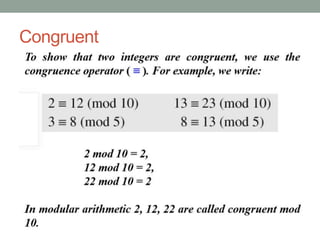
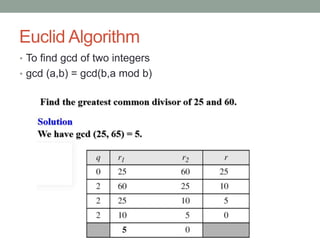
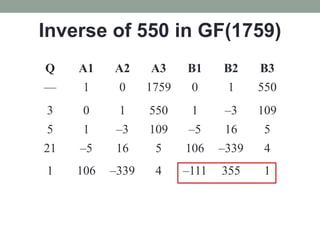
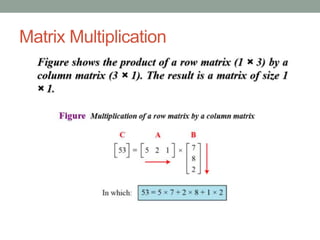
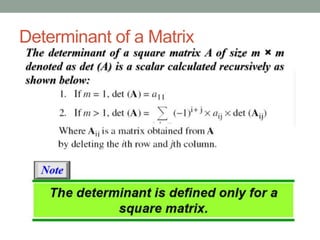
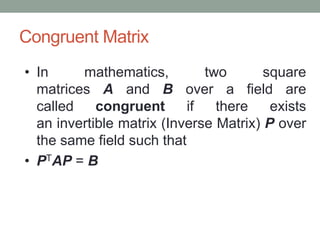
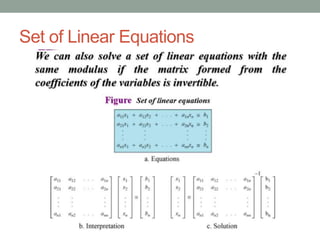
This document provides an overview of topics related to cryptography and network security including the Euclid algorithm, matrices, determinants, congruent matrices, and linear congruences. It discusses how matrices are useful for storing values, solving systems of equations, and transforming coordinates. It also explains how to use the Euclid and extended Euclid algorithms to find the greatest common divisor and modular inverses. Finally, it defines congruent matrices as two square matrices that are related by an invertible change of basis matrix, and how linear congruences are used to solve sets of linear equations.