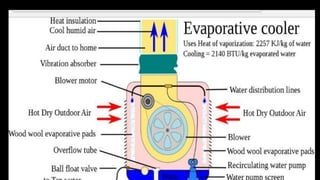
Evaporative coolers lower air temperature by employing water's high enthalpy of vaporization. As air passes over water, the water evaporates and absorbs heat from the air, lowering its temperature. This process converts sensible heat in the air to latent heat in water vapor. Most coolers contain fans that blow this cooler air into rooms, as well as a water source to replenish the evaporating water. While cheaper to operate than vapor-compression coolers, evaporative coolers increase humidity and require more maintenance.