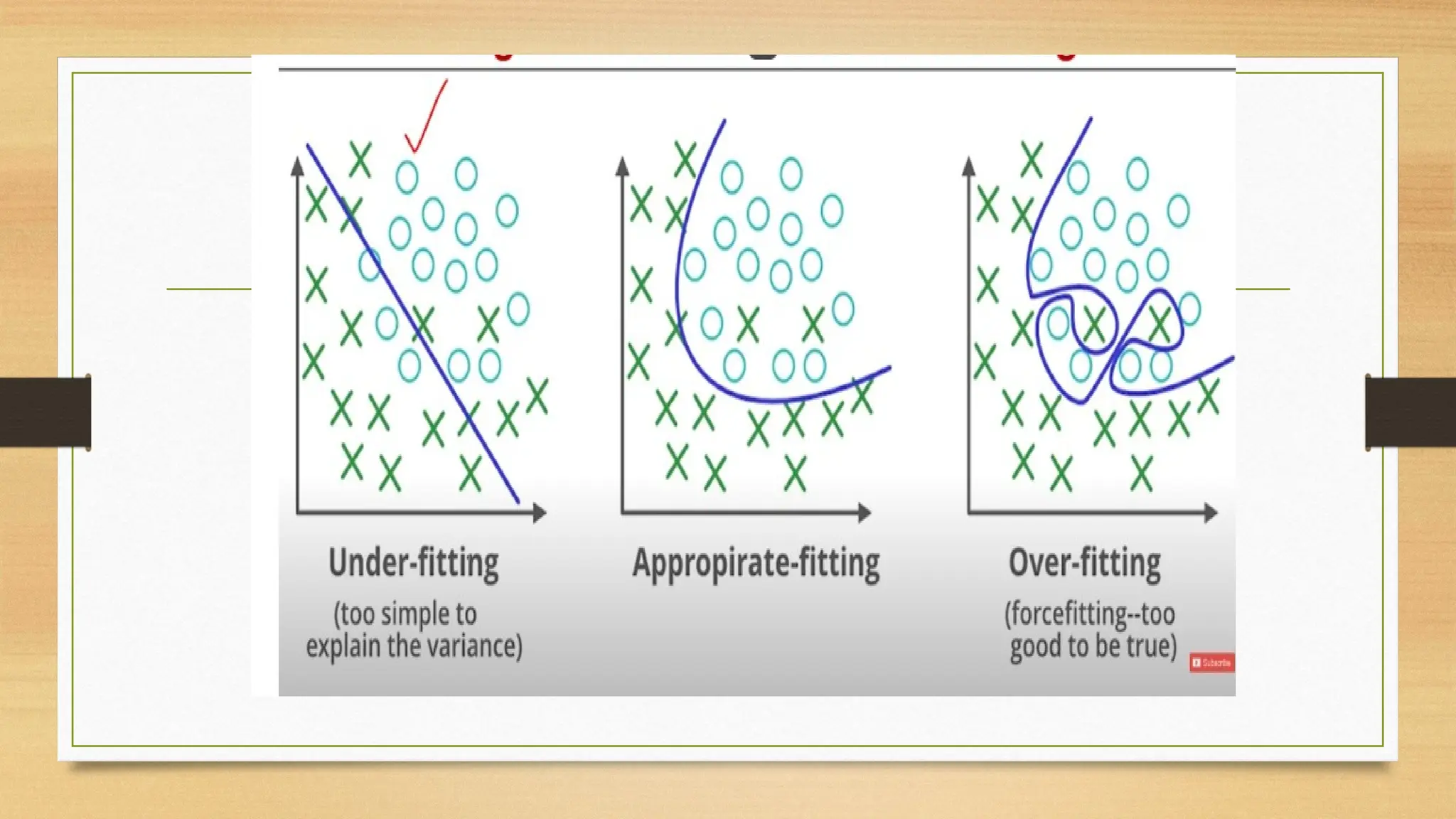
The document discusses underfitting and overfitting in machine learning, explaining that underfitting occurs when a model is too simple to capture data patterns, while overfitting happens when a model learns too much detail, including noise. Solutions for underfitting include using more complex models and training longer, whereas overfitting can be addressed with regularization techniques and simpler models. It also covers dependency modeling in classification, which aims to understand feature relationships to improve accuracy, utilizing methods like Bayesian networks and neural networks.