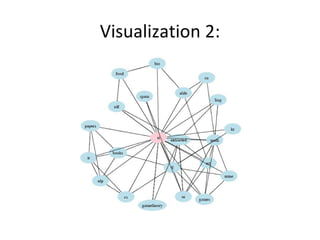
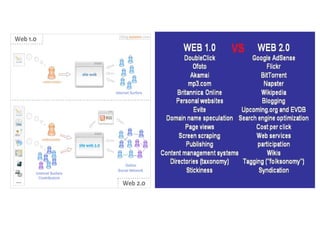
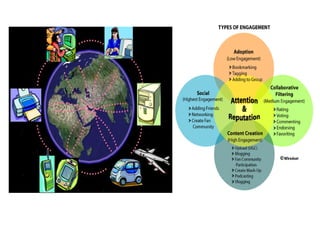
The document discusses several emerging technologies including del.icio.us, wikis, blogs, podcasts, and the evolution of the World Wide Web from Web 1.0 to Web 2.0 to Web 3.0 (proposed Web 3.0). Del.icio.us is described as a social bookmarking service that allows flexible organization of bookmarks using tags. Wikis are defined as collaborative websites that allow users to edit pages. Blogs, podcasts, and their key features are also summarized. The differences between Web 1.0, 2.0, and the vision for Web 3.0 are outlined at a high level.