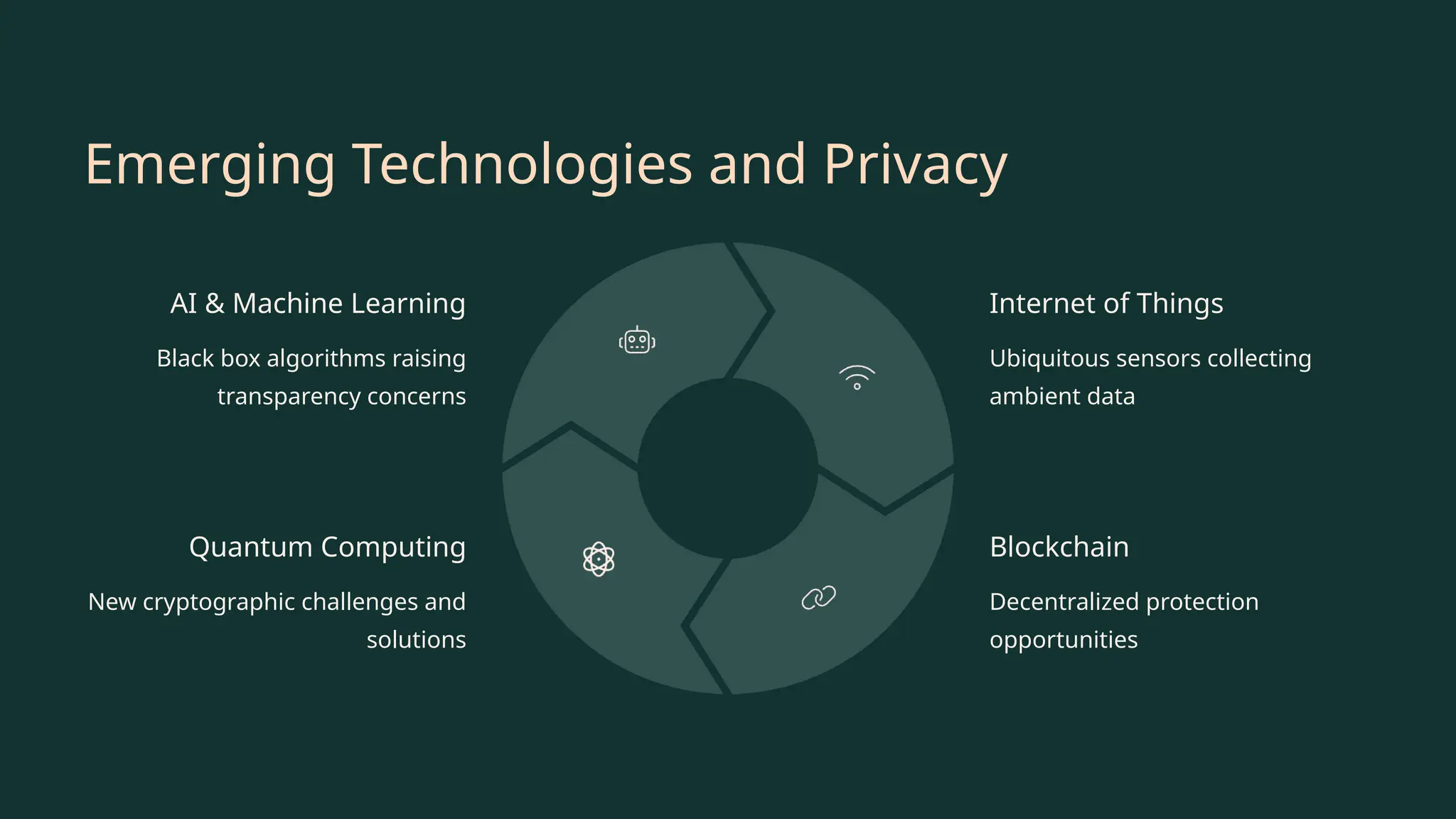
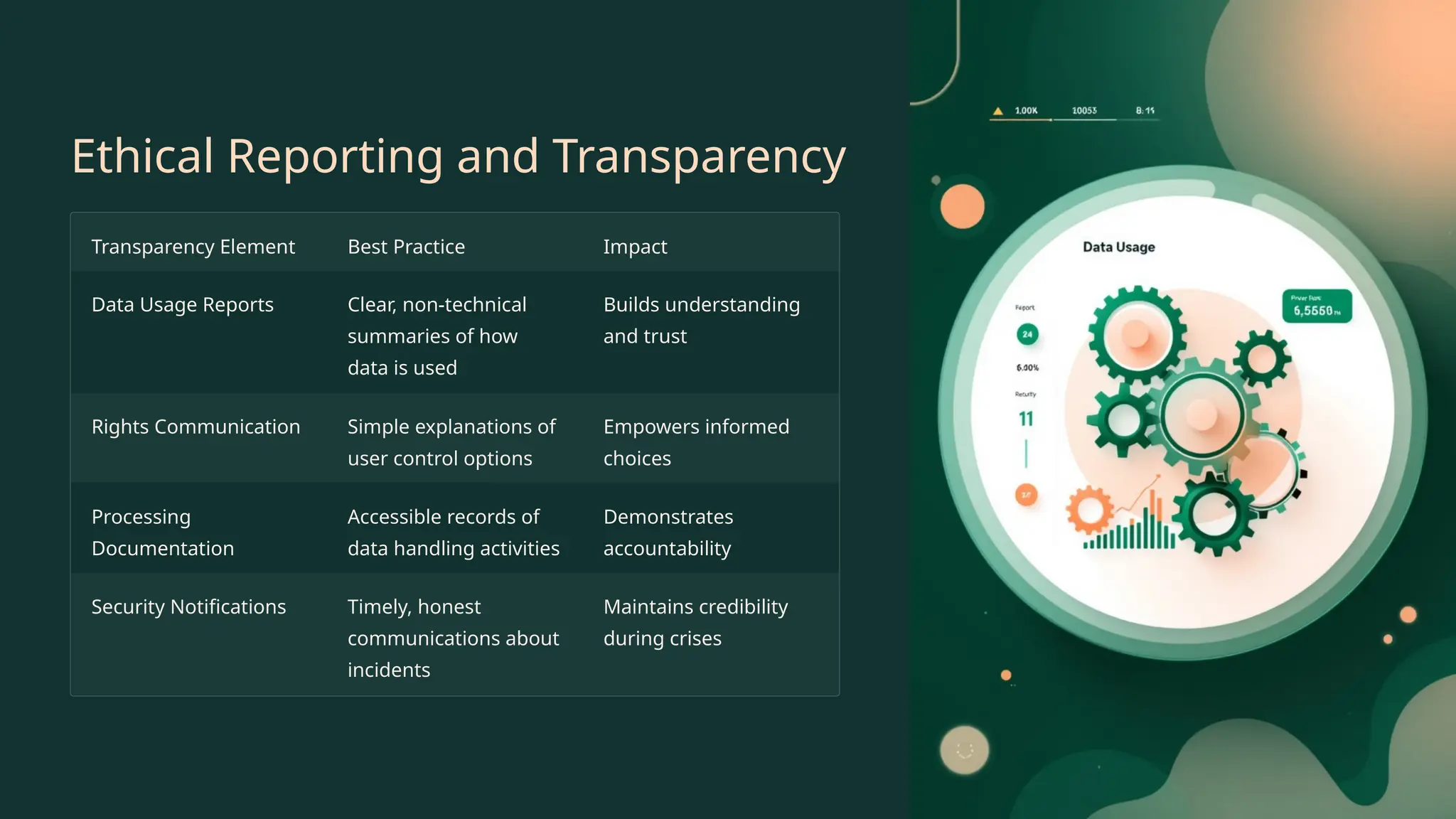
In the era of big data and AI, ethical data handling is no longer optional—it's essential. This presentation explores the core principles of data ethics, data privacy regulations (like GDPR), consent, bias, and the responsibilities analysts must uphold. Learn how to protect users and build trust through responsible data practices.