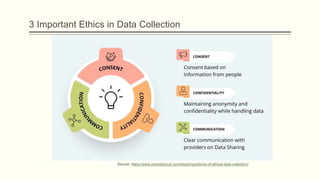
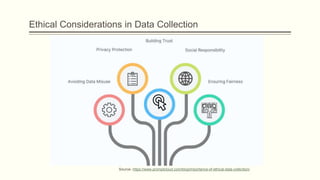
This document discusses several ethical issues related to data collection. It begins by defining data ethics and explaining that data ethics involves considering individuals' rights, transparency, and fairness in how data is collected and used. It then discusses the types of data collection and lists privacy protection, avoiding misuse, building trust, and ensuring fairness as important ethical considerations. Finally, it outlines some common ethical issues like privacy concerns, obtaining consent, data security, bias, transparency, legal compliance, intellectual property, and provides seven principles of data ethics.