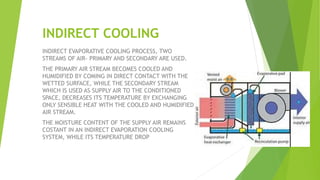
An evaporative cooler uses the principle of evaporative cooling to lower air temperature by passing air through a wet membrane. This causes the evaporation of water into the air, using the latent heat of vaporization to reduce the air's temperature. Evaporative coolers differ from air conditioners which use vapor-compression or absorption refrigeration cycles. Direct evaporative cooling lowers temperature and increases humidity by changing liquid water to vapor, while indirect cooling cools and dehumidifies supply air through heat exchange with cooled humid air. Evaporative cooling is less expensive to install and operate than air conditioning but provides less temperature reduction and requires clean water.