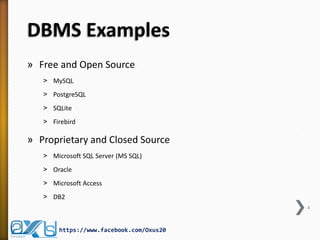
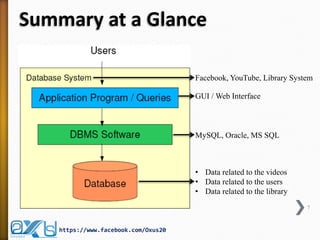
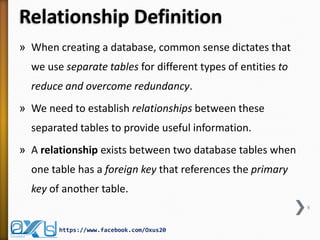
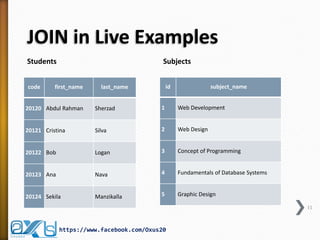
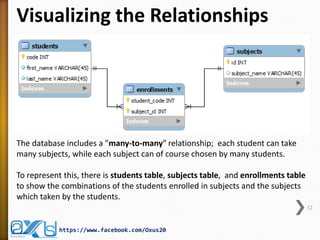
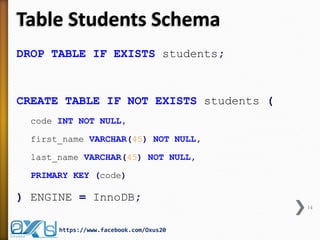
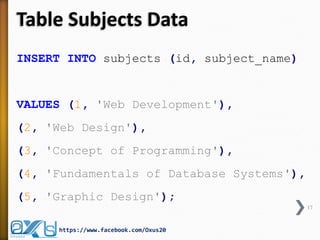
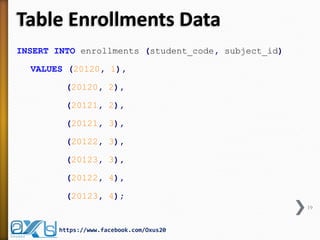
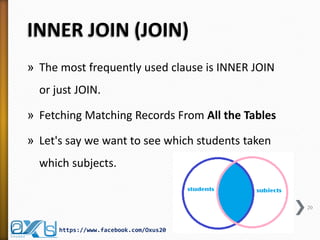
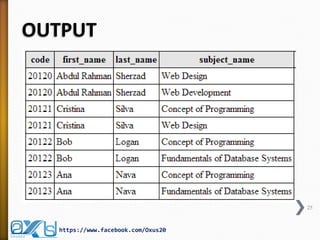
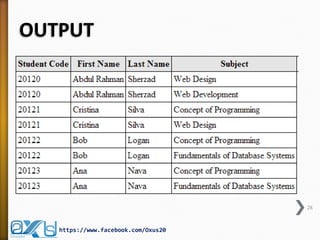
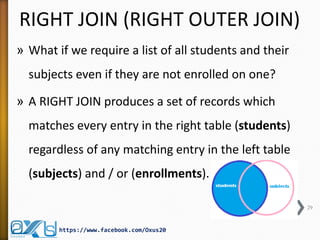
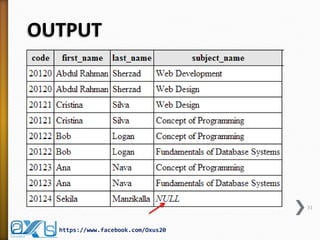
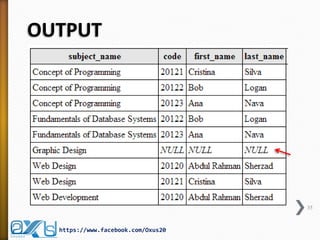
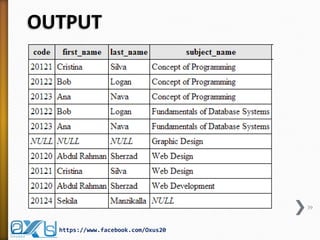
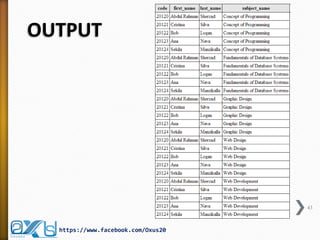
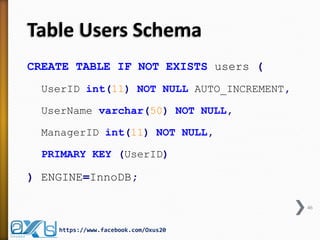
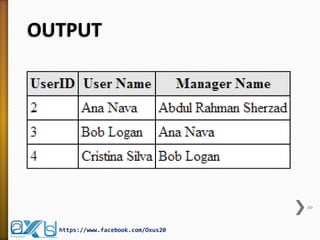
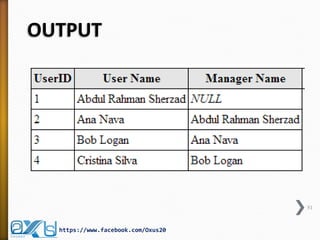
The document provides an overview of database concepts, focusing on database joins and relationships. It defines key terms such as databases, database management systems (DBMS), and application programs while elaborating on types of relationships (one-to-one, one-to-many, many-to-many) and various SQL join operations (inner, left, right, full, and cross joins). Several examples and SQL code snippets illustrate how to implement these concepts in practice.